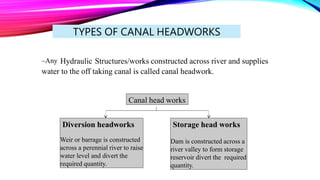
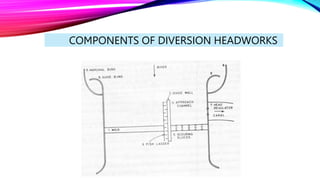
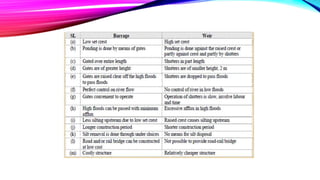
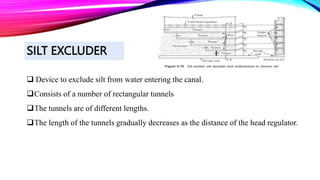
Canal headworks are civil engineering structures designed to regulate and divert river water into canals, addressing irregular river flow. The types of headworks include diversion headworks and storage headworks, each serving specific purposes such as raising water levels and controlling silt entry. Key components of diversion headworks include weirs, divide walls, fish ladders, and canal head regulators, which facilitate effective water management and distribution.