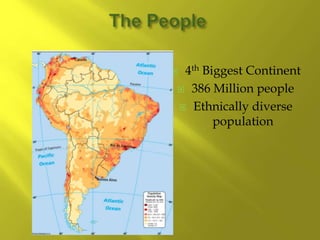
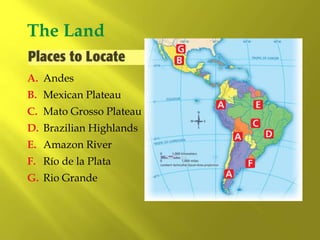
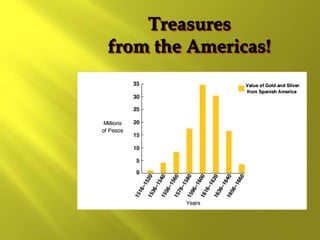
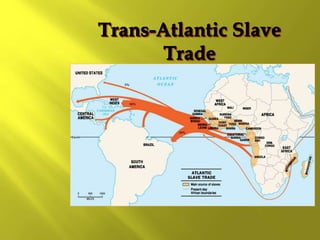
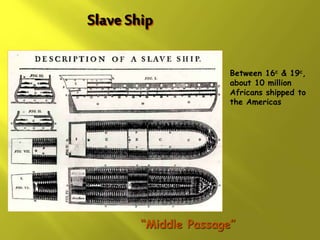
This document provides information about the population and demographics of South America. It notes that South America's population is ethnically diverse as a result of blending indigenous, European, African, and Asian cultures. Some key points include:
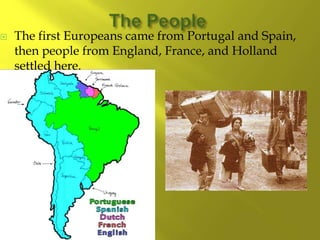
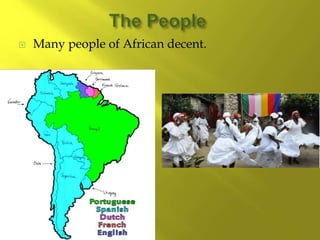
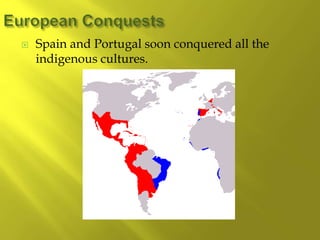
- There are over 350 indigenous groups still living in the Andes and Amazon regions. Early European settlers were Portuguese and Spanish, followed by English, French, and Dutch. Enslaved Africans and contract workers from India also contributed to the ethnic diversity.
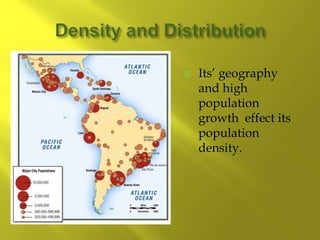
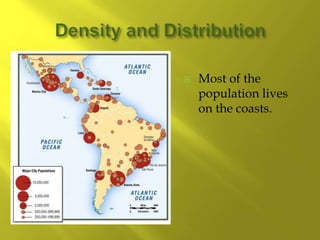
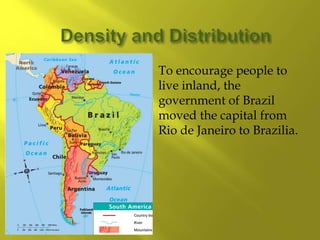
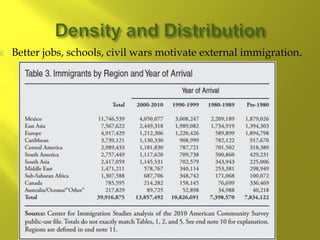
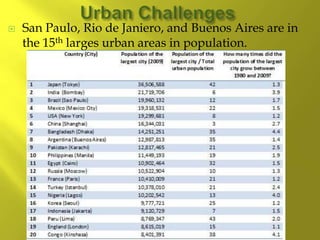
- The population is highly urbanized, with over 80% living in cities, especially along the coasts. The largest and most populated cities are Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Buenos Aires, which have large income