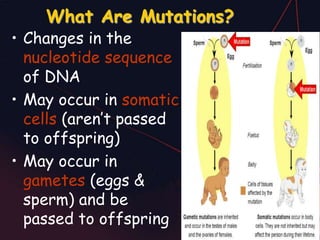
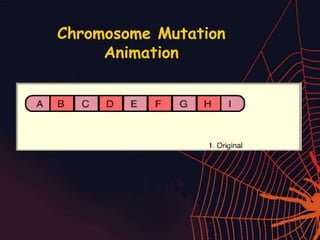
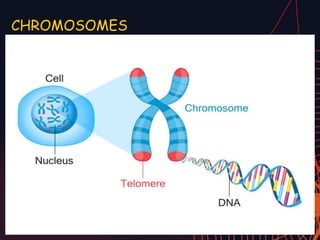
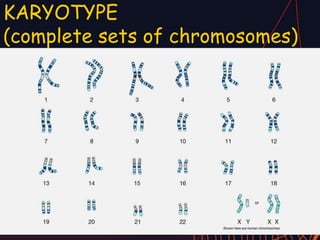
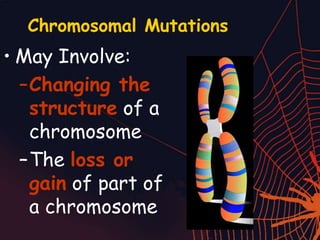
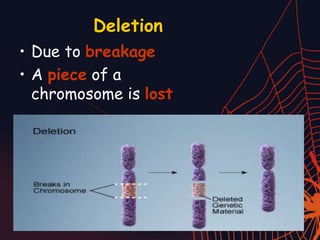
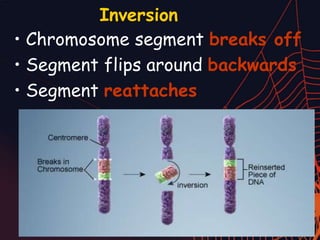
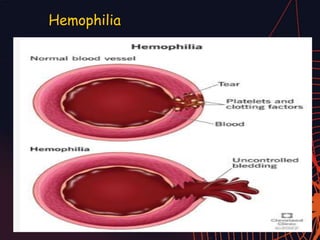
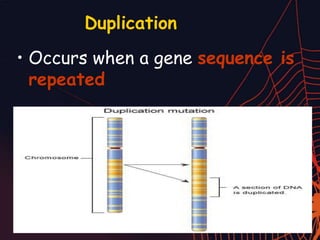
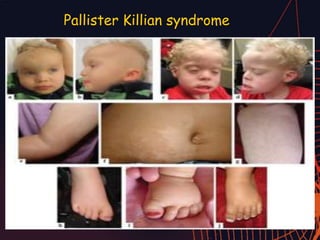
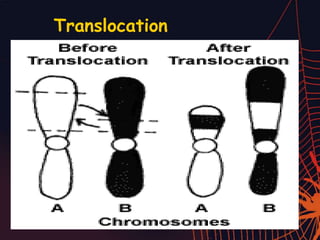
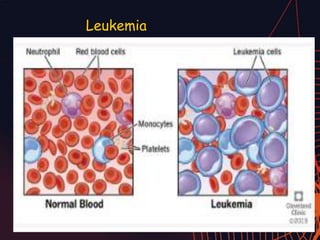
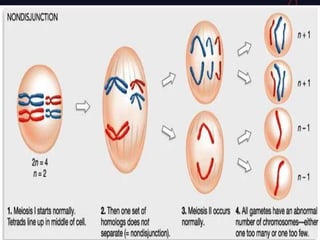
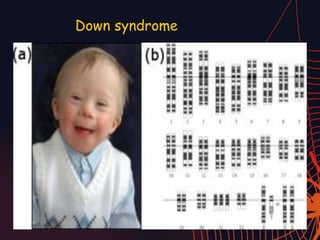
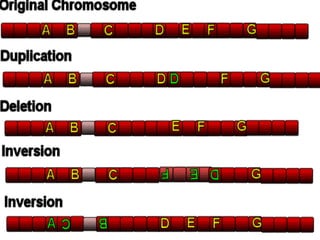
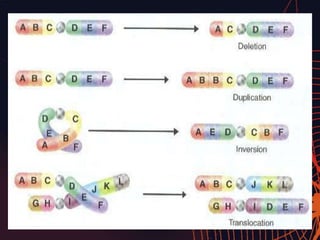
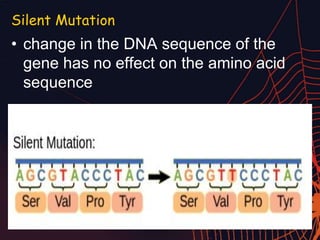
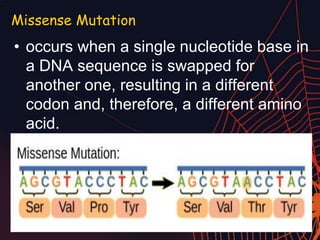
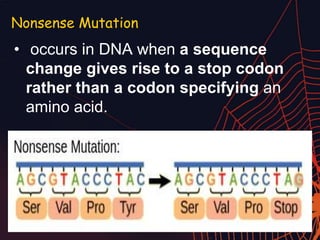
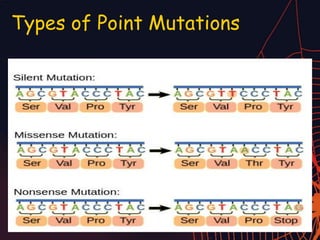
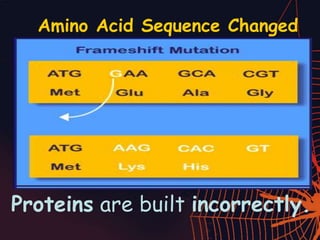
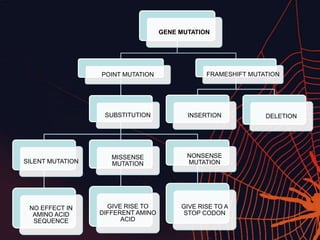
This document discusses different types of mutations that can occur in DNA. It defines mutations as changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that can happen either in somatic cells or gametes. There are two main types of mutations: chromosomal mutations, which involve changes to the structure or number of chromosomes, and gene mutations, which are changes to a single gene. Chromosomal mutations include deletions, inversions, translocations, nondisjunction, and duplications. Gene mutations can be point mutations such as substitutions, silent mutations, missense mutations, or nonsense mutations. Frameshift mutations are also a type of gene mutation that change the reading frame of DNA. Mutations can be either harmful if they cause diseases or beneficial if they improve organism