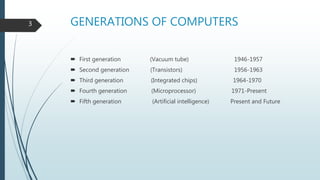
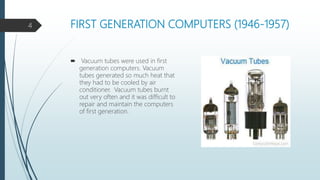
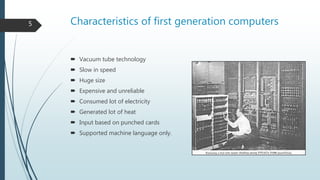
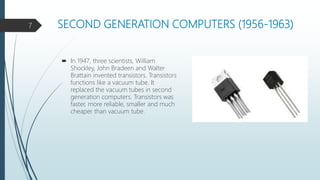
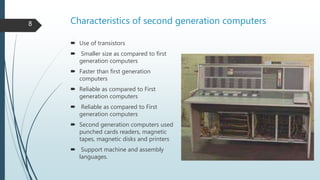
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the first to the present. The first generation used vacuum tubes from 1946-1957 and were large, expensive, unreliable, and generated a lot of heat. The second generation used transistors from 1956-1963, which made computers smaller, faster, and more reliable. The third generation from 1964-1970 used integrated circuits, improving speed and memory while reducing size and cost. The fourth generation from 1971-present used microprocessors and VLSI chips, making computers smaller, more powerful, and affordable with a variety of software. The goal of the ongoing fifth generation is to develop artificial intelligence for natural language understanding and thinking capabilities.