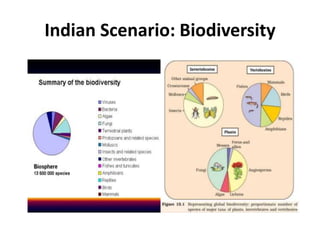
The Biological Diversity Act of 2002 was passed in India to comply with the Convention on Biological Diversity and promote conservation of biodiversity as well as sharing benefits from genetic resources. The Act aims to conserve biological diversity, ensure sustainable use of resources, and facilitate fair benefit-sharing. It regulates access to biological resources, protects local community knowledge, and involves state governments in implementation. Biological diversity refers to variability among living organisms, including diversity within and between species and ecosystems. Intellectual property rights play an ambiguous role, as they can both encourage commercial farming that threatens biodiversity, but can also promote its conservation through technologies that ensure its protection and sustainable use.



![Definitions
(Biological Diversity Act, 2002)
• Biological Diversity: means the variability among living organisms from all
sources and the ecological complexes of which they are part and includes
diversity within species or between species and of eco-systems [chapter I
Clause 2b].
• Biological resources: means plants, animals and microorganisms or parts
thereof, their genetic material and by –products with actual or potential
use or value but does not include human genetic material [Chapter I
Clause 2c].
• Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): rights to ideas and information, which
are used in new inventions or processes. These rights enable the holder to
exclude imitators from marketing such inventions or processes for
specified period of time; in exchange the holder is required to disclose the
formula or idea behind the product/process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iprandbiodiversity-210719082603/85/Ipr-and-biodiversity-4-320.jpg)