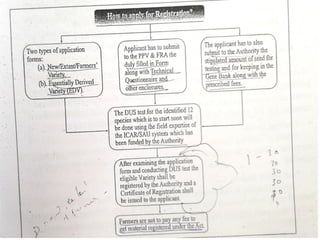
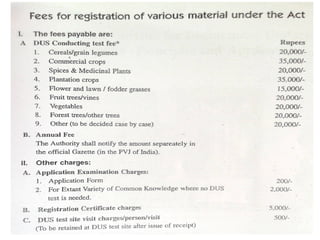
The document outlines the procedure for registering plant varieties under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act (PPVFR) of 2001 in India, detailing types of crops eligible for protection and the registration criteria for different varieties. It also explains the rights of both breeders and farmers regarding the use and commercialization of registered varieties, as well as penalties for infringement and provisions for farmer protections. Additionally, the document includes guidelines for benefit sharing, compulsory licensing, and the renewal process for registrations.