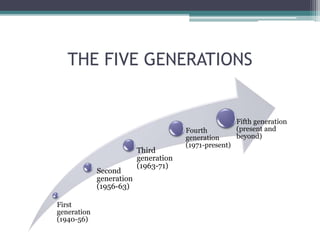
The document outlines the history of computers, divided into five generations, each characterized by significant technological advancements. The five generations include: first generation (vacuum tubes, 1940-56), second generation (transistors, 1956-63), third generation (integrated circuits, 1963-71), fourth generation (microprocessors, 1971-present), and fifth generation (artificial intelligence, present and beyond). Key developments for each generation illustrate the progression in speed, size, and efficiency of computers over time.