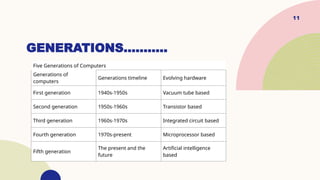
The document outlines the different types and generations of computers, detailing each generation from the first (vacuum tubes) to the fifth (artificial intelligence). It describes various computer types, including supercomputers, mainframes, and personal computers, along with their characteristics and applications. The evolution of computing technology is highlighted through the transitions from vacuum tubes to microprocessors and AI, emphasizing improvements in speed, size, and efficiency.