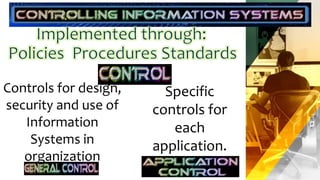
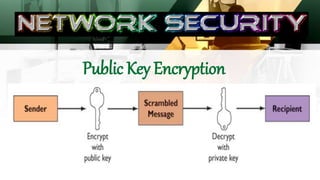
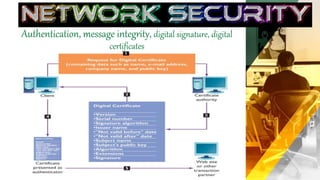
The document outlines the establishment of security policies and procedures for protecting organizational information assets, detailing specific controls such as input, processing, output, and storage controls to ensure data accuracy and integrity. It emphasizes the significance of automated and manual procedures for authorizing data access and highlights various security standards for both wired and wireless networks. Additionally, it addresses risks to computer systems from various hazards and suggests measures for protection against failures.