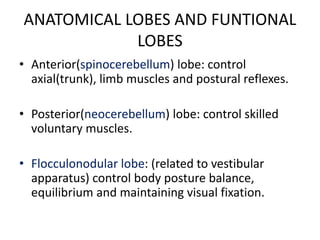
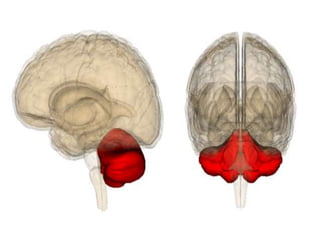
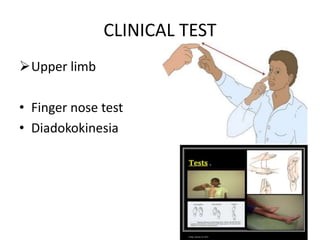
Cerebellar dysfunction can cause ataxia, a lack of muscle coordination. The cerebellum controls fine movements and posture. Damage to the cerebellum disrupts these functions. Ataxia affects walking, limb movements, speech, and eye movements. It is diagnosed through clinical exams like finger-nose and Romberg tests. The causes include lesions, tumors, or injuries to the cerebellum. While incurable, treatment focuses on easing symptoms to improve quality of life.



![CAUSES OF ATAXIA
• Damage, degeneration or loss of nerve cells in
the part of cerebellum.
• Destroy the part of the brain(cerebellum) that
controls muscle coordinations.
• Caused by cerebellar lesionor(localised) and
vermis lession(effect both side).
[ Note: common cause is thrombosis, tumor and
injuries]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/afrantopiccerebellar-dysfunction-ppt-190731124254/85/cerebellar-dysfunction-ppt-6-320.jpg)




![TREATMENT
Ataxia is generally not curable but we can just
ease the symptoms to make the patients life
better.
[http://puhuahospital.com/case-
studies/ataxia/omar?gclid=Cj0KCQjwsvrpBRCsARI
sAKBR_0JKxSec95R6Mkl5cvlEwjzPiobM_S8-
qXaNQjFCqdNVA6KnMdUn4E8aAmfXEALw_wcB]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/afrantopiccerebellar-dysfunction-ppt-190731124254/85/cerebellar-dysfunction-ppt-19-320.jpg)