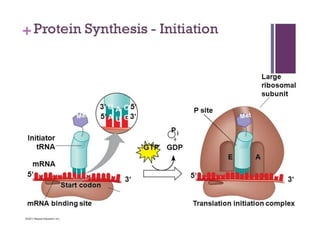
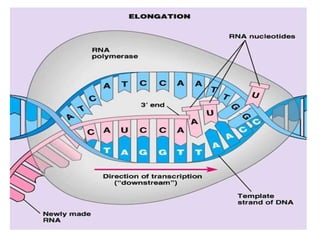
Protein biosynthesis is the process by which cells synthesize proteins. It involves the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain based on the genetic code. The main stages are activation of amino acids, initiation of translation at start codons on mRNA, elongation of the polypeptide chain by adding amino acids one by one, and termination when a stop codon is reached. Chaperones assist in protein folding and post-translational modifications further process the protein.


![1] REQUIREMENT OF THE
COMPONENT
Amino acids
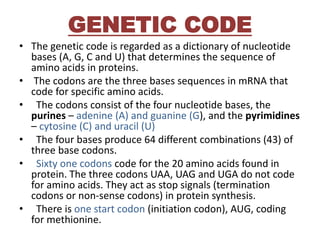
• Of the 20 amino acids found in protein structure,
half of them (10) can be synthesized by man.
• About 10 essential amino acids have to be
provided through the diet.
• Therefore, a regular dietary supply of essential
amino acids, should be maintained.
• In prokaryotes, there is no requirement of amino
acids, since all the 20 are synthesized from the
inorganic components.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-6-320.jpg)

![2]ACTIVATION OF AMINO ACIDS
• For the incorporation of amino acids into a
polypeptide chain, amino acids are first activated and
get to their appropriate tRNA carriers.
• Linkage of an amino acid to the tRNA requires energy
and is catalyzed by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
• The amino acid is first attached to the enzyme
utilizing ATP to form enzyme-AMP amino acid
complex.
• The amino acid is then transferred to the 3’ end of
the tRNA to form aminoacyl tRNA. A misacylated
tRNA is recognized and removed (deacylated) by
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-10-320.jpg)
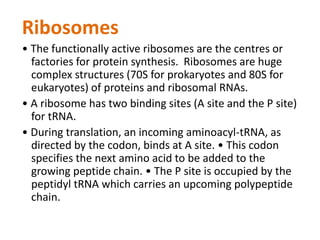
![3] PROTEIN SYNTHESIS PROPER
• The protein or polypeptide synthesis occurs
on the ribosomes.
• The mRNA is read in the 5’→ 3’ direction and
the polypeptide synthesis proceeds from N-
terminal end to C-terminal end.
• Translation is directional and collinear with
mRNA.
• The prokaryotic mRNAs are polycistronic
where as eukaryotic mRNA is monocistronic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-11-320.jpg)


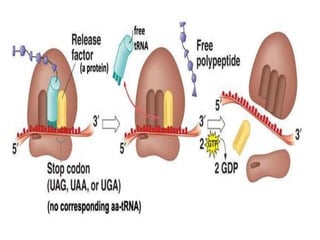
![TERMINATION
• There is a universal release factor, eRF1, that
recognizes all three stop codons [UAA,UGA
and UAG].
• The protein release factor interacts with the
stop codon to terminate translation.
• The ribosome dissociates and the mRNA is
released and can be used again.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-19-320.jpg)
![4]CHAPERONS AND PROTEIN
FOLDING
• molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the covalent
folding or unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of other
macromolecular structures. The first protein to be called a
chaperone assists the assembly of nucleosomesfrom folded
histones and DNA and such assembly occur in nucleus.
• the newly-formed peptide chain is folded and processed into
its biologically-active form. At some point of time, during or
after protein synthesis, the polypeptide chain spontaneously
assumes its native conformation by forming sufficient number
of hydrogen bonds and van der Waals, ionic, and hydrophobic
interactions. In this way, the linear (or one dimensional)
genetic message encoded in mRNA is converted into the 3-
dimensional structure of the protein.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-21-320.jpg)
![5]POST TRANSLATIONAL
MODIFICATION
• N-terminal and C- terminal modification:
The formyl group at the N-terminus of bacterial
proteins is hydrolyzed by a deformylase. One or
more N-terminal residues may be removed by
aminopeptidases.
• Loss of signal sequences: In certain proteins,
some (15 to 30) amino acid residues at the N-
terminus play a role in directing the protein to
its ultimate destination in the cell. Such signal
sequences, as they are called, are ultimately
removed by specific peptidases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subincology-180706184822/85/Subin-cology-22-320.jpg)


