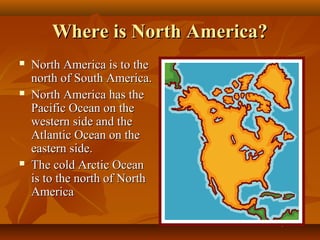
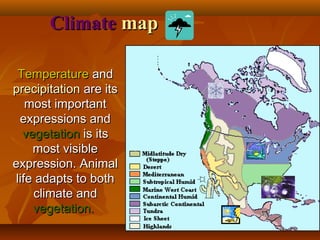
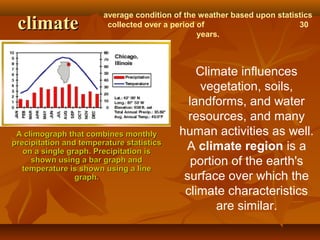
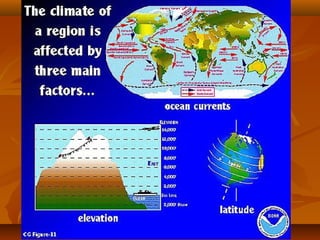
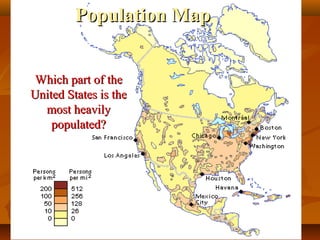
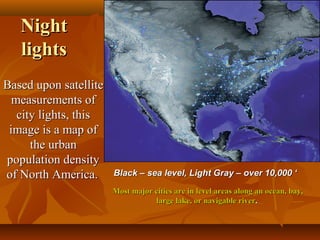
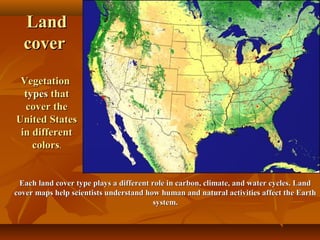
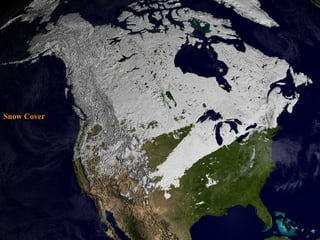
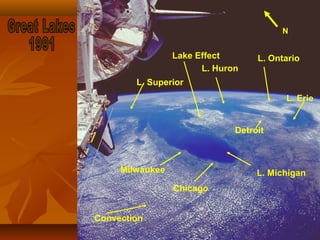
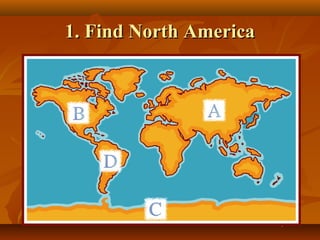
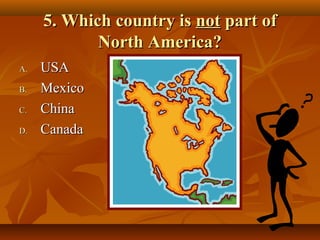
North America is located between the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Arctic Ocean to the north. It contains several countries including the USA, Canada, and Mexico. The climate and environment varies greatly from region to region, ranging from tropical rainforests to grasslands to tundra. Many different animal species have adapted to these diverse landscapes across the continent.