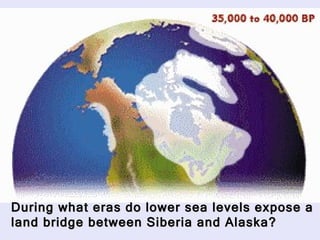
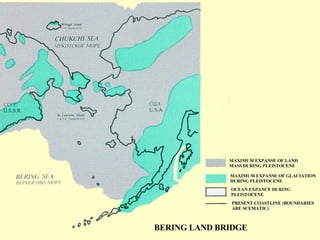
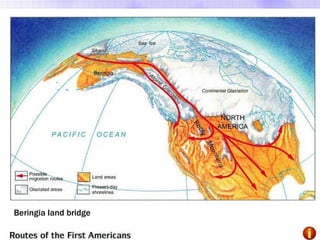
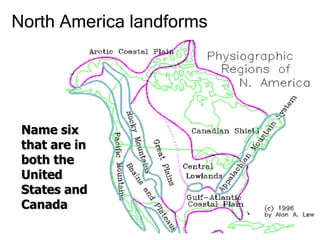
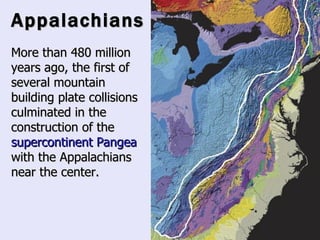
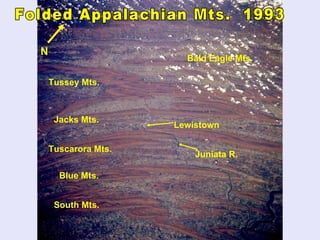
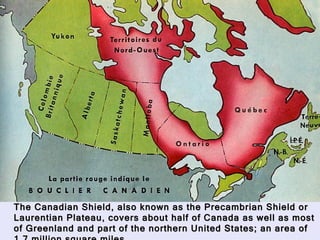
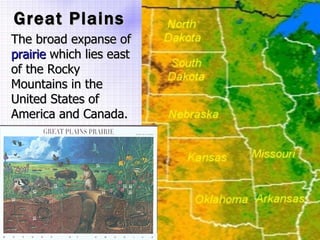
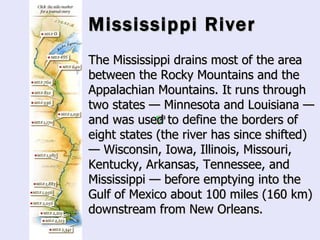
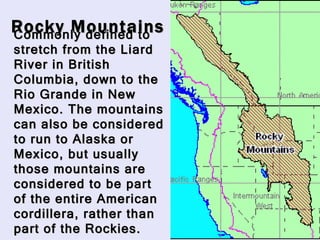
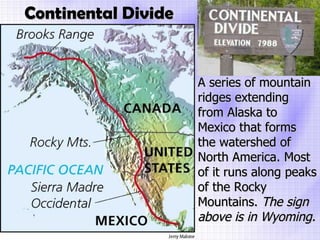
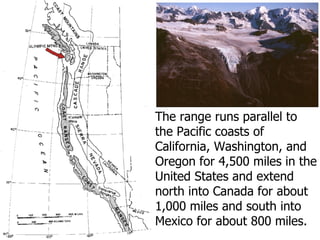
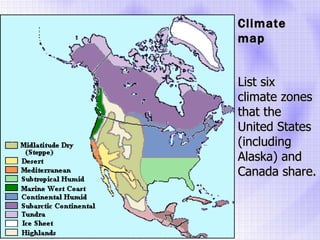
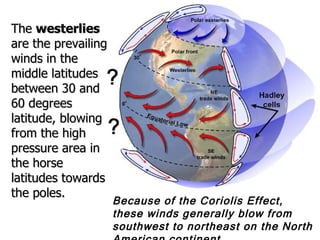
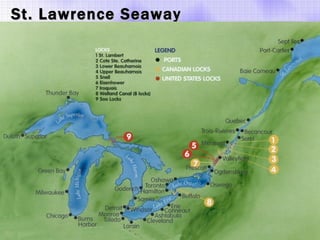
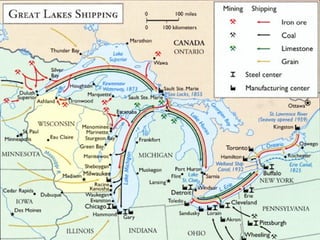
The Beringia land bridge exposed during the last ice age, between 12,000-9,000 years ago, allowed humans, animals, and plants to migrate between Siberia and Alaska. Around this time, many large mammal species in North America went extinct, possibly due to overhunting by humans or climate change. Key landforms shared between the US and Canada include the Appalachian Mountains, Canadian Shield, Great Plains, Mississippi River, Rocky Mountains, and Continental Divide.