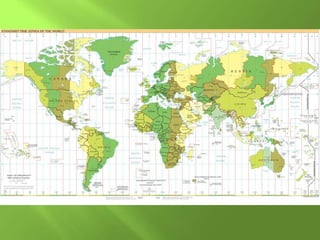
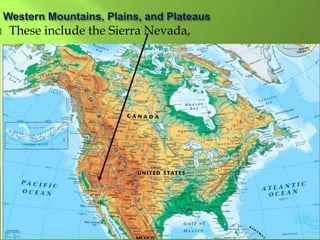
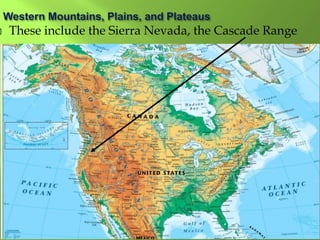
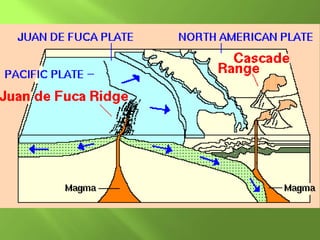
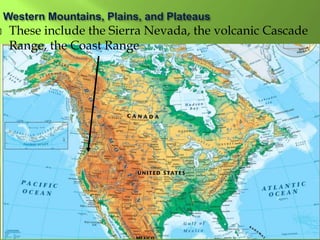
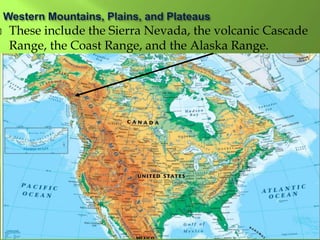
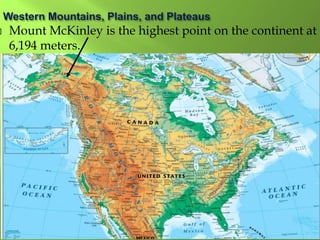
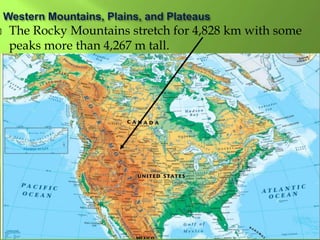
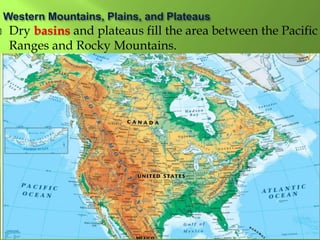
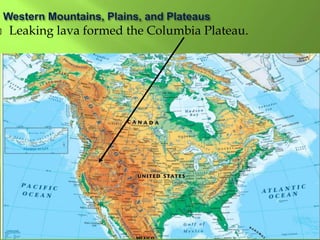
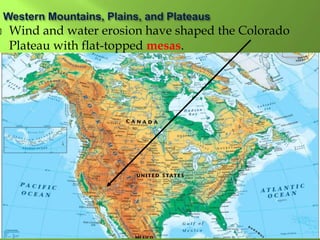
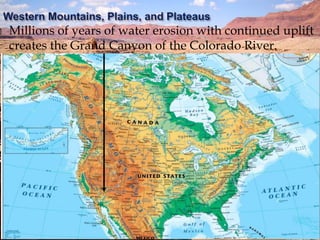
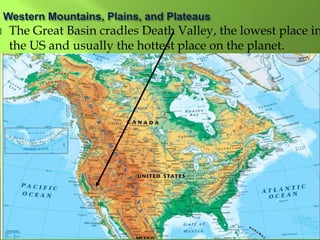
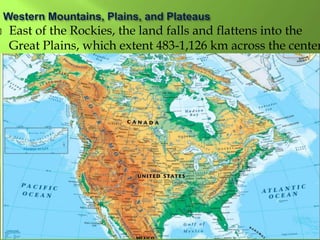
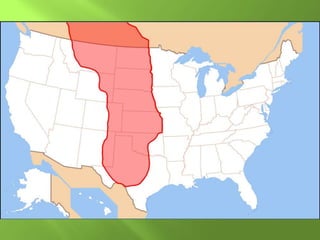
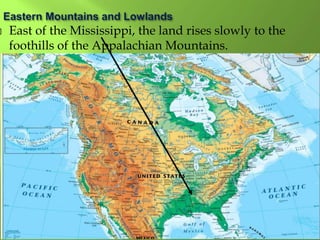
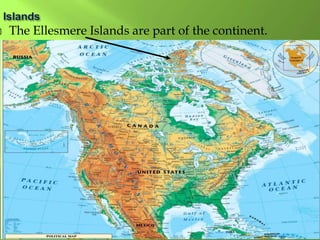
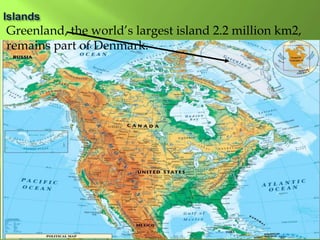
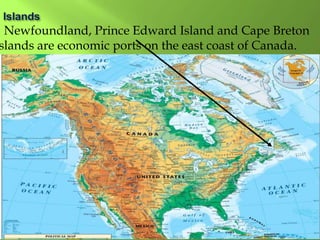
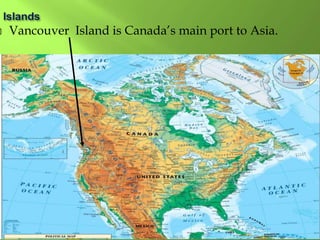
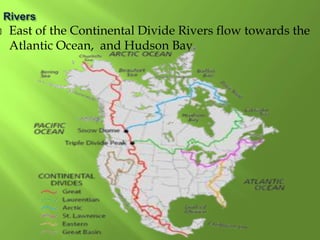
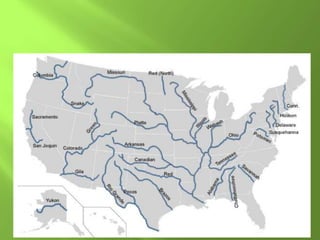
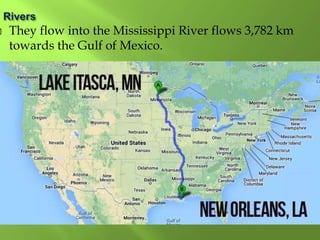
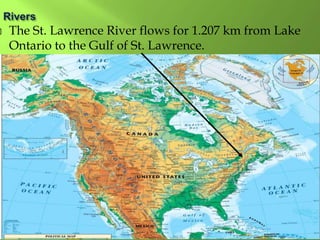
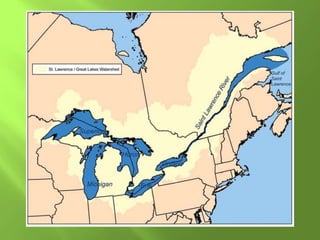
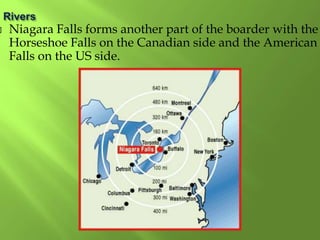
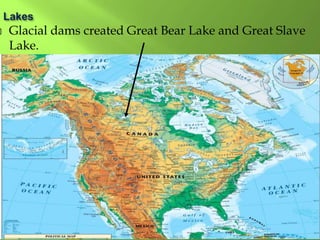
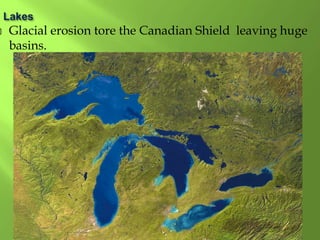
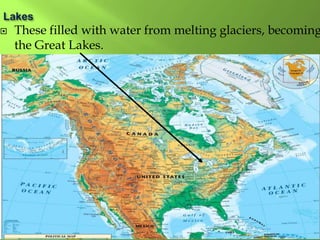
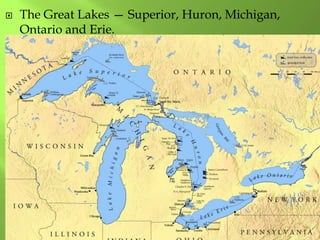
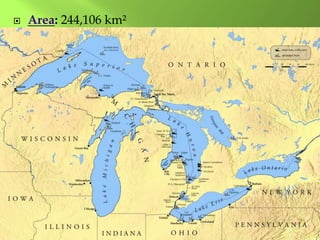
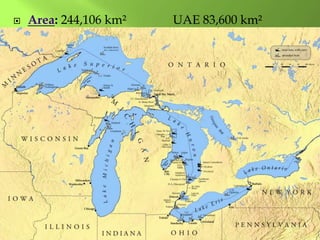
The document summarizes the major geographic features and natural resources of North America. It describes the various mountain ranges, plains, basins and plateaus that were formed by tectonic activity and erosion. It notes the continent's wealth of natural resources like gold, silver and food and how resources have contributed to the economic strength of the United States and Canada. Major rivers like the Mississippi and St. Lawrence are also outlined for their importance to trade and transportation.




















































































![World[8] 75,212,696
1 United States 18,561,930
— European Union[n 1][8] 16,518,723
2 China[n 2] 11,391,619
3 Japan 4,730,300
4 Germany 3,494,900
5 United Kingdom 2,649,890
6 France 2,488,280
7 India 2,250,990
8 Italy 1,852,500
9 Brazil 1,769,600
10 Canada 1,532,340](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-161119064307/85/Geography-North-America-132-320.jpg)