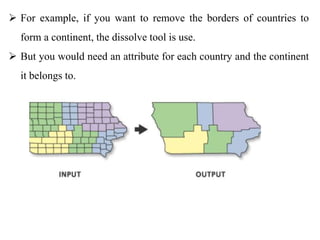
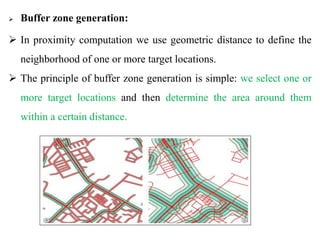
Chapter Five discusses spatial data analysis within GIS, emphasizing its importance in understanding real-world processes through manipulation and modeling. It covers various operations such as attribute queries, spatial queries, and geo-processing techniques like merging, dissolving, union, and intersecting layers for effective spatial data management. Additionally, it highlights the buffer zone generation concept for proximity analysis around target locations.