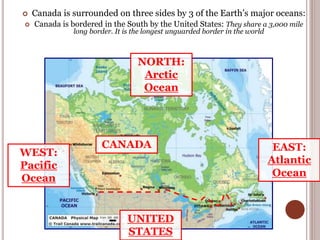
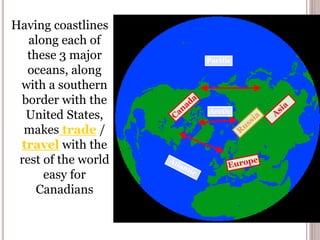
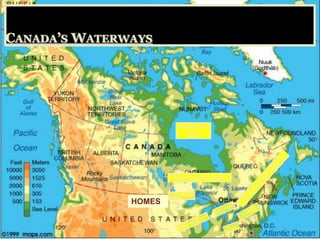
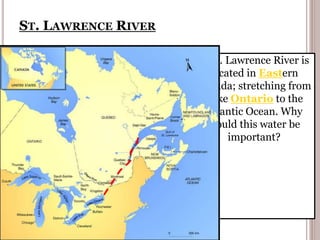
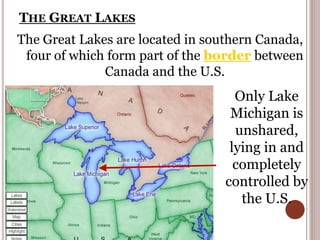
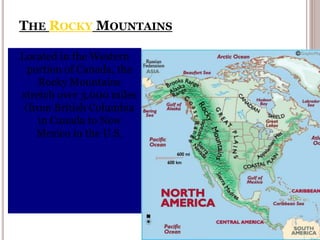
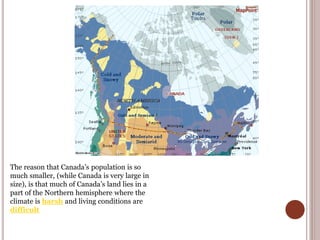
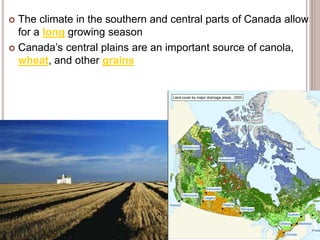
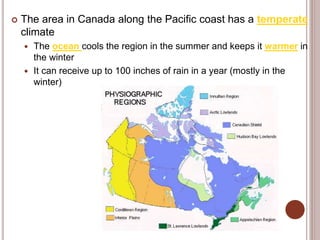
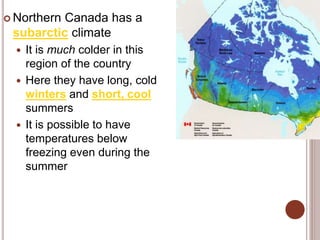
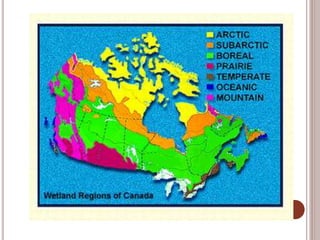
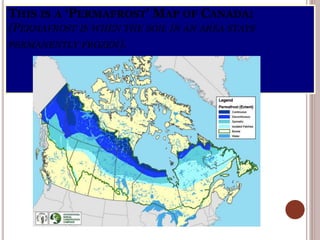
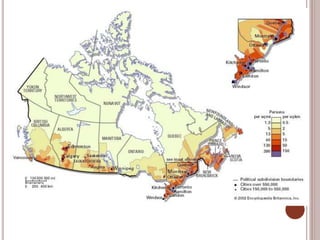
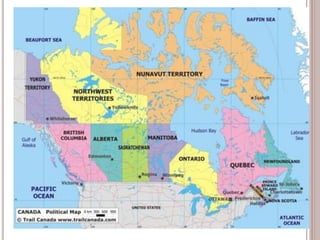
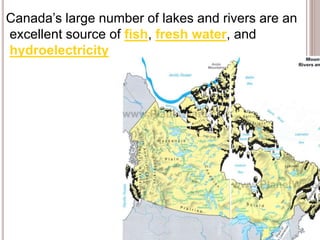
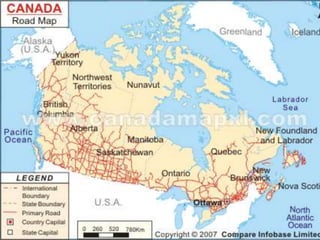
Canada is located in northern North America, bordered by three oceans (the Arctic, Atlantic, and Pacific) and one country (the United States) to the south. While Canada has a large land area, most of its population lives near the southern border due to the harsh climate further north. The country's location and natural resources have contributed to its development and trade.