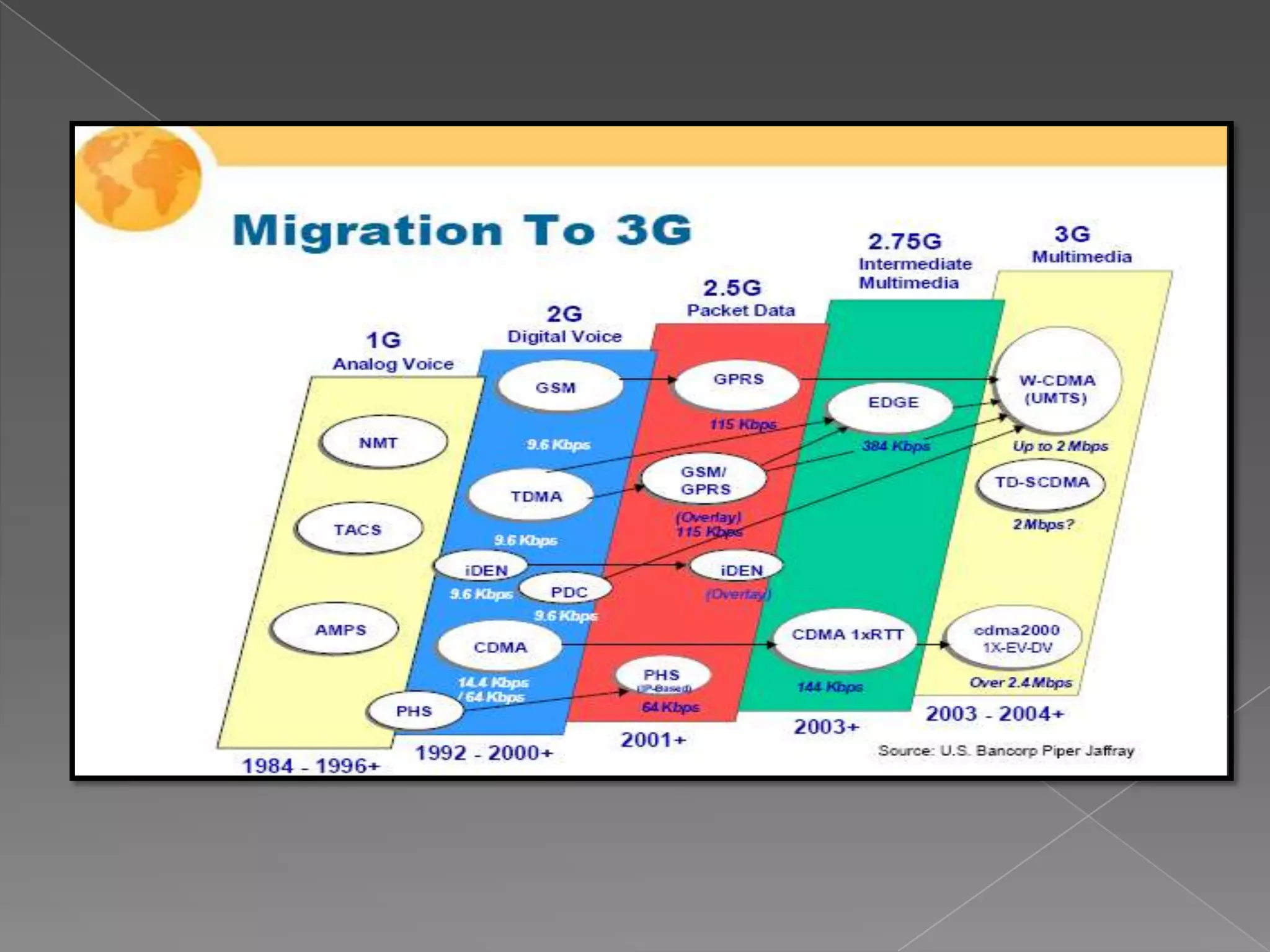
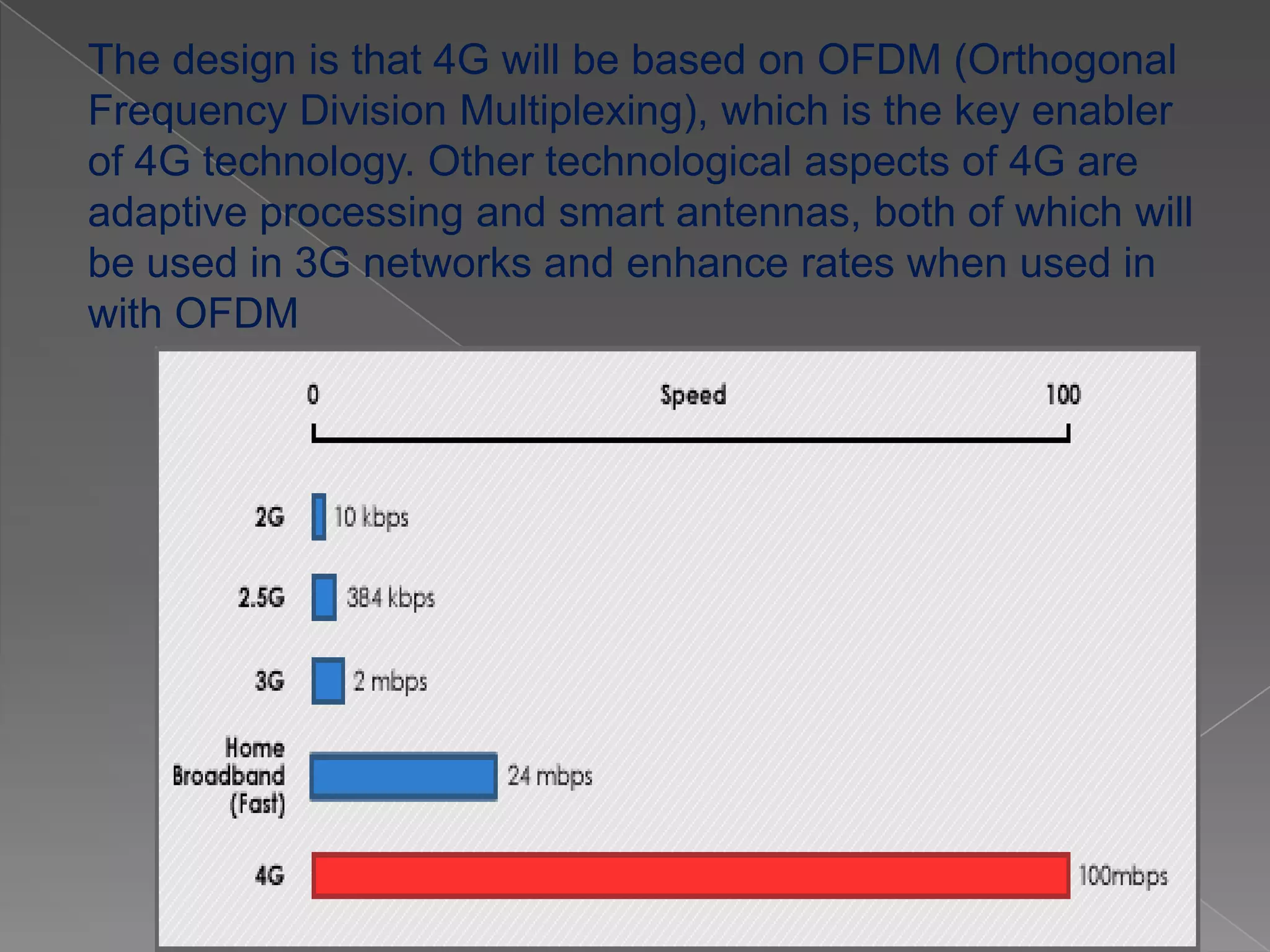
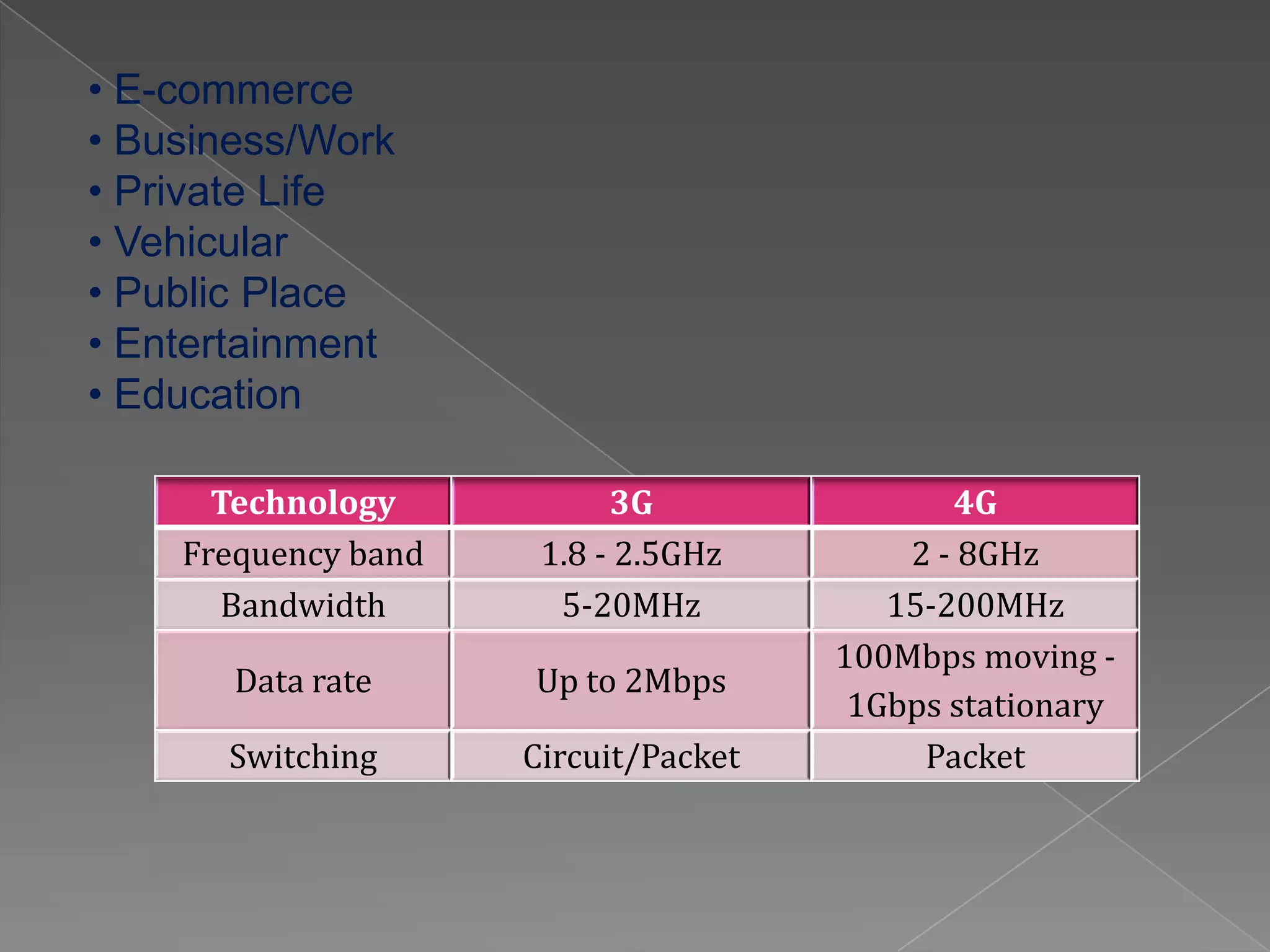
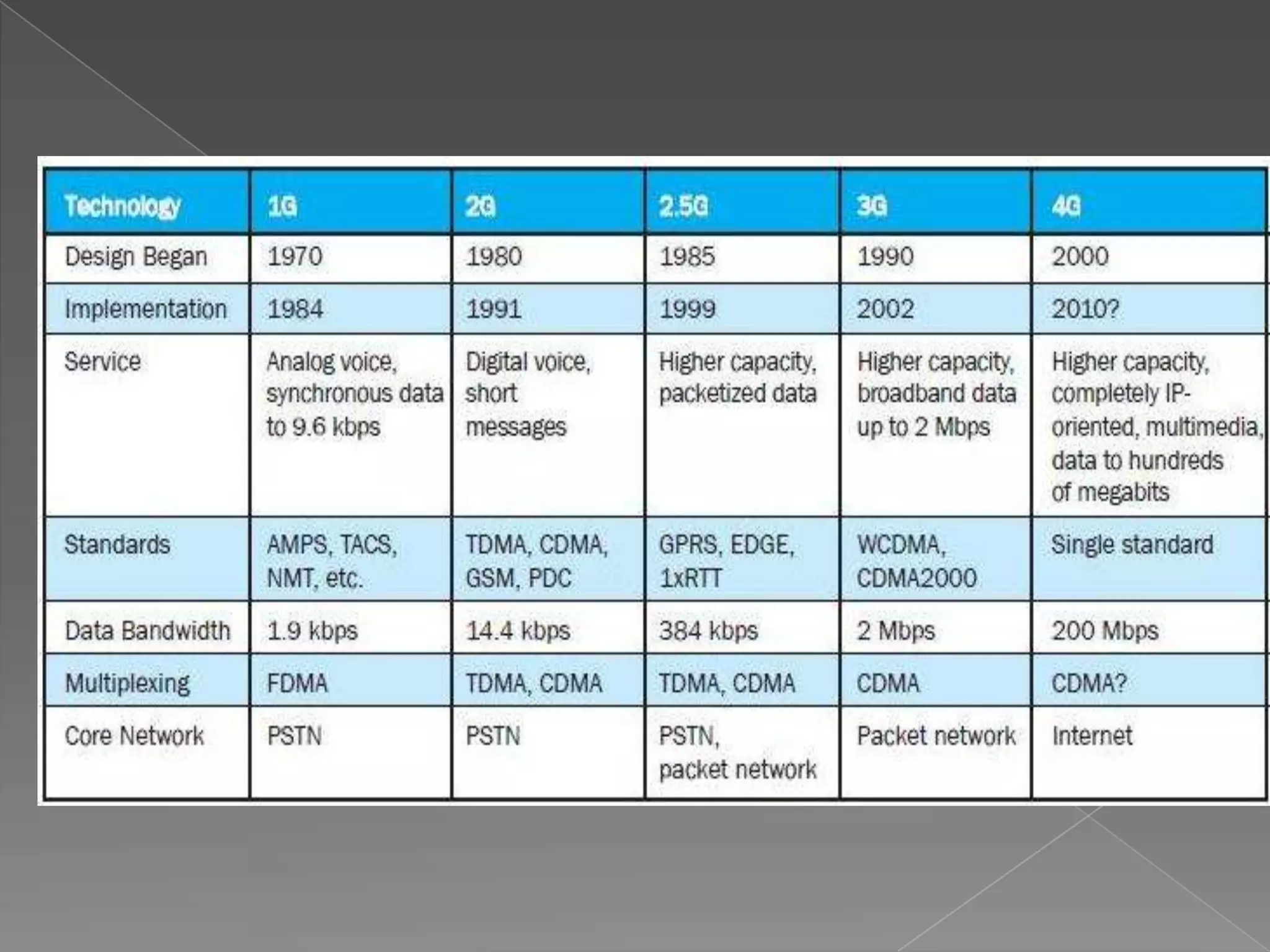
Mobile communication technologies have evolved from 1G analog networks to 2G digital networks to 3G networks that allow data and voice. 4G networks aim to provide speeds of 100Mbps to 1Gbps using technologies like LTE and WiMax. 5G is envisioned to provide even higher bandwidth and connectivity through technologies that have not been fully developed yet. Each generation brings higher speeds and more advanced applications, but also faces challenges in areas like costs, bandwidth requirements, and developing technology standards.