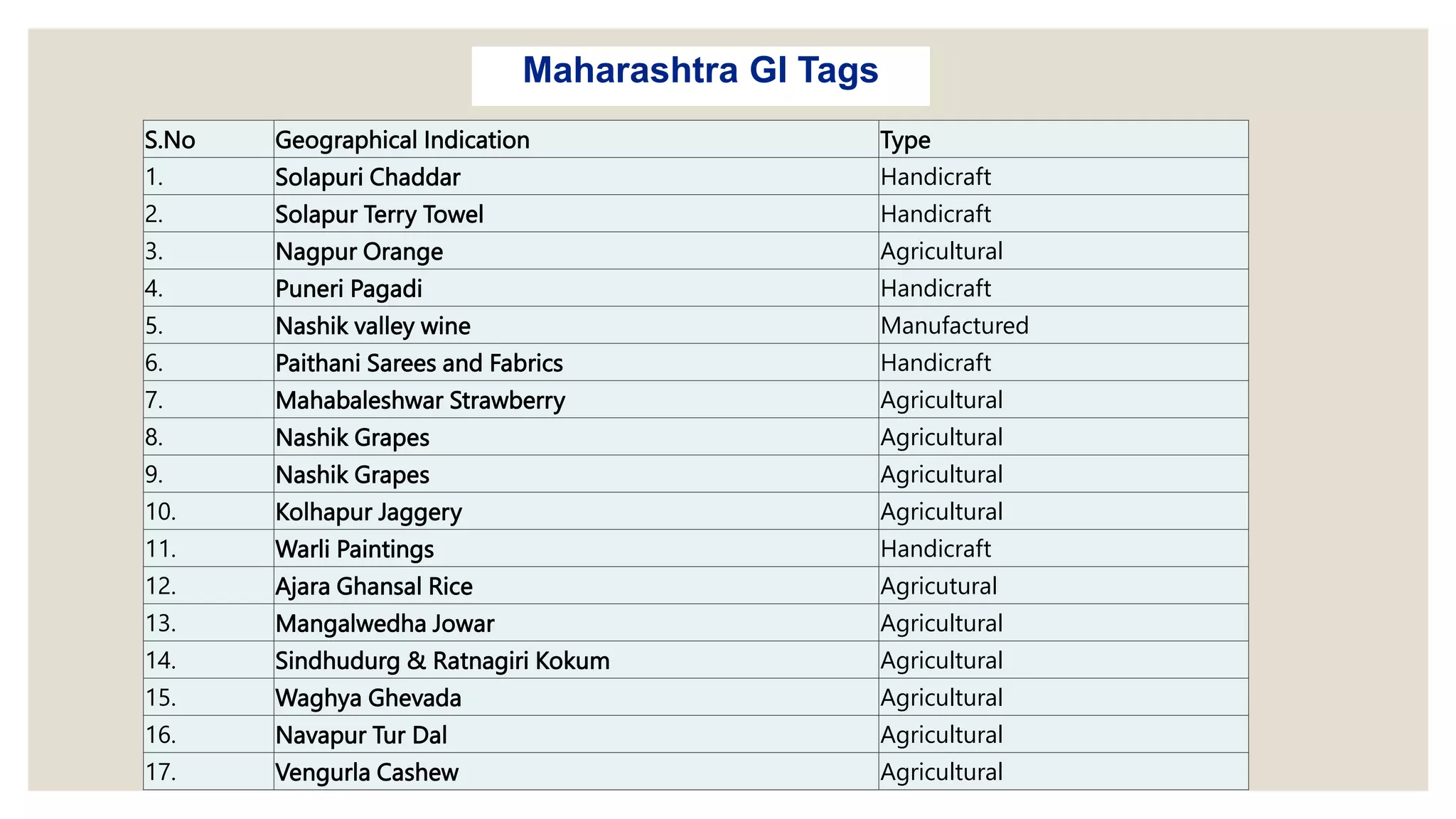
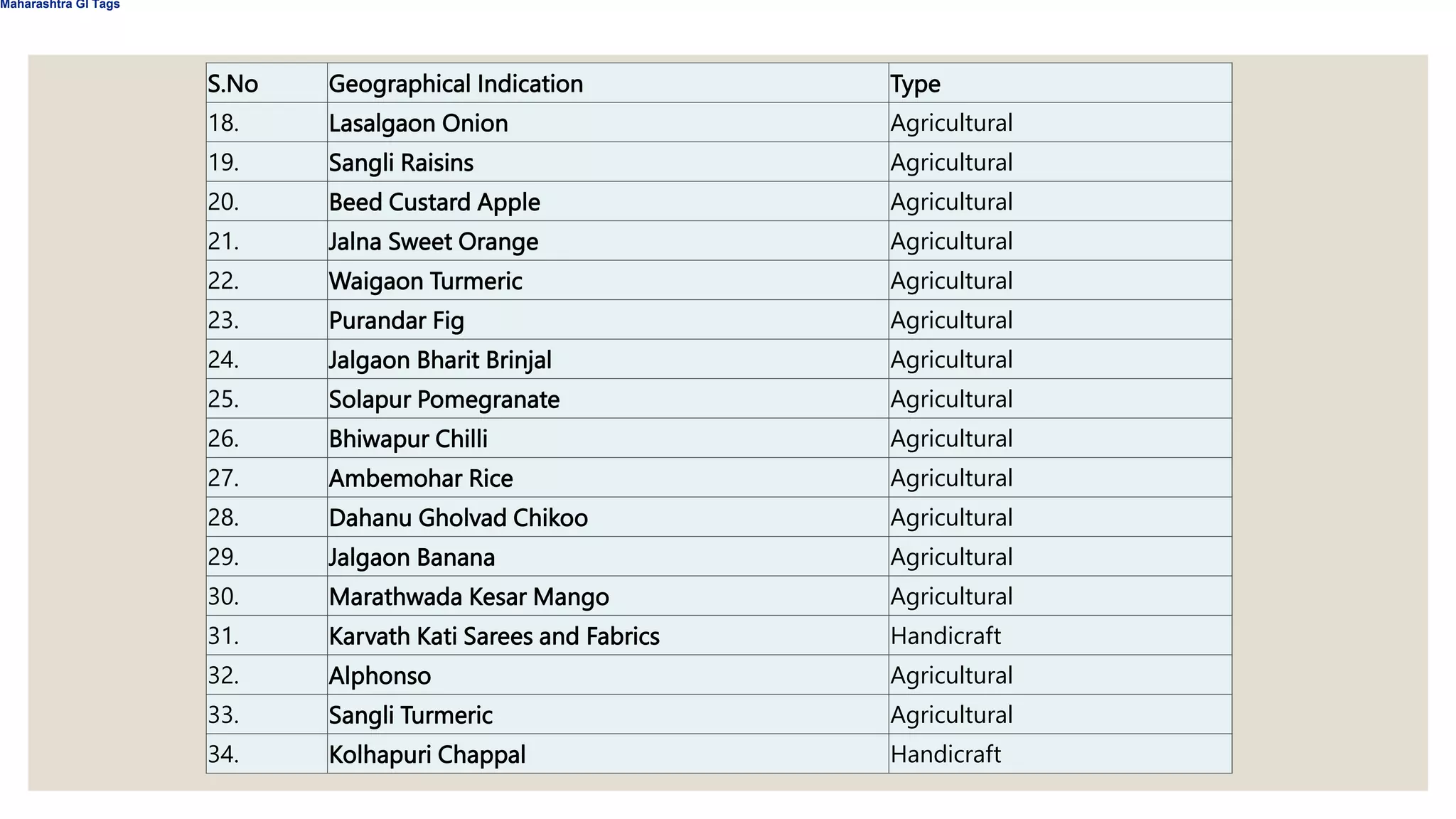
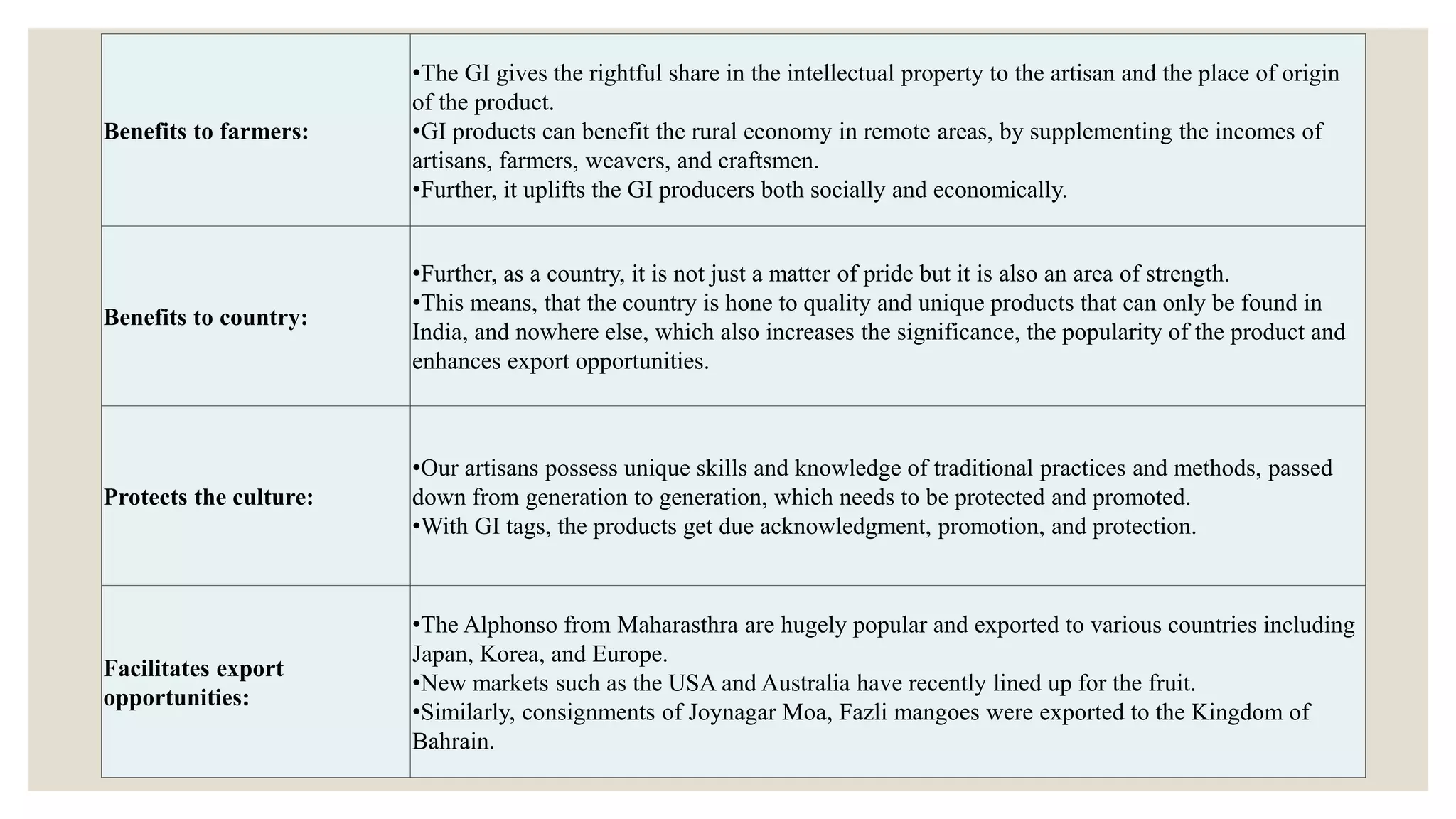
Geographical indications (GIs) identify products that originate from specific regions and have qualities or reputations due to their geographic origin. GIs are protected under intellectual property laws to prevent unauthorized use of place names. The document lists several Indian products that have received GI status, such as Kashmir Saffron, Manipuri Black Rice, and Mizo handicrafts. It describes the benefits of GI protection for producers, consumers, and countries in promoting economic prosperity, preserving cultural heritage, and facilitating export opportunities. GI rights allow authorized users to prevent others from using protected names for non-compliant products. GIs are protected through sui generis systems, collective/certification marks, and administrative approval schemes depending on the country