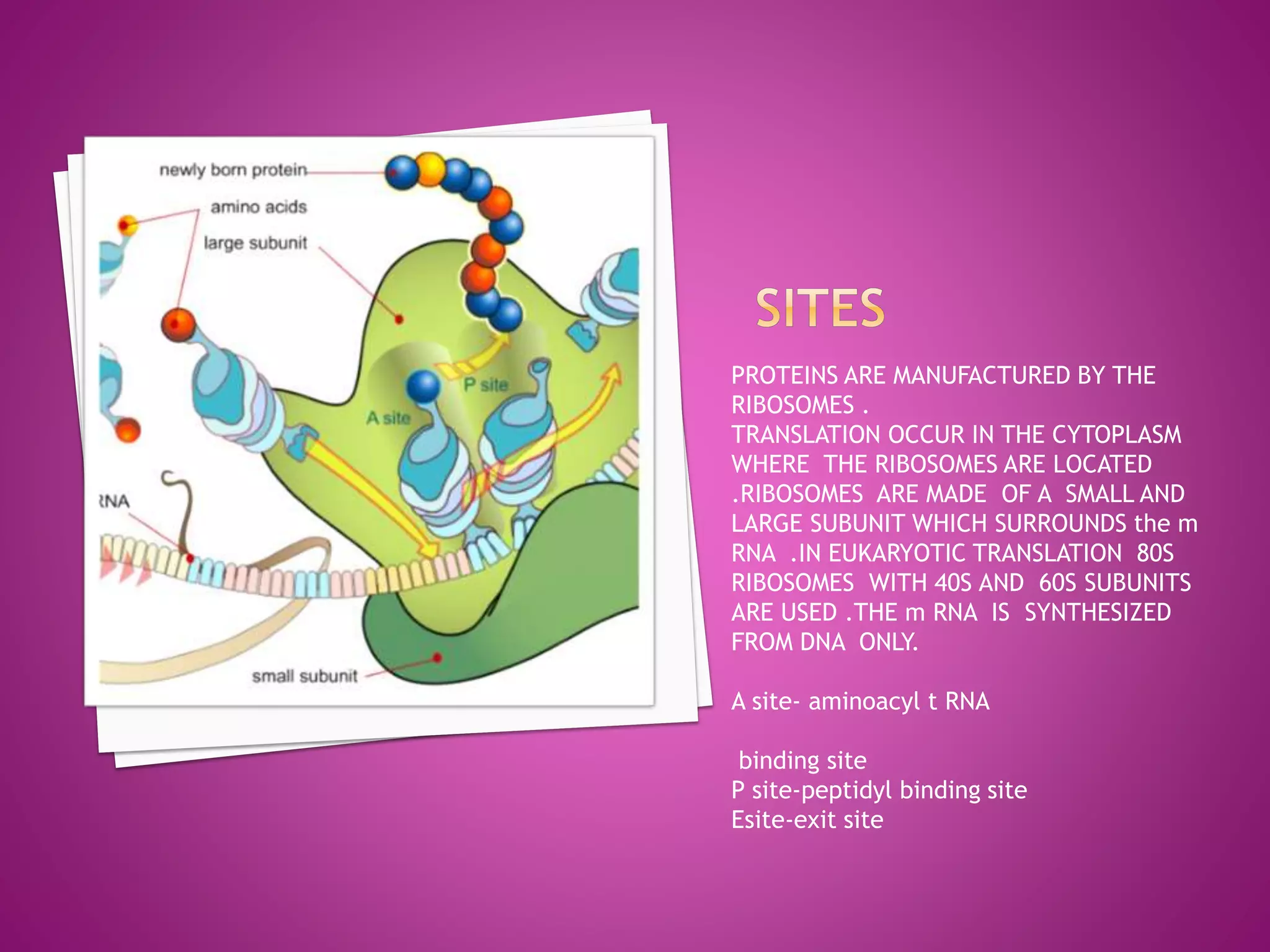
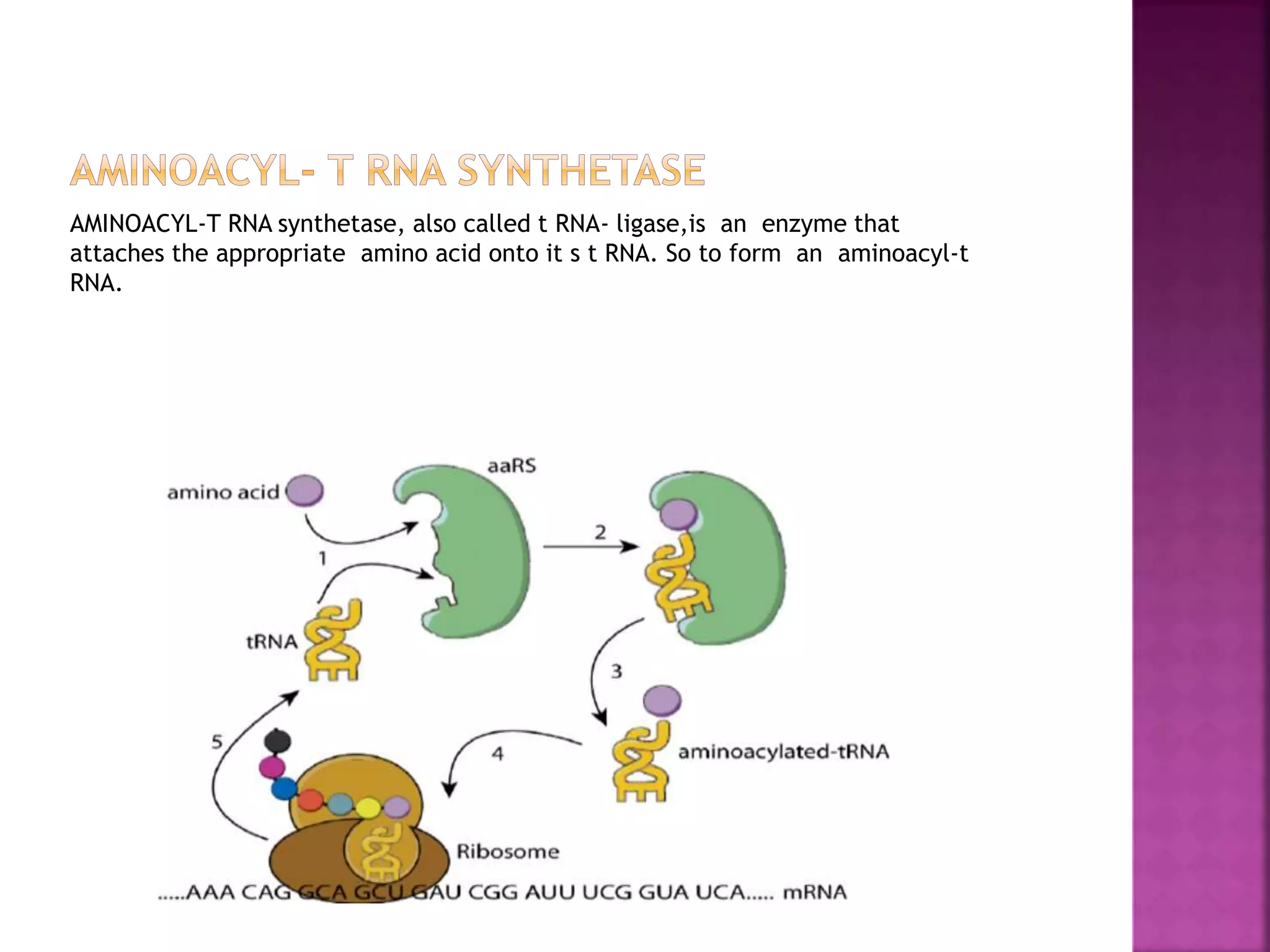
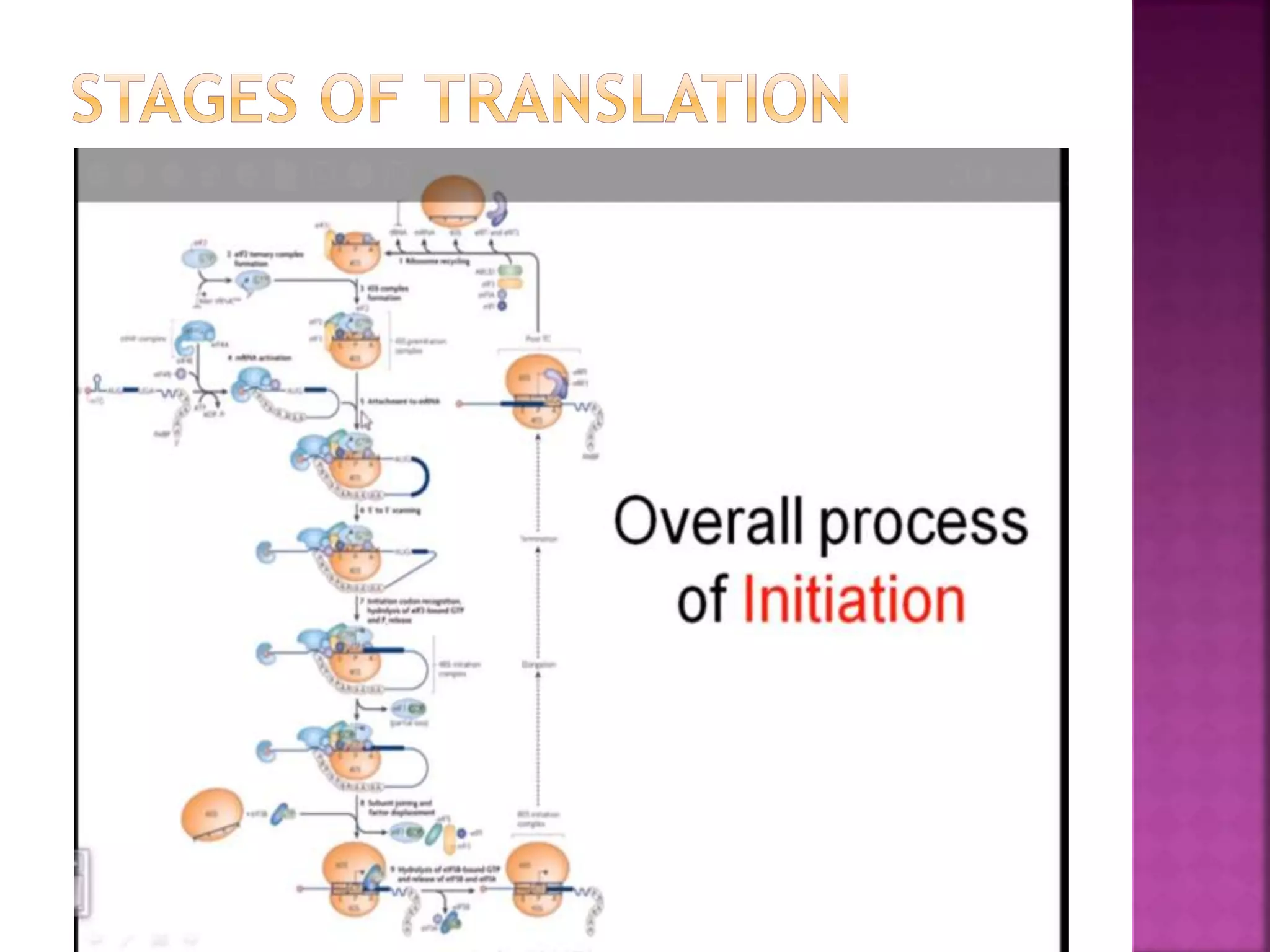
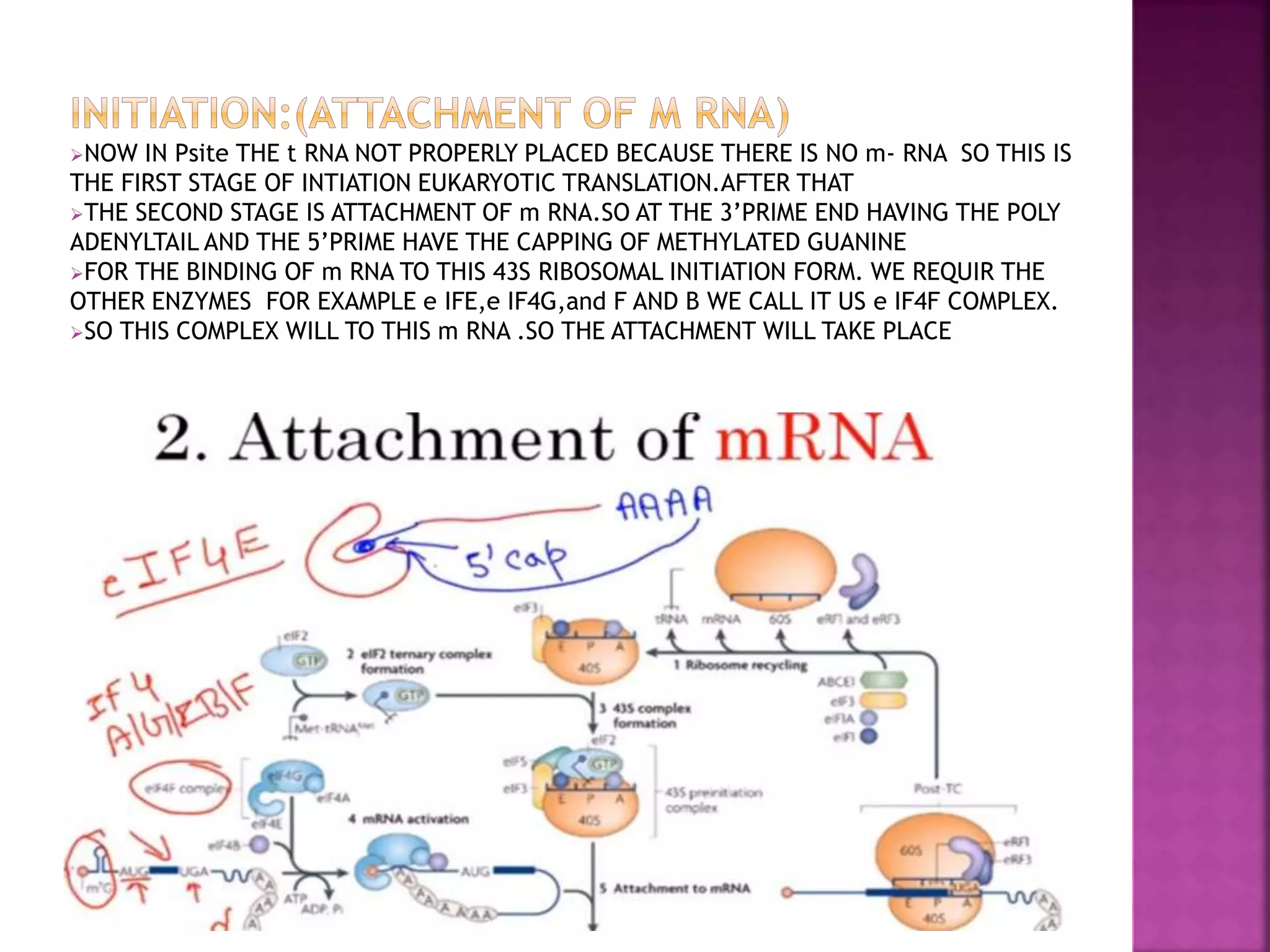
Translation is the process by which the information contained in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It occurs in the cytoplasm and involves ribosomes, tRNA, and various translation factors. The mRNA binds to the ribosome and is read three nucleotides at a time, known as codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, which is delivered to the ribosome by tRNA. The amino acids are then linked together to form a polypeptide chain in an elongation process driven by the movement of the ribosome along the mRNA. Translation terminates when a stop codon is reached, releasing the complete protein.