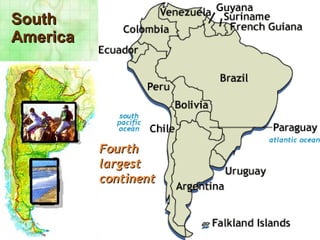
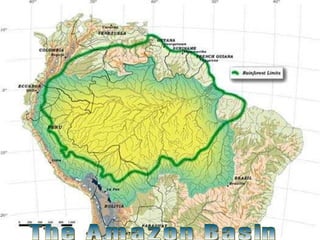
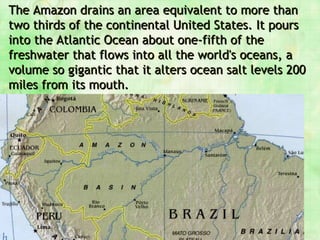
The Andes mountains run the entire length of South America. They contain unique ecosystems like the páramo between the forest line and snow line. South America also contains the world's driest desert (the Atacama), the highest commercially navigable lake (Lake Titicaca), and the fertile Pampas grasslands. The mighty Amazon river basin drains much of north Brazil and contains the greatest biodiversity on Earth in the Amazon rainforest.