Embed presentation
Downloaded 99 times










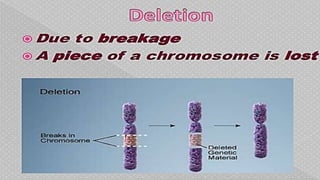
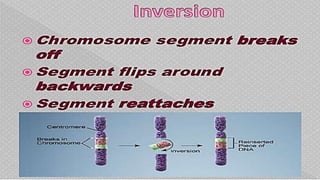
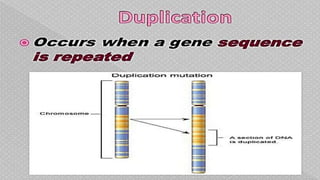

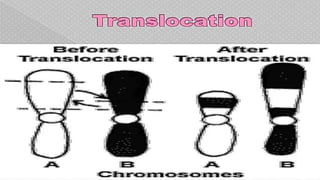
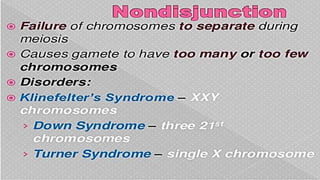



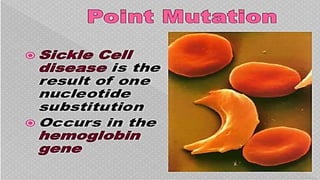







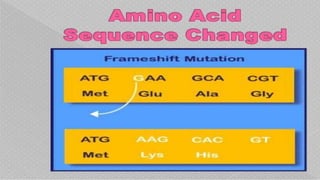

Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that may occur in somatic or gamete cells. Most mutations are neutral or harmful, causing diseases like cancer, but some may provide benefits like improved survival. There are two classes of mutation: spontaneous mutations, which naturally occur during DNA replication, and induced mutations caused by mutagens like UV light and radiation. Different types of mutations include chromosome mutations like deletions or inversions, as well as morphological, lethal, conditional, and biochemical mutations.



























