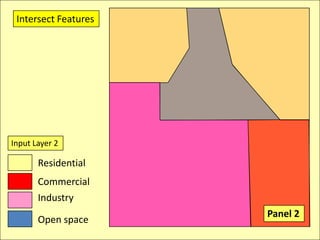
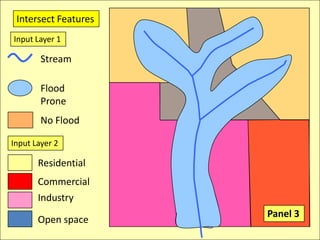
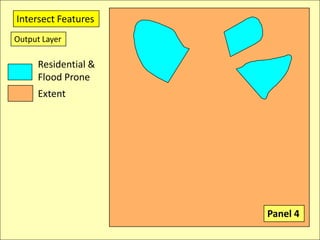
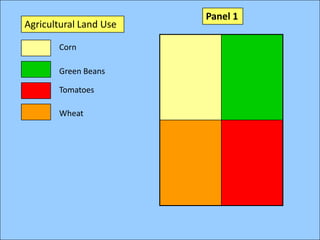
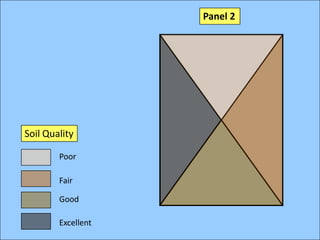
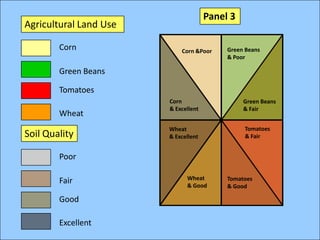
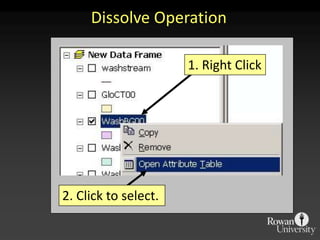
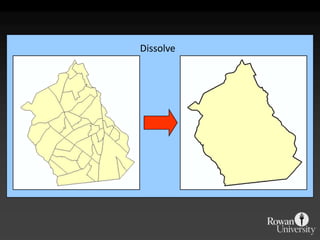
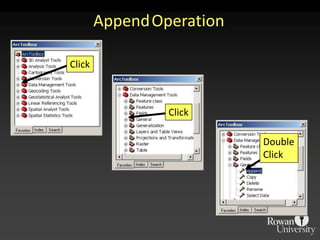
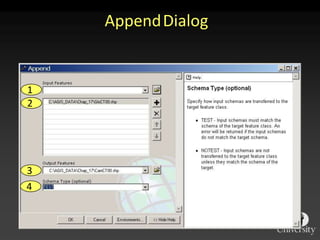
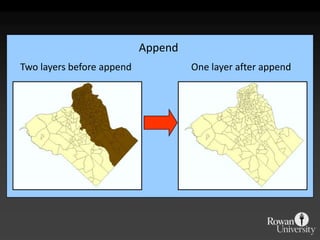
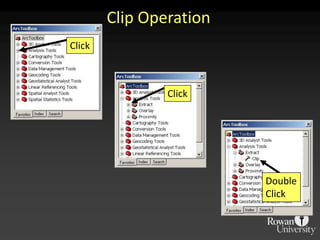
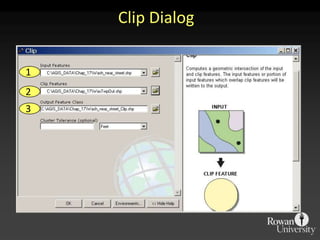
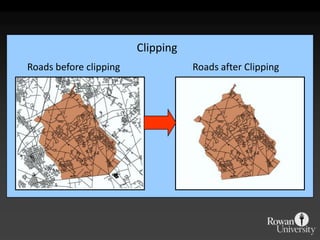
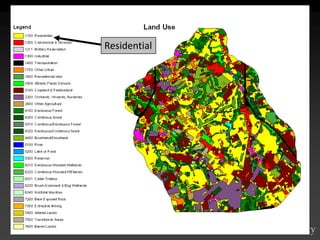
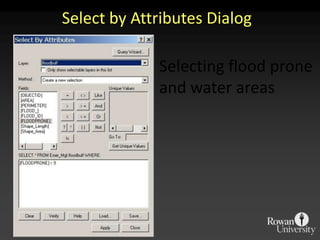
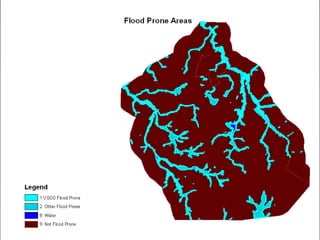
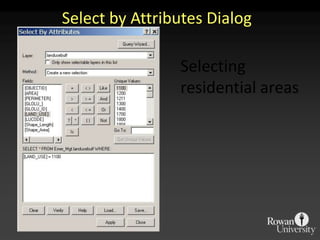
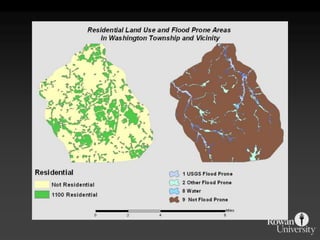
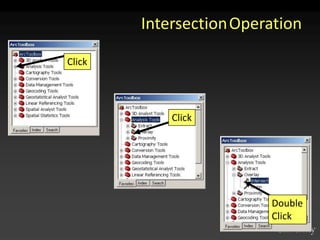
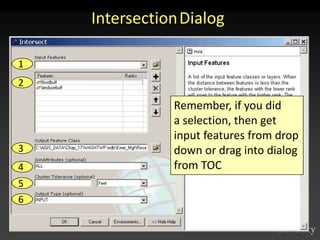
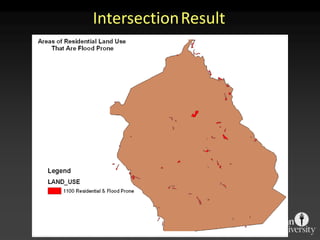
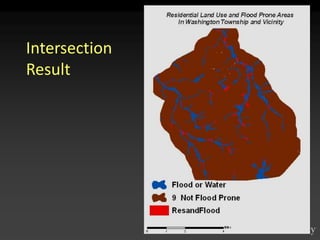
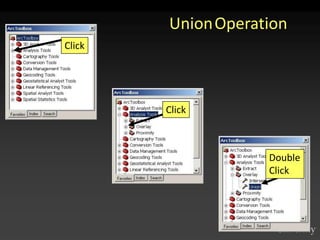
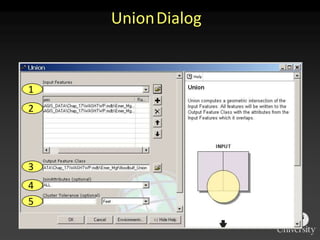
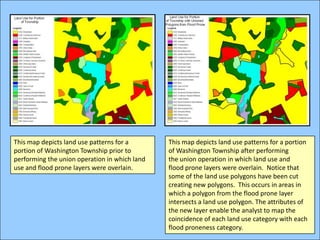
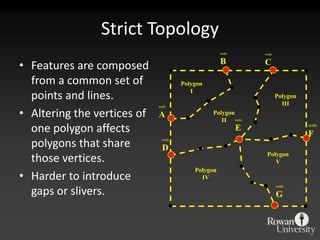
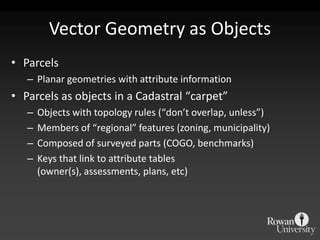
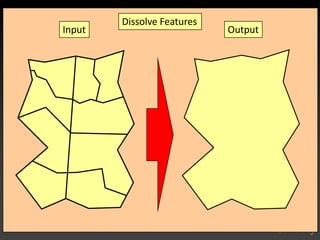
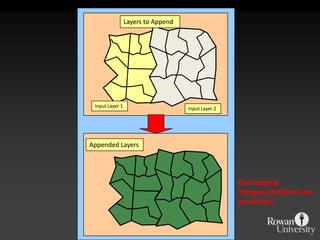
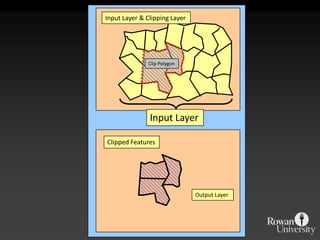
The document describes various models and operations used in GIS, including vector, raster, object models and common vector analysis operations such as selection, dissolve, append, clip, intersect, and union. It provides examples of how each operation works and the input and output layers involved. Key points covered include how topology is maintained in vector models, attributes can be linked as objects, and how selection and overlay operations can be used to analyze spatial relationships between layers.



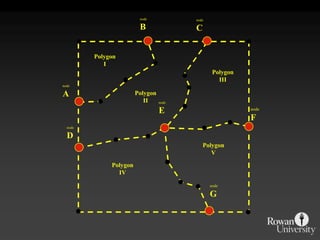
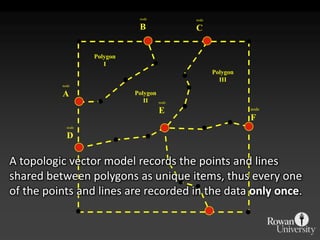
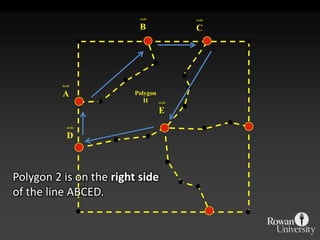
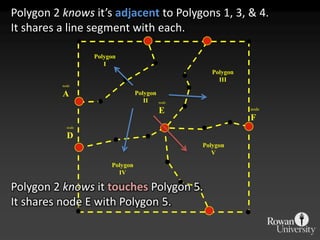











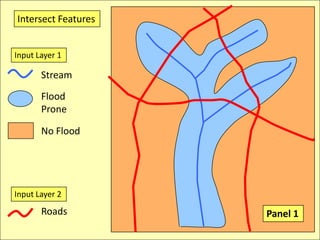
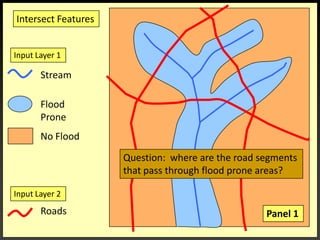
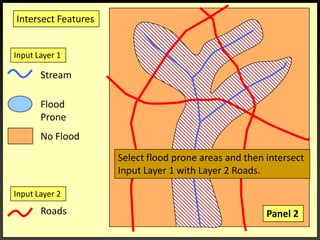
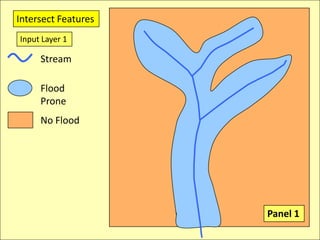
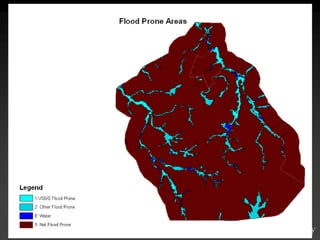
![IntersectionWhere are the Road segments that are in flood prone areas.Select flood prone from Input Layer 1Intersect roads and flood prone [Layer 2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gislecture03-110131212921-phpapp01/85/Data-Storage-and-Processing-24-320.jpg)