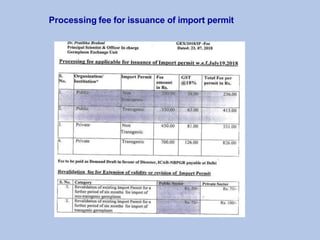
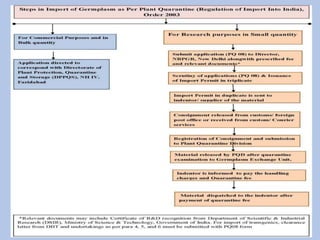
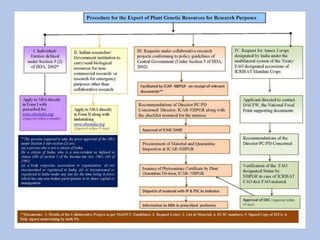
This document discusses germplasm introduction and exchange. It defines germplasm introduction as the transfer of crop plants or genetic resources from one area to another where they have not been cultivated before. The objectives of germplasm introduction include introducing new plant species, high yielding varieties, enriching germplasm collections, and obtaining new sources of biotic and abiotic stress resistance. The document outlines the types, agencies, and steps involved in plant introduction and exchange in India and internationally. It discusses the merits of introducing new germplasm, but also notes some potential demerits such as introducing new weeds, pests, or diseases.