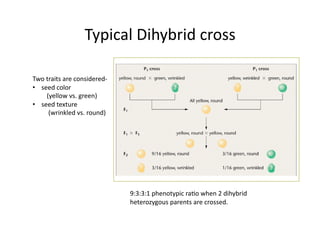
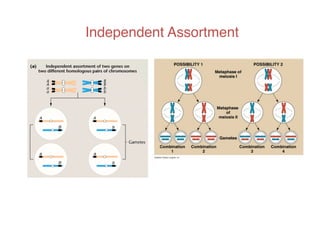
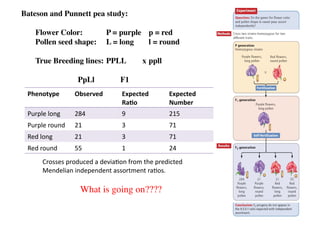
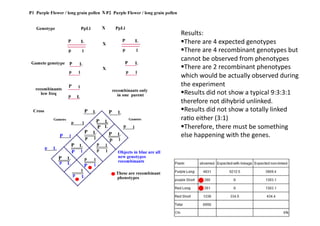
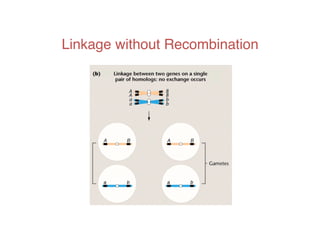
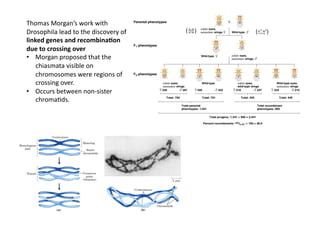
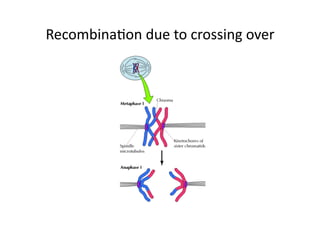
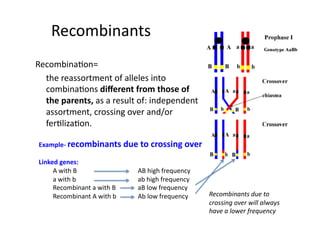
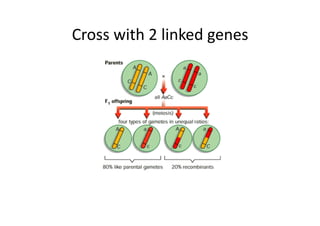
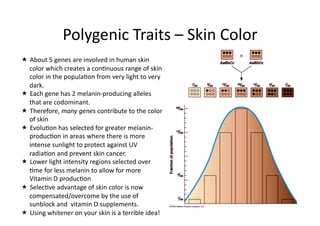
This document discusses gene linkage and recombination. It provides examples from early experiments on pea plants that showed deviations from expected Mendelian ratios, indicating linkage between genes for flower color and pollen shape. The discovery of crossing over during meiosis provided an explanation for how genes can be reshuffled during reproduction. Linkage maps were developed that show the relative distances between genes on chromosomes based on crossover frequencies. Polygenic traits like human skin color are also summarized, which involve multiple genes contributing to a continuous variation in a phenotype.