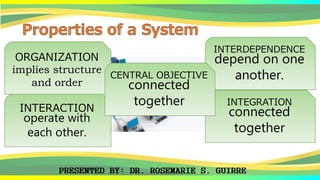
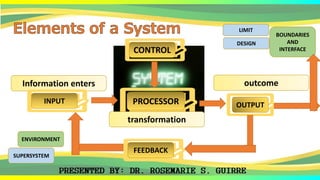
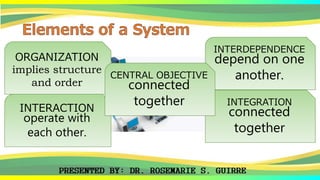
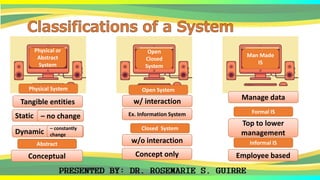
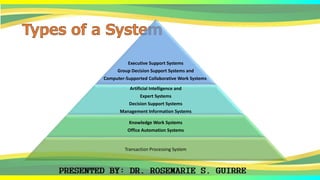
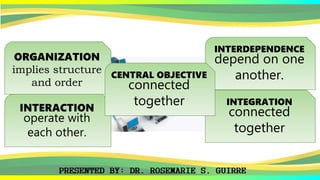
The document provides an overview of systems, defining their nature, classifications, and types, while highlighting the significance of both business systems and information systems. It discusses fundamental principles, interdependence among components, and various system examples, including management information systems and decision support systems. Additionally, it emphasizes the organization, integration, and objectives of systems within an interactive environment.