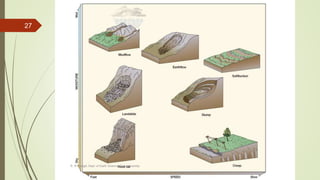
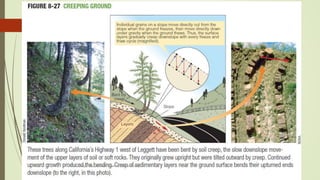
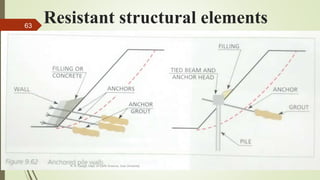
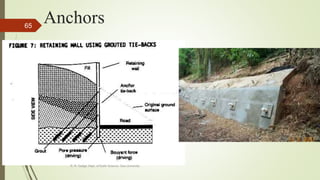
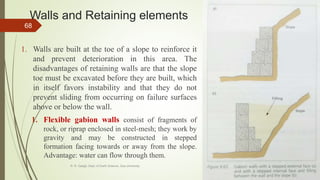
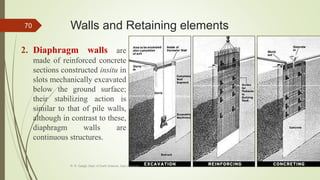
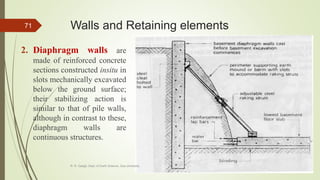
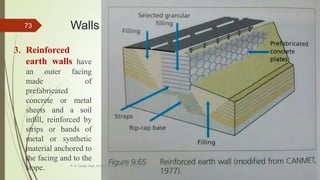
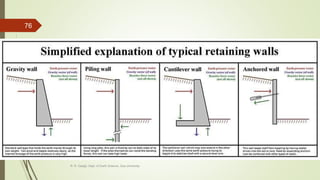
1. Mass wasting refers to the downslope movement of rock and soil due to gravity. It occurs on all slopes and can range from very slow to sudden movements.
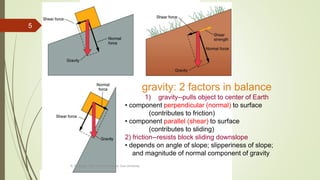
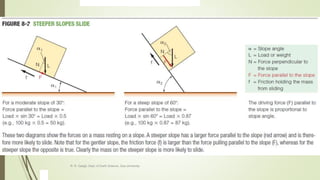
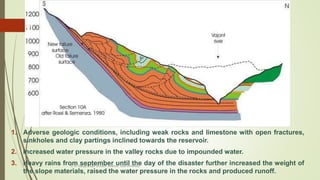
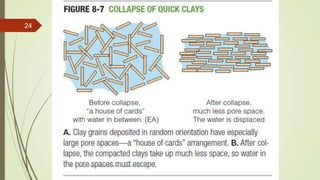
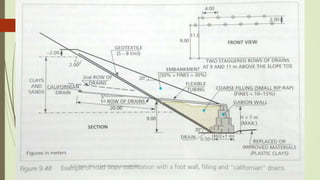
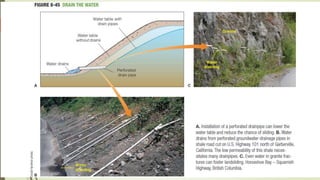
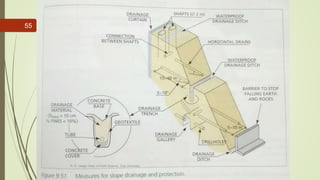
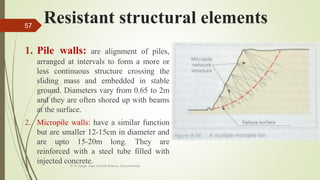
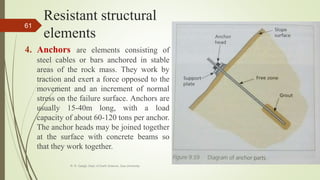
2. The stability of a slope depends on a balance between the downward force of gravity and friction/shear strength resisting movement. Steeper slopes and saturated soils or rock are more prone to failures.
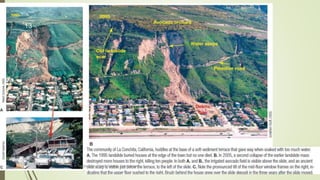
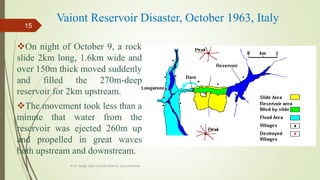
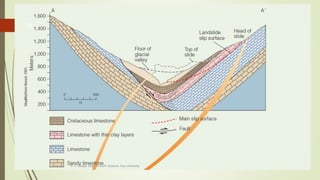
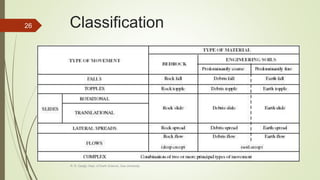
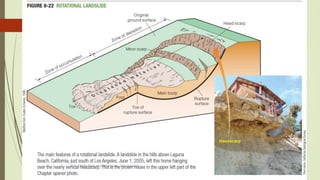
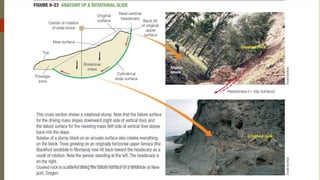
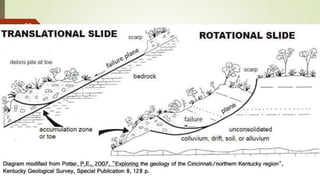
3. Common landslide types include rotational slumps and translational slides, which move along concave and planar surfaces, respectively. Earthquakes and rapid addition of water can also trigger landslides.