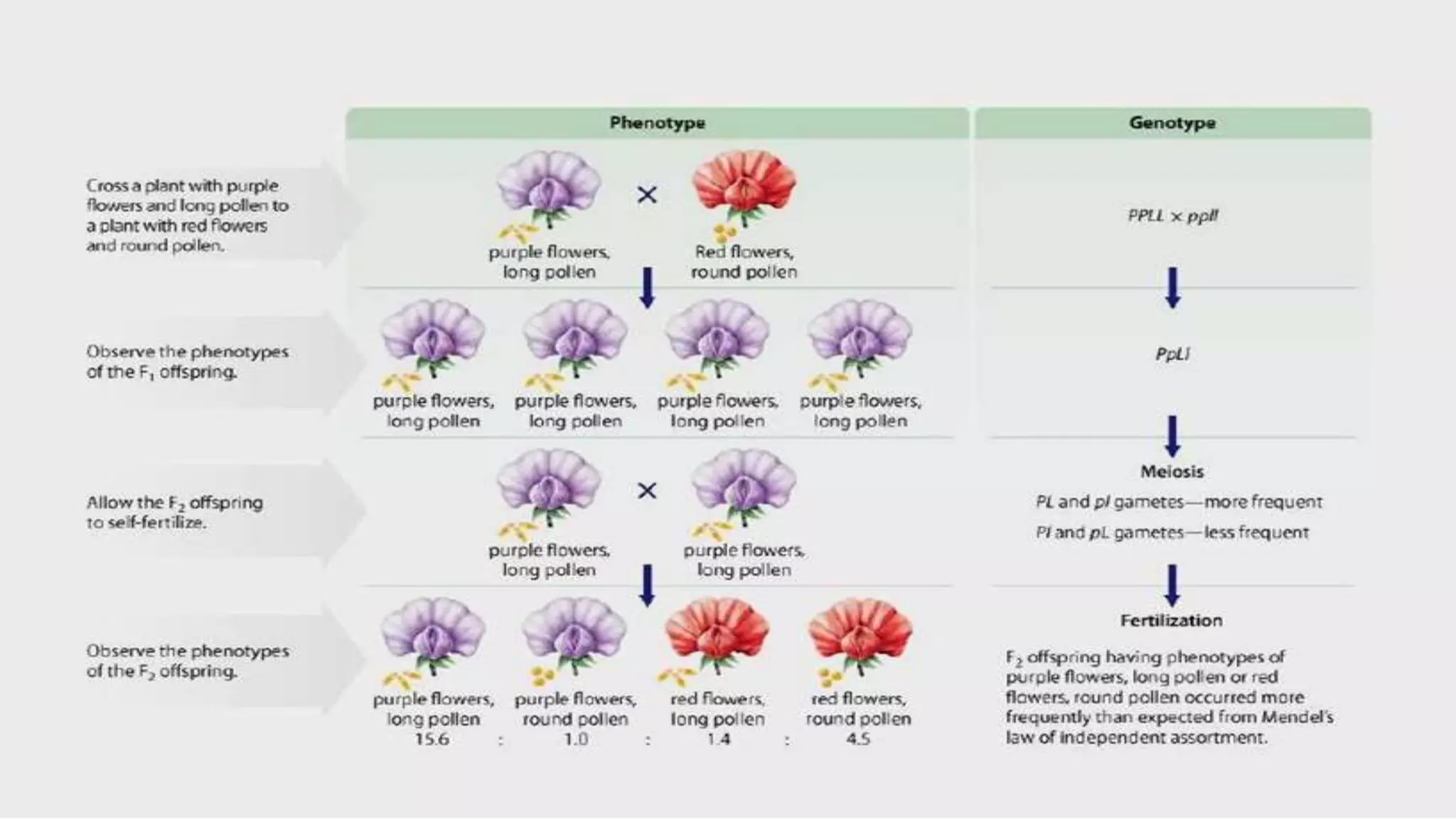
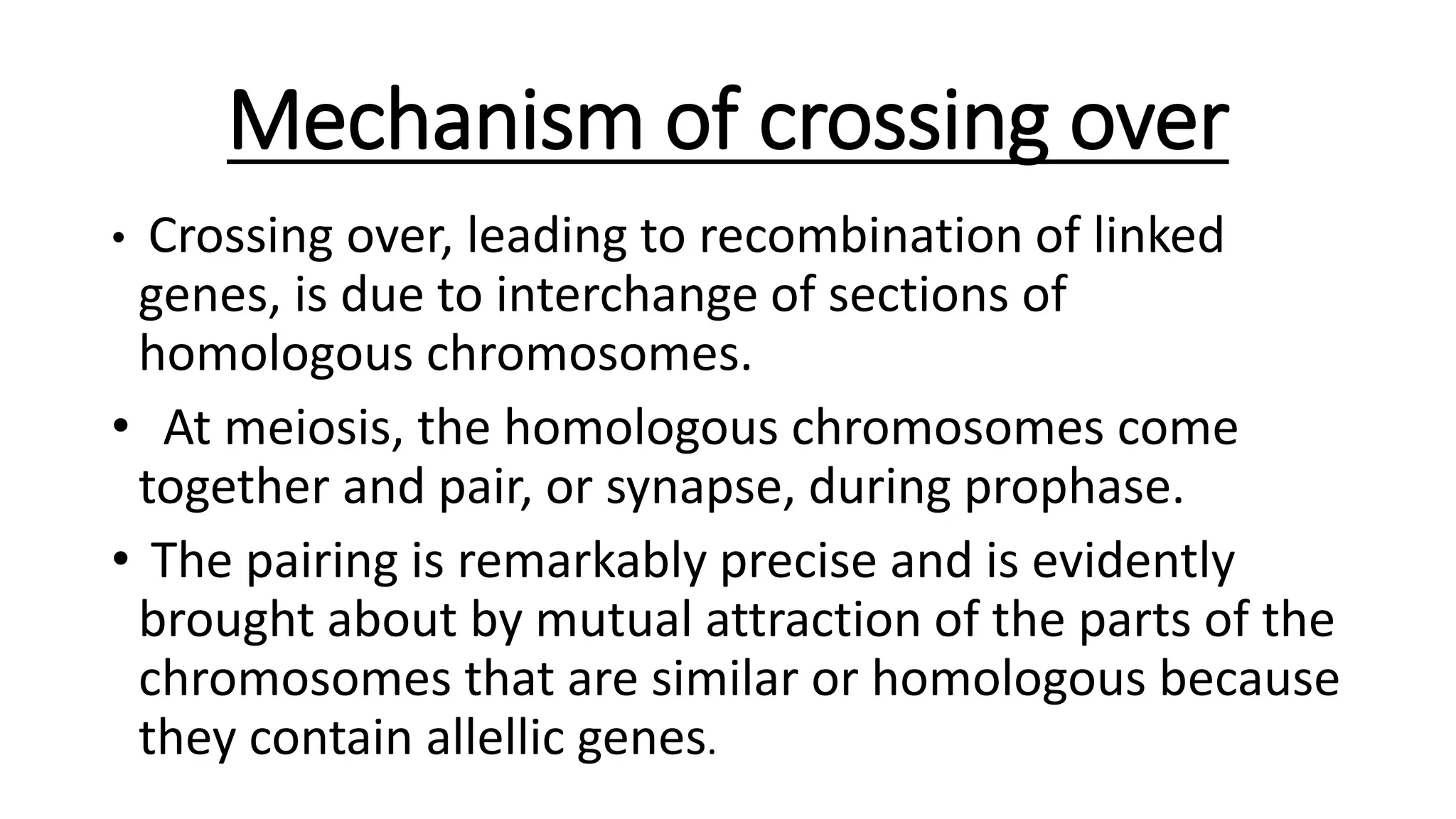
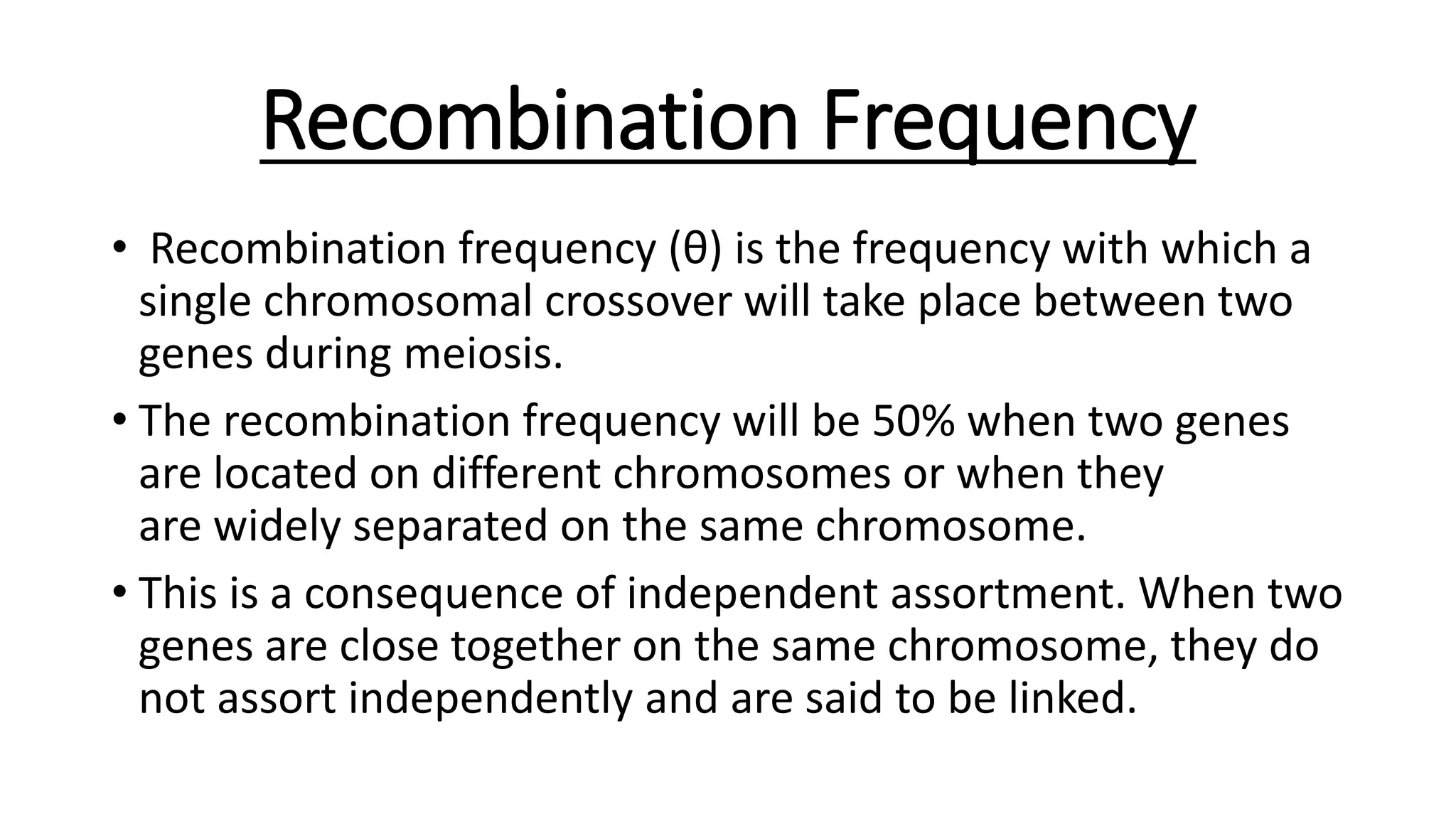
The document discusses genetic linkage and crossing over, detailing how alleles close together on a chromosome tend to be inherited together, contrasting independent assortment. It explains the concepts of complete and incomplete linkage, the significance of crossing over in producing genetic diversity, and the factors influencing crossover frequency. Key figures in the discovery of these concepts, such as William Bateson and Reginald Punnett, are also highlighted along with the mechanisms and types of crossing over.