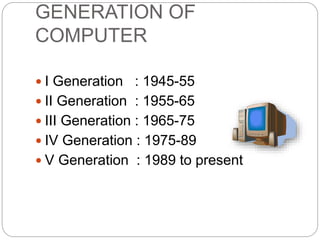
The document explains the evolution of computer generations from their inception in 1945 to the present, detailing the transition from vacuum tubes in the first generation to the development of artificial intelligence in the fifth generation. Each generation showcases significant technological advancements, including the introduction of transistors, integrated circuits, and microprocessors, leading to smaller, faster, and more reliable devices. The fifth generation is currently focused on achieving human-like intelligence through advanced technologies such as quantum computation and nanotechnology.