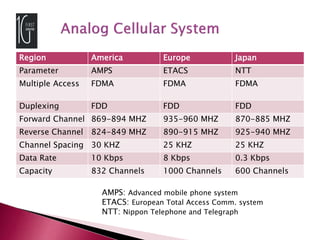
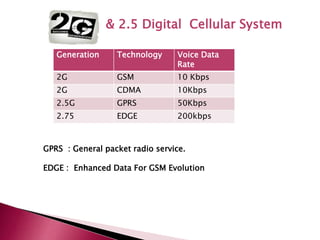
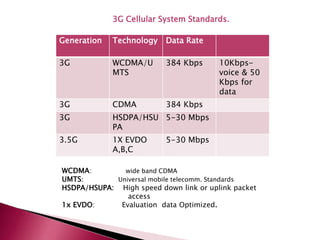
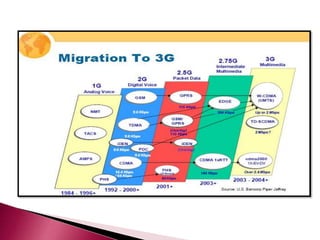
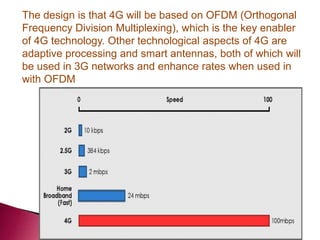
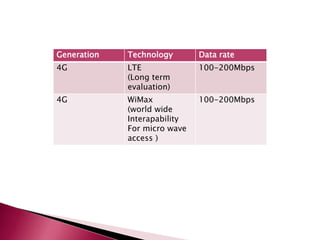
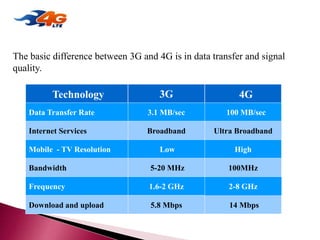
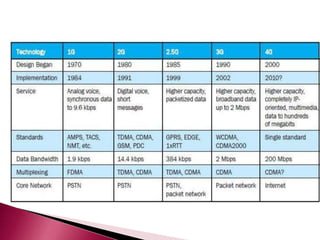
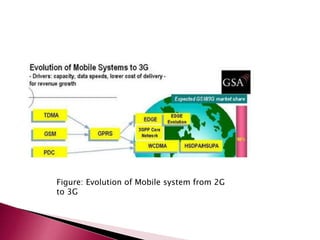
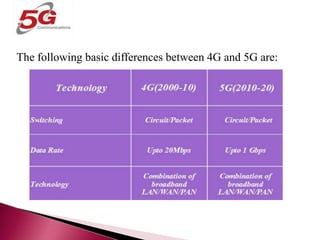
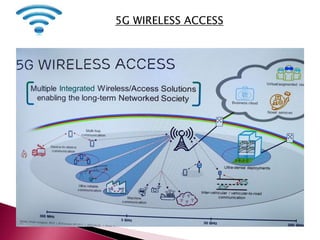
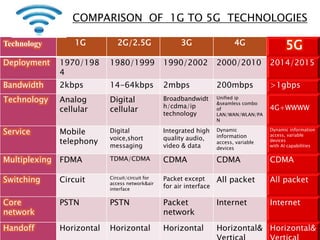
The document discusses the evolution of mobile communications technology from 1G to 5G standards. It provides details on the key technologies, features, and limitations of each generation. 1G systems used analog signals for voice only, while 2G introduced digital networks. 3G enabled broadband data and multimedia. 4G aimed for ultra-broadband speeds up to 1Gbps. 5G is expected to offer wireless internet access with almost no limitations at speeds over 1Gbps. Each new standard aimed to improve on the capabilities and speeds of prior generations.