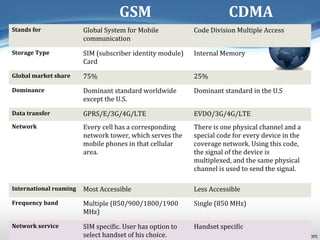
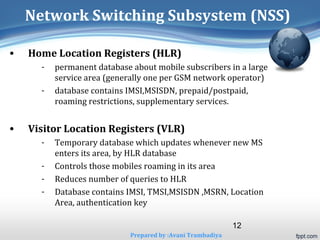
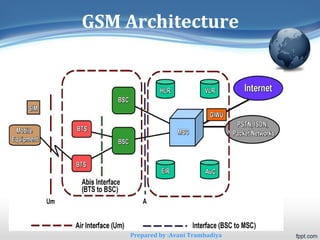
The document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), detailing its definition, history, architecture, advantages, disadvantages, and various applications. GSM is a digital cellular communication standard widely adopted globally, with over 3 billion subscribers and substantial market share. It emphasizes interoperability, security, and a range of telecommunication services, positioning itself as a significant component of modern mobile telephony.