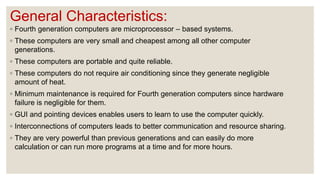
The document outlines the evolution of computers through five generations, highlighting key technological advances and characteristics of each generation. Starting from vacuum tubes in the first generation to ULSI and AI applications in the fifth generation, it explains how each evolution has led to smaller, more efficient, and powerful computing devices. Additionally, it provides examples and specifics about programming languages, maintenance needs, and user interfaces related to each generation.