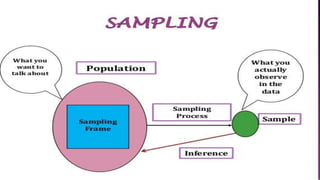
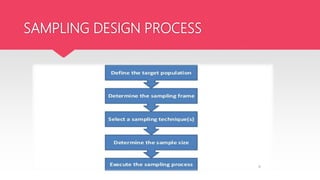
This document discusses different sampling methods used in research. It describes probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, systematic random sampling, and multistage sampling. It also describes non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgmental sampling, snowball sampling. The document notes that probability sampling allows inferences about the population, while non-probability sampling does not. It also discusses sources of sampling error and ways to reduce them, such as using appropriate sampling techniques and sample size.