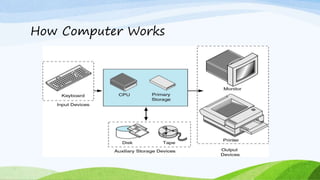
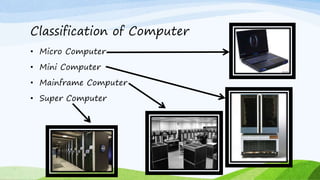
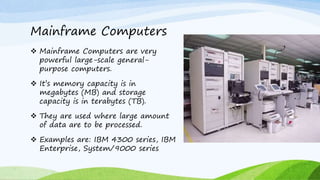
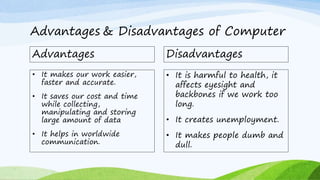
This document provides an introduction to computers, including how they work and their key characteristics. It defines a computer as an electronic device that accepts input, processes data, stores data, and produces output. It then describes the main components of a computer and how data is processed. The document outlines the main characteristics of computers as being fast, accurate, having large memory and storage, being diligent and versatile. It also categorizes the different types of computers as analog, digital, and hybrid and provides examples of each type. Finally, it classifies computers as microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes, and supercomputers and describes the defining features of each.