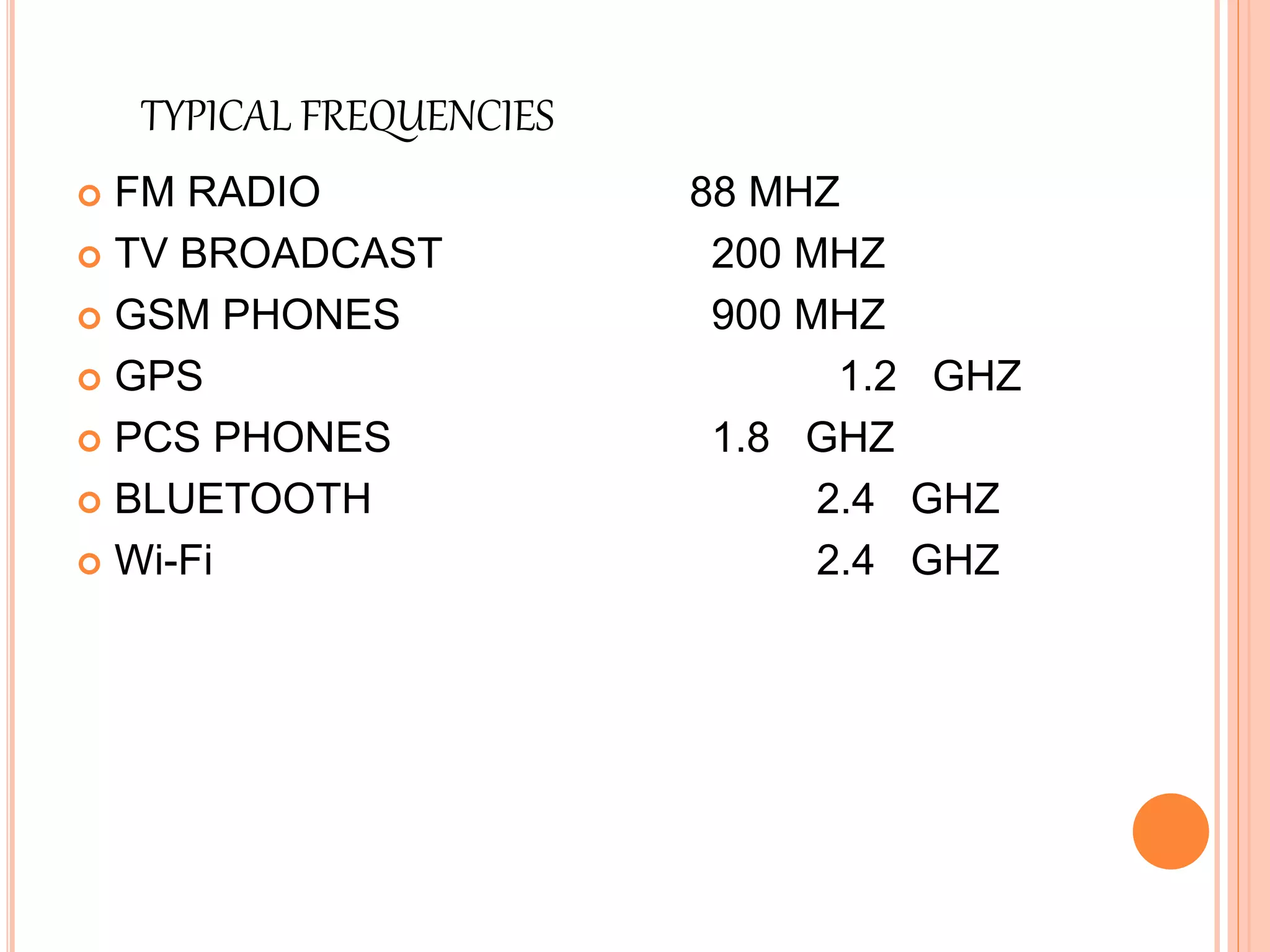
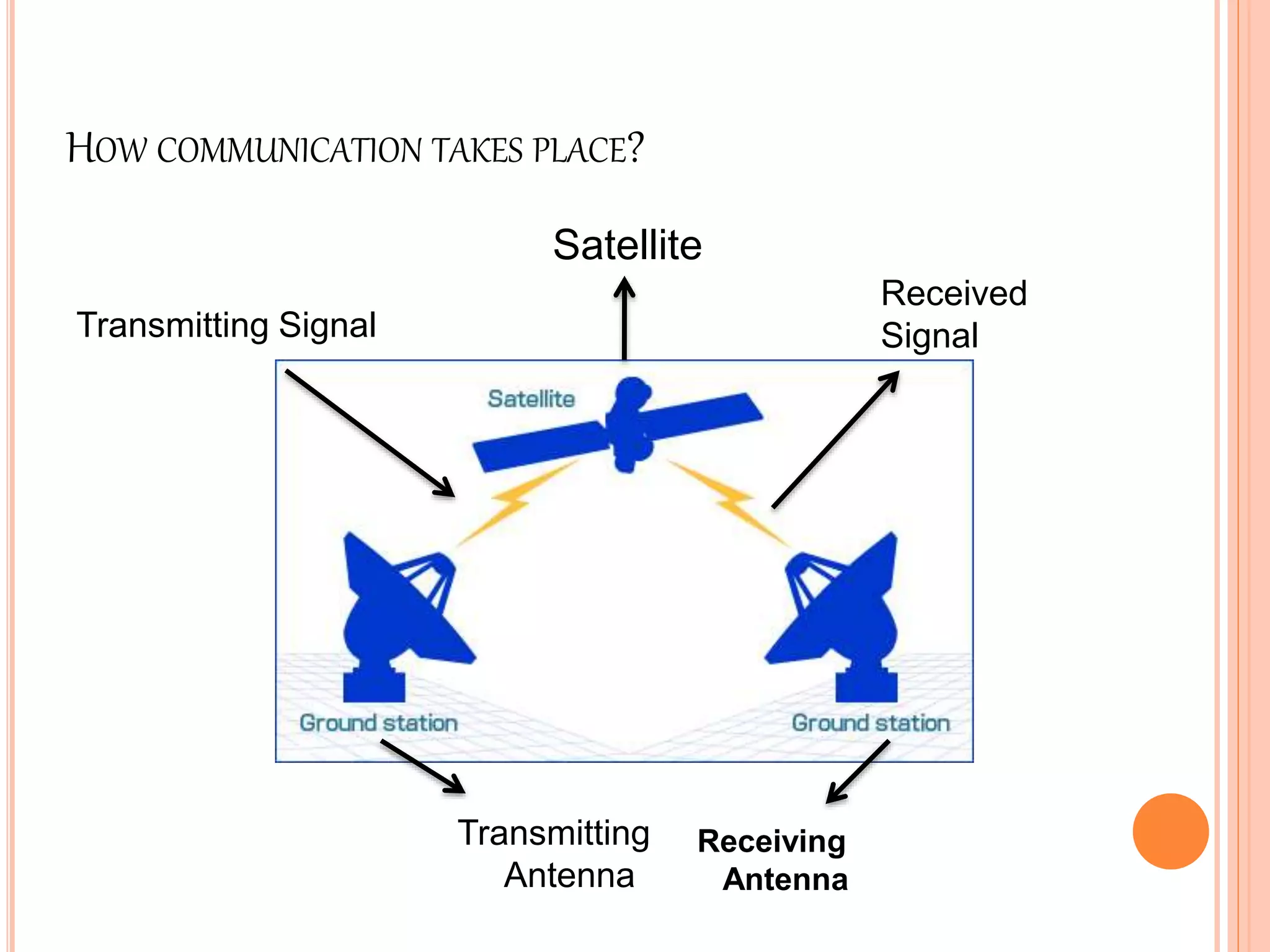
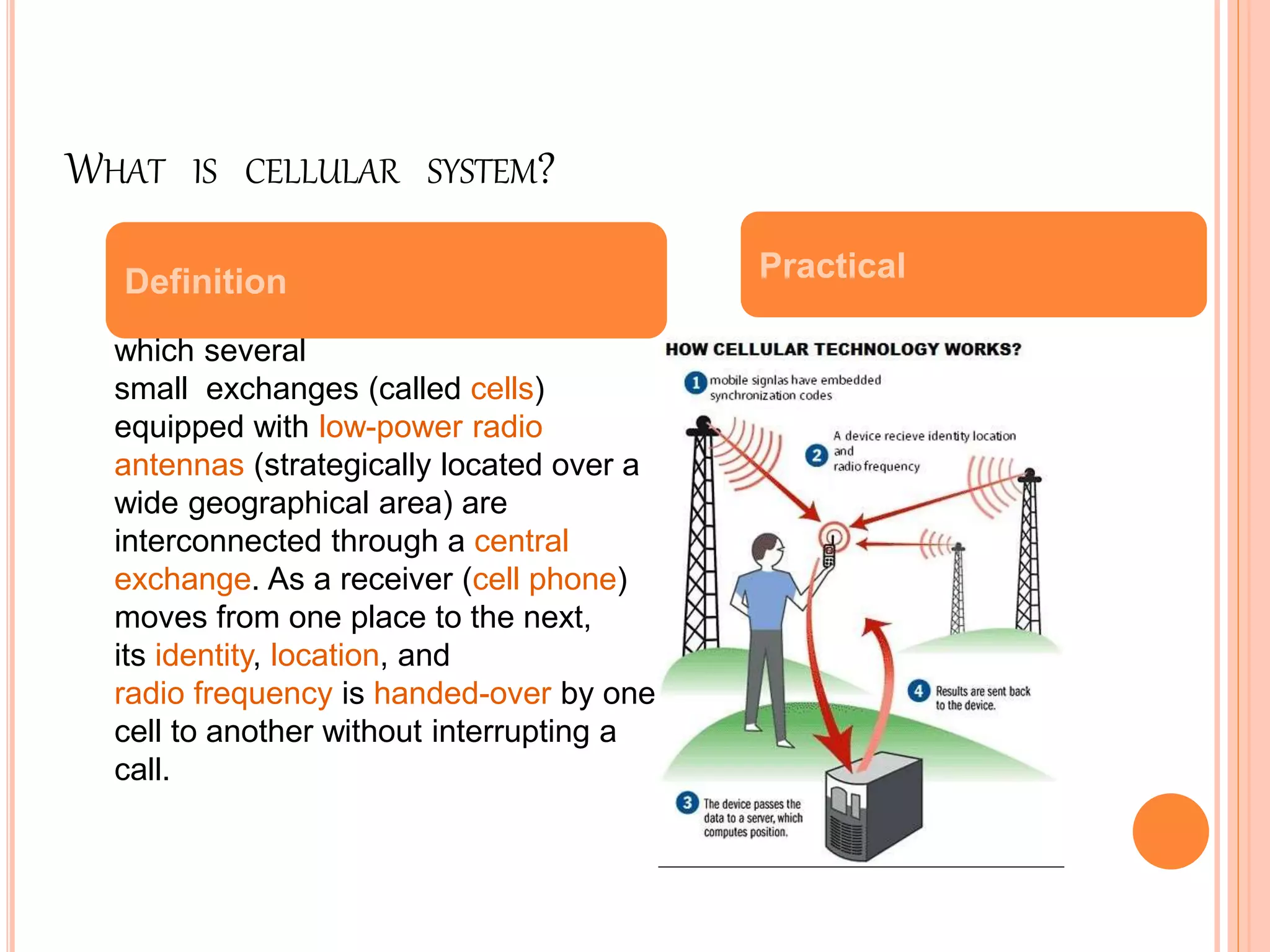
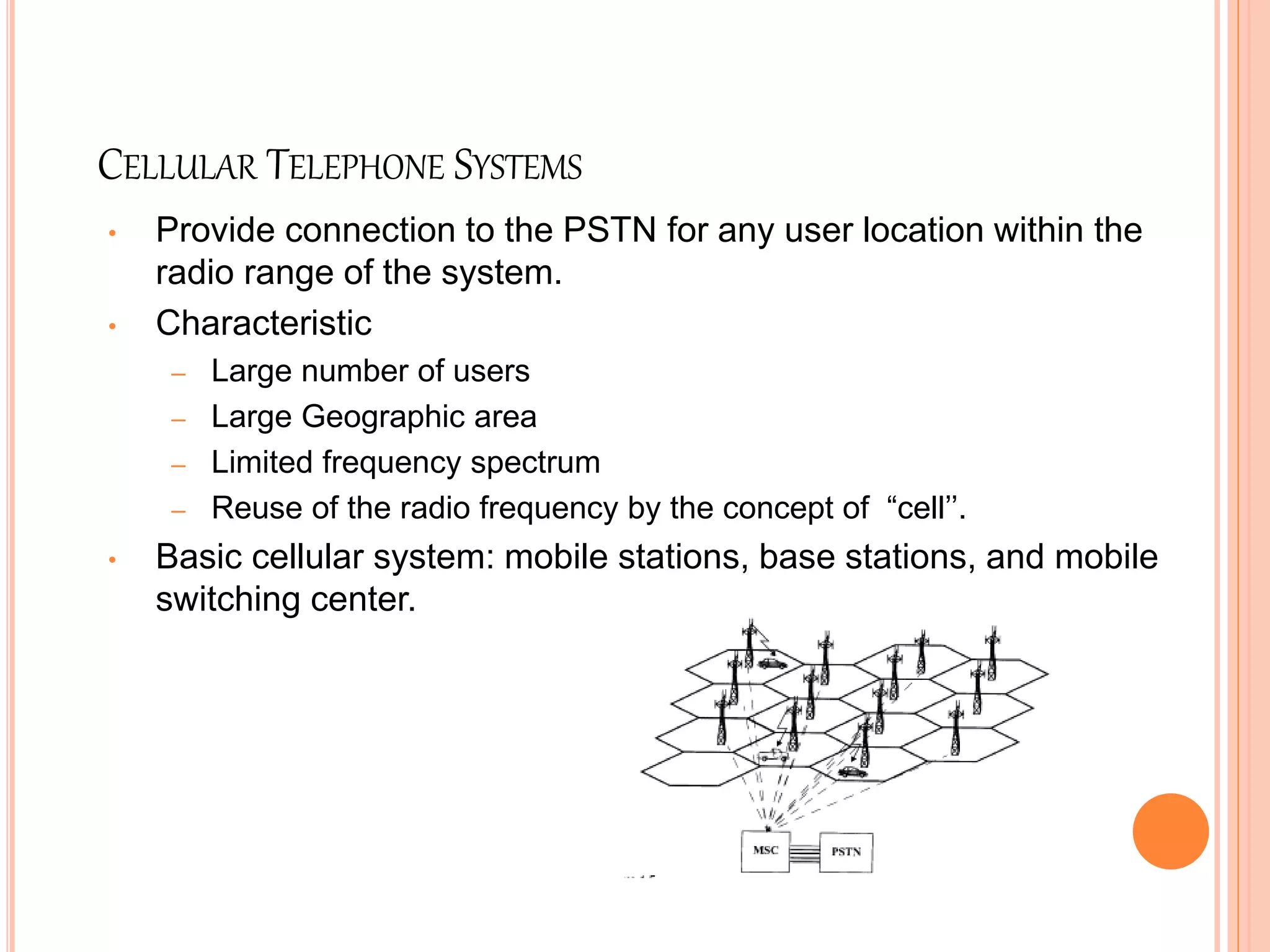
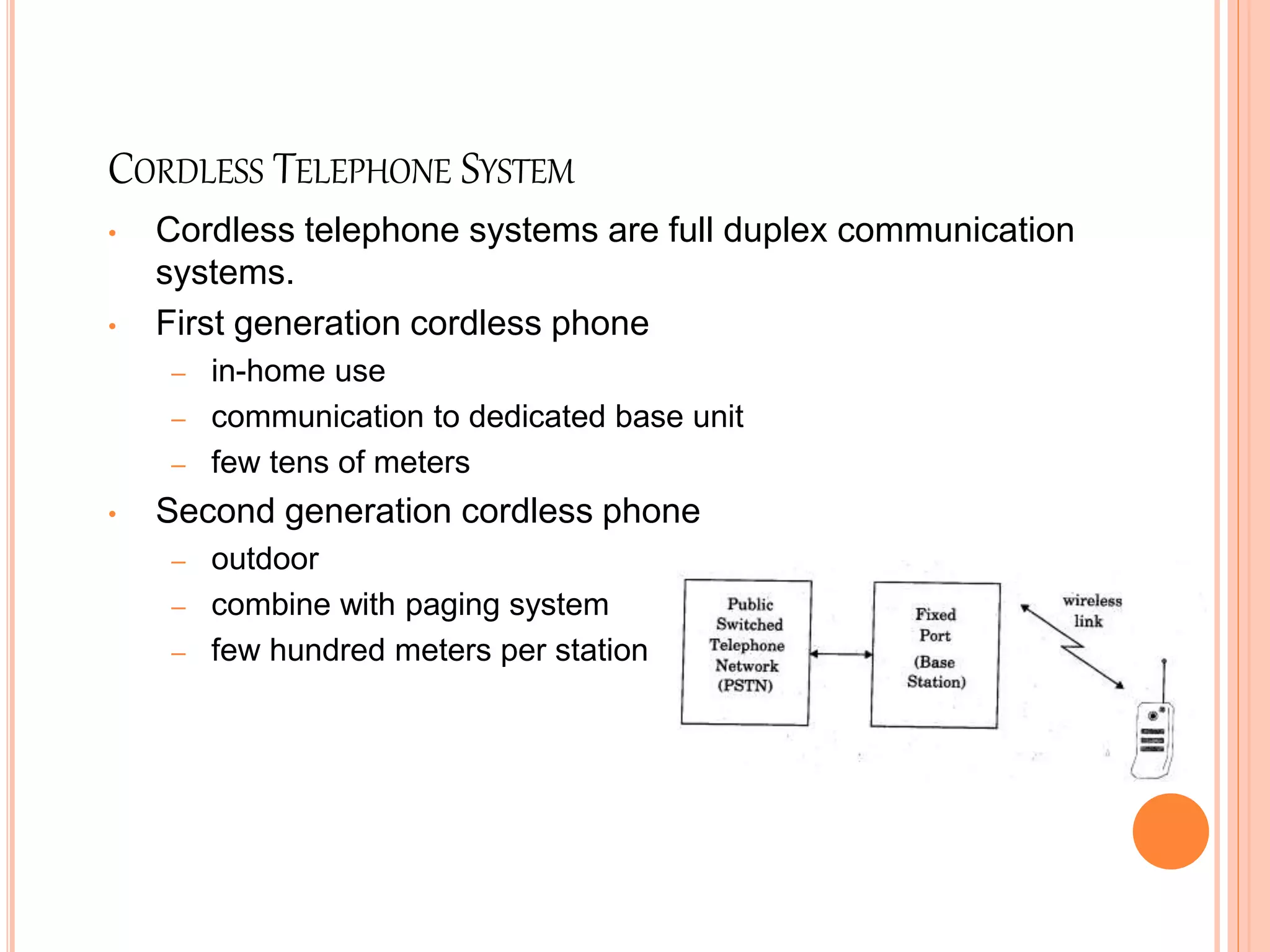
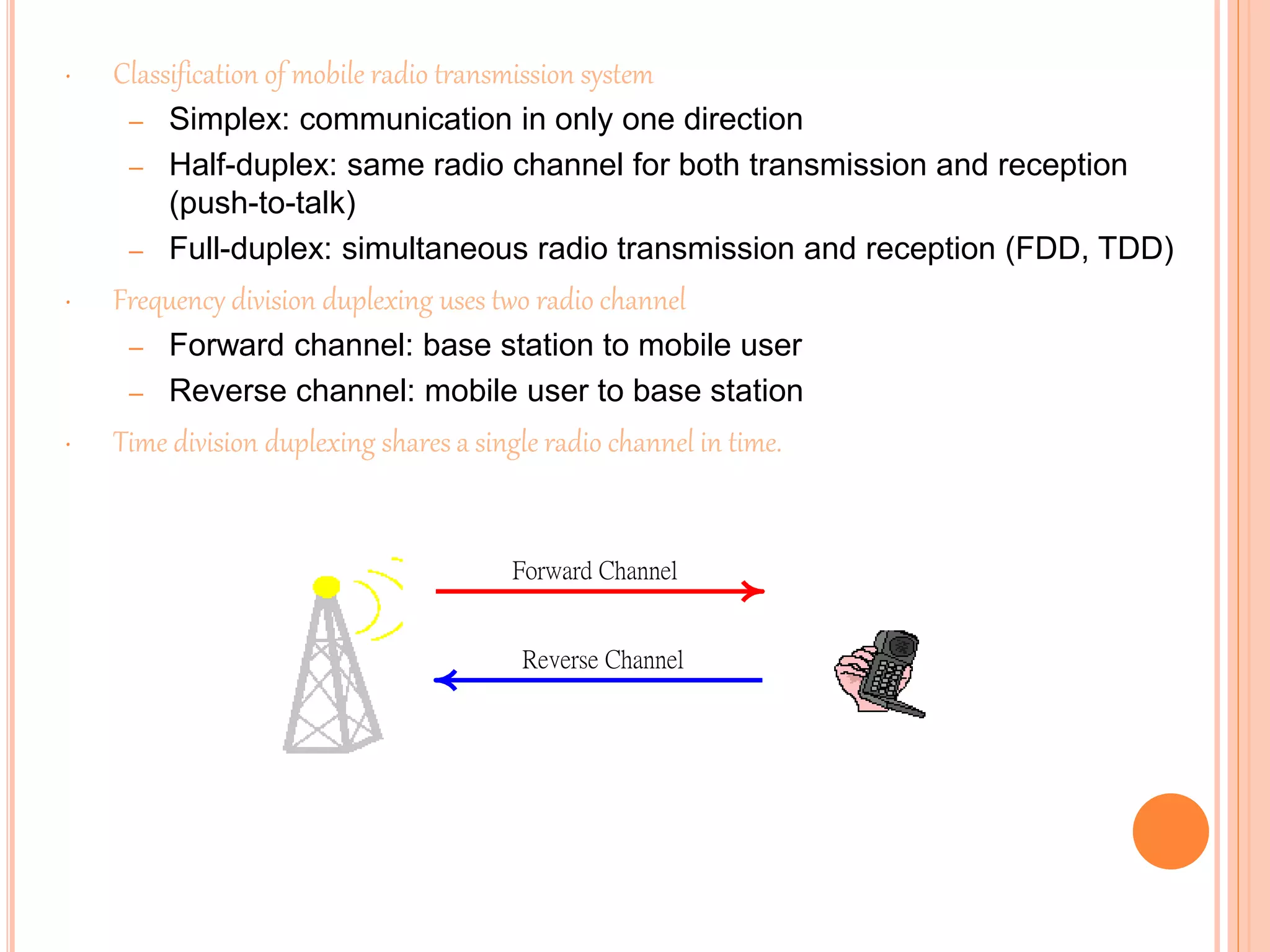
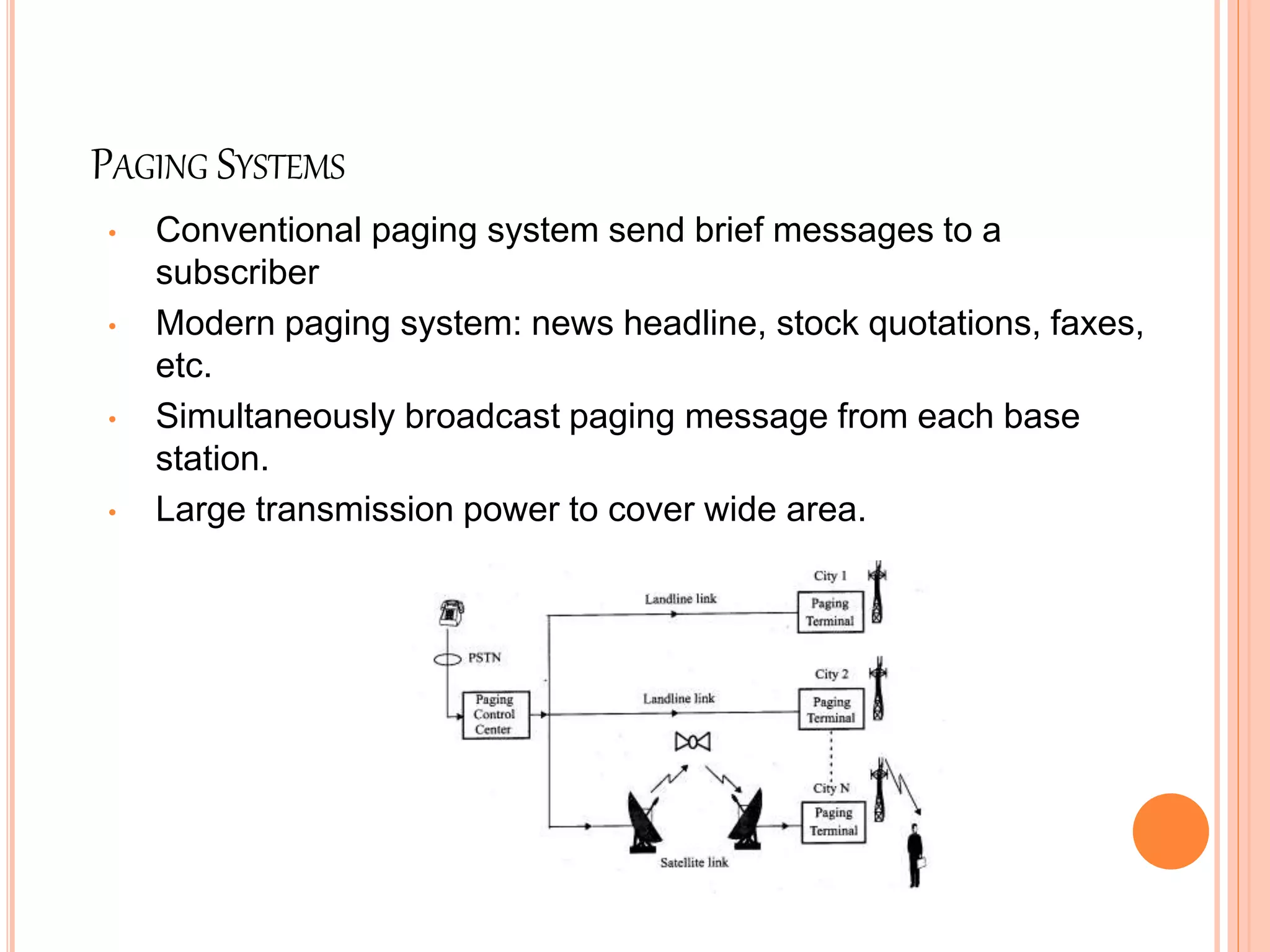
Wireless communication allows for freedom from wires and global connectivity. It transmits voice and data using radio waves without physical connections. Common wireless technologies include radio frequencies, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks. Wireless communication provides flexibility but also has disadvantages like security issues and signal interference. Major wireless systems include cellular networks for phone calls over large areas, wireless LANs for local connectivity, satellite systems for global coverage, paging systems for brief messages, and personal area networks like Bluetooth.