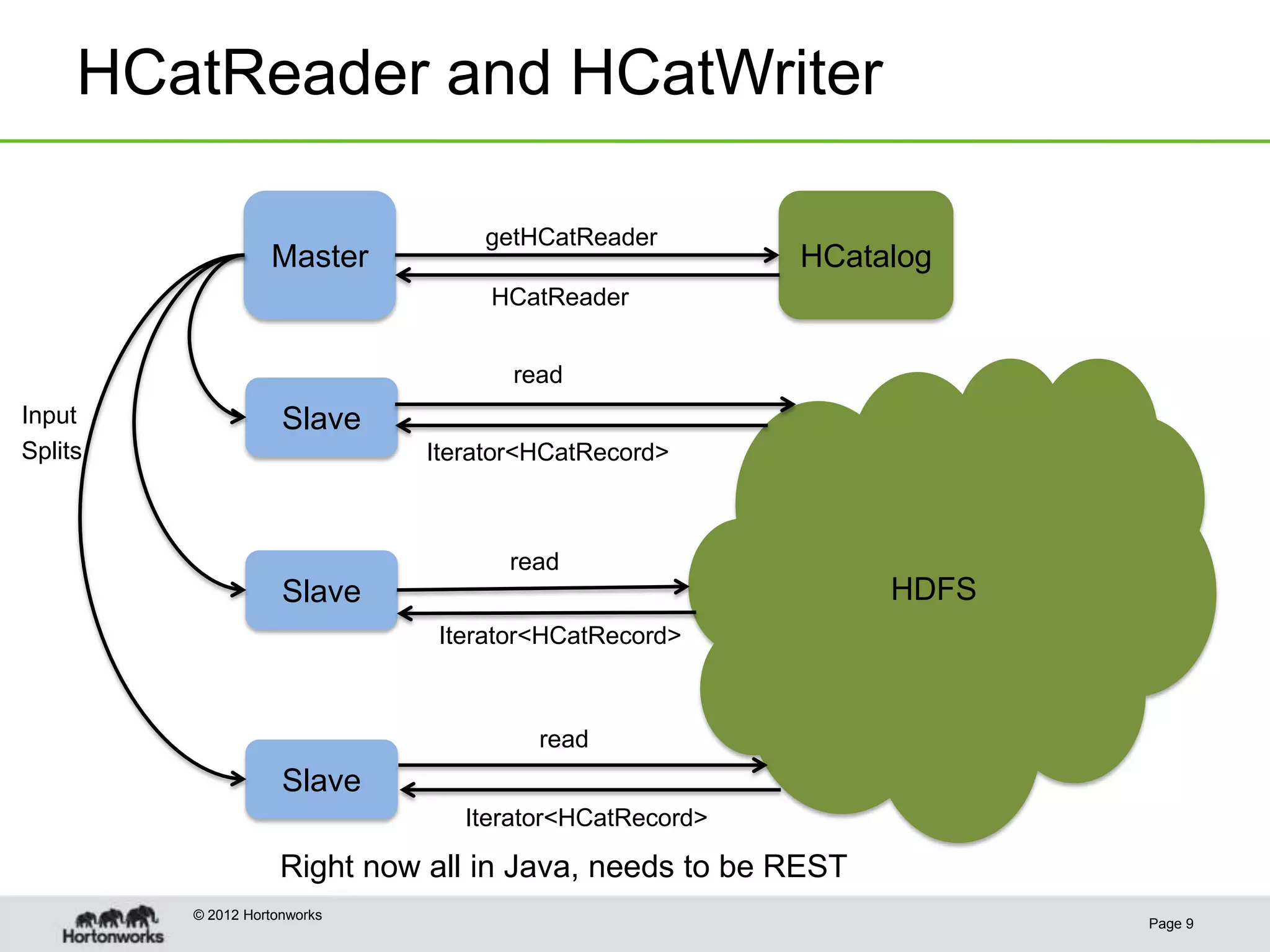
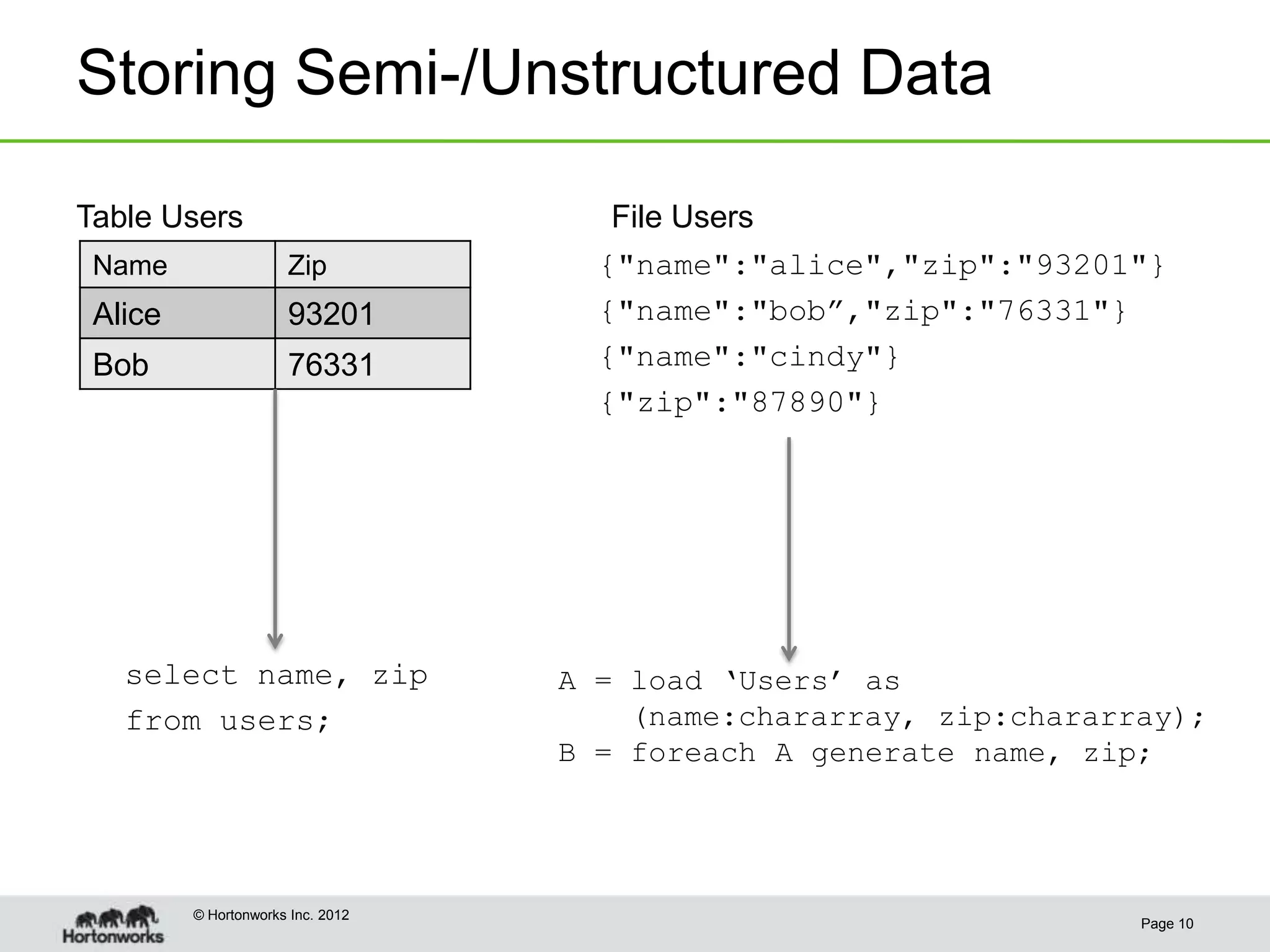
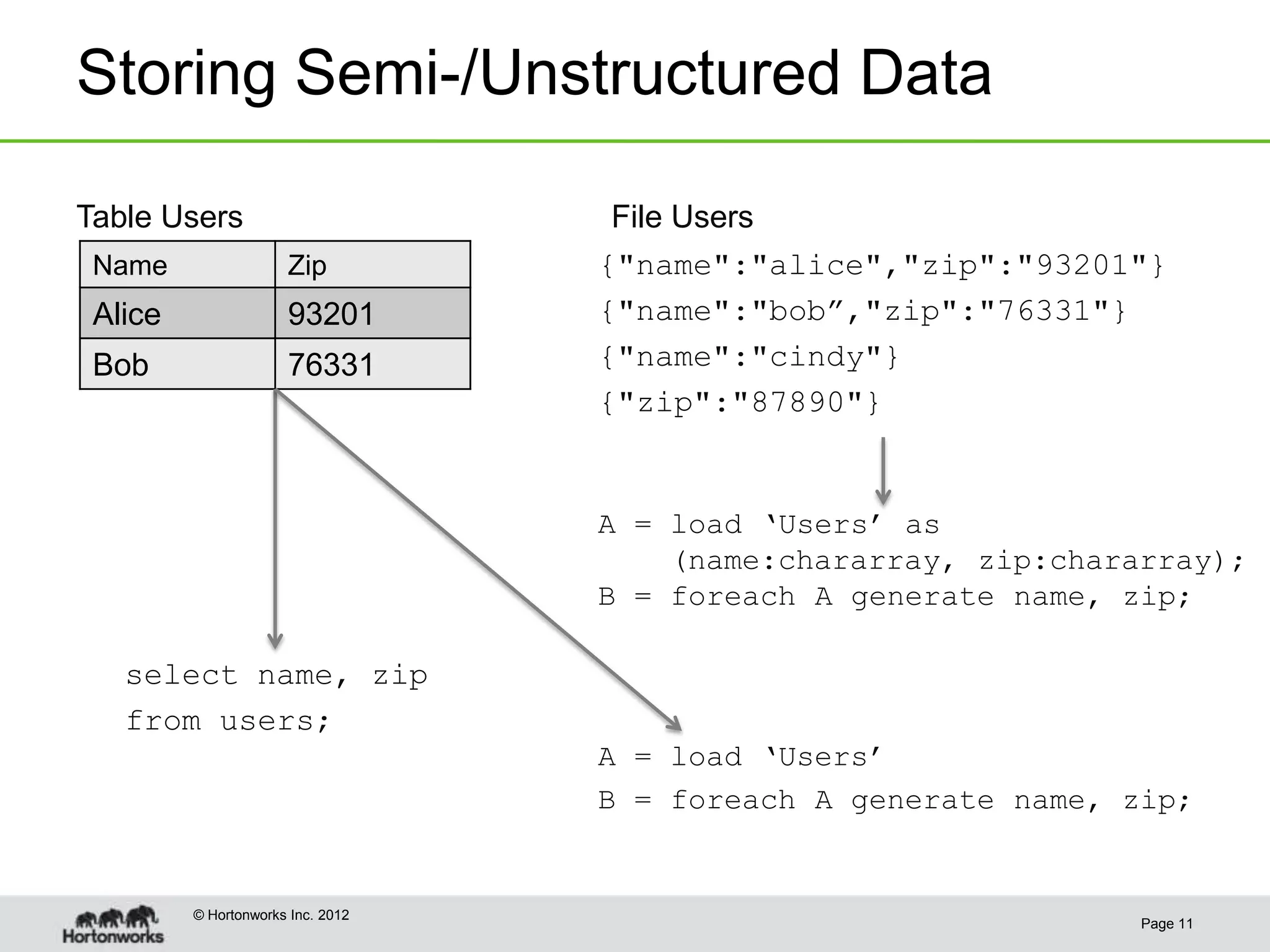
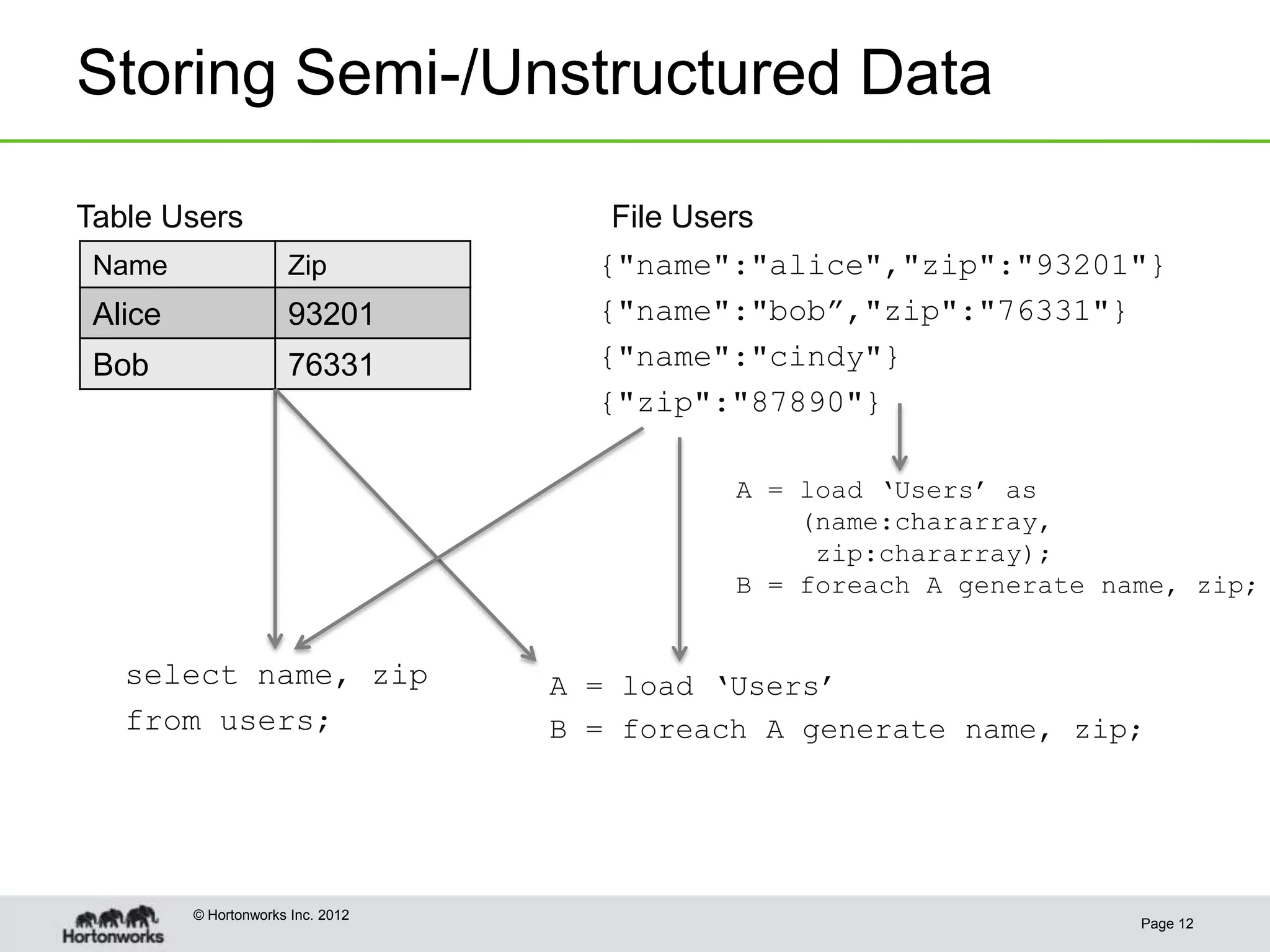
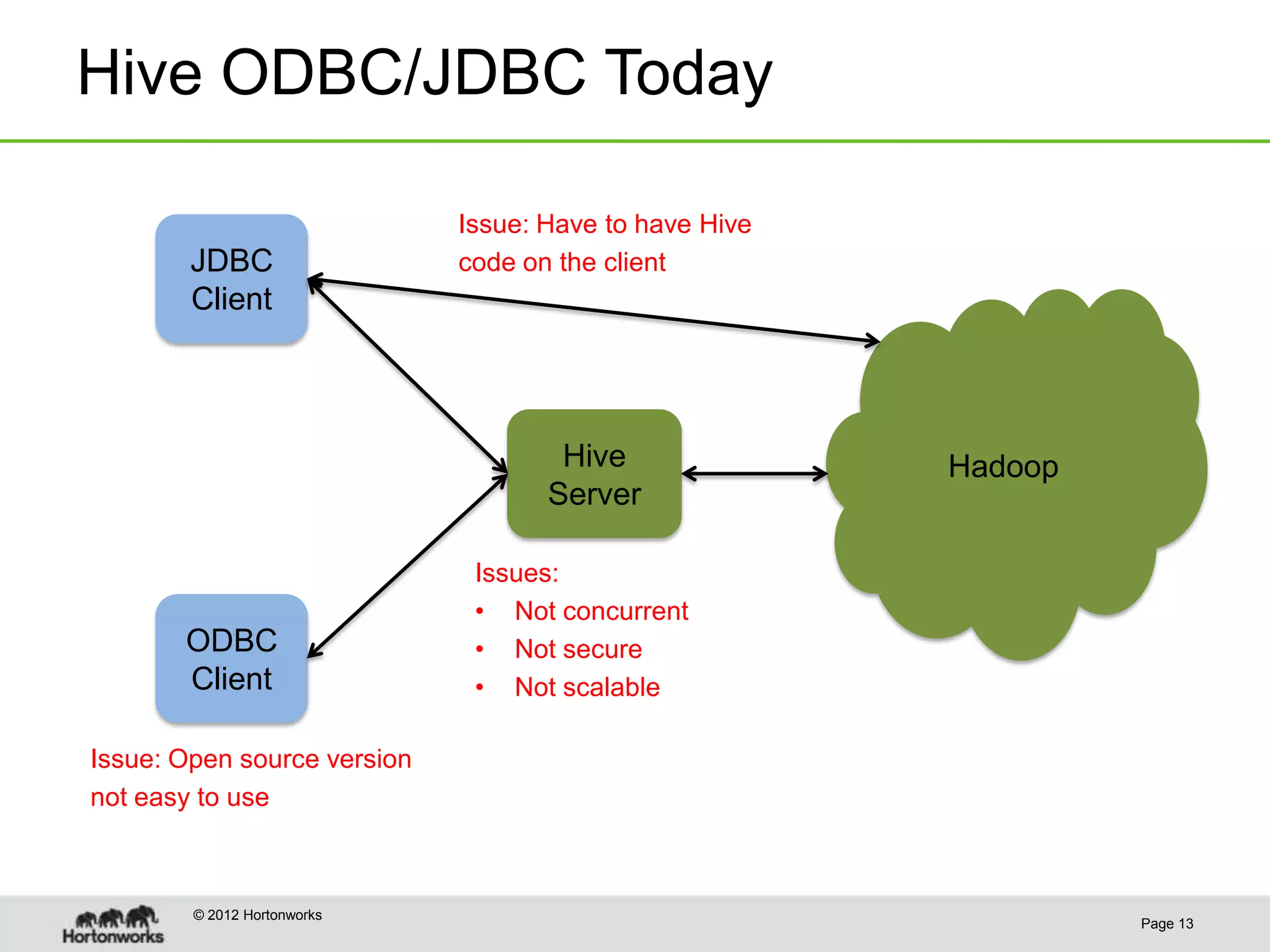
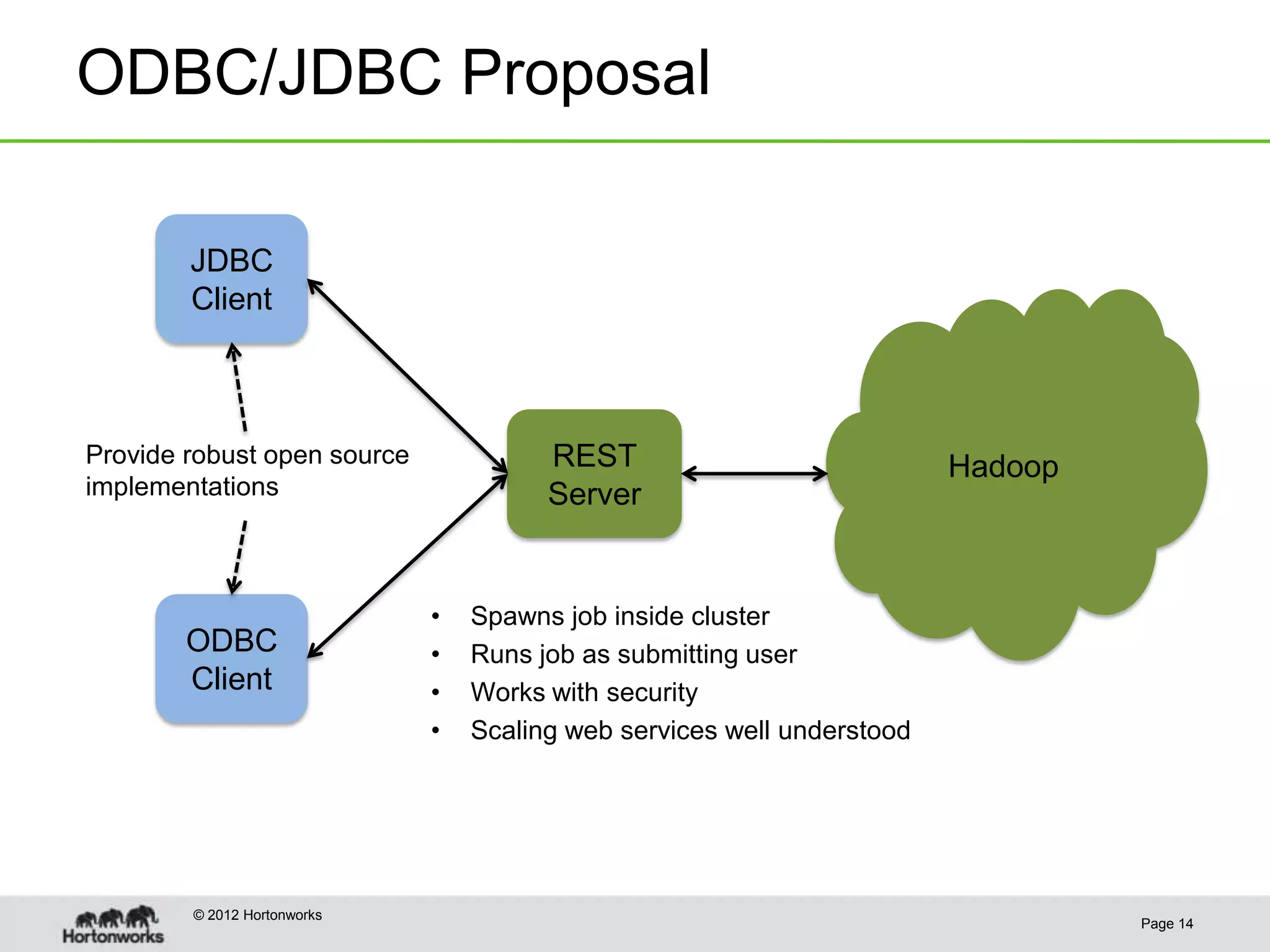
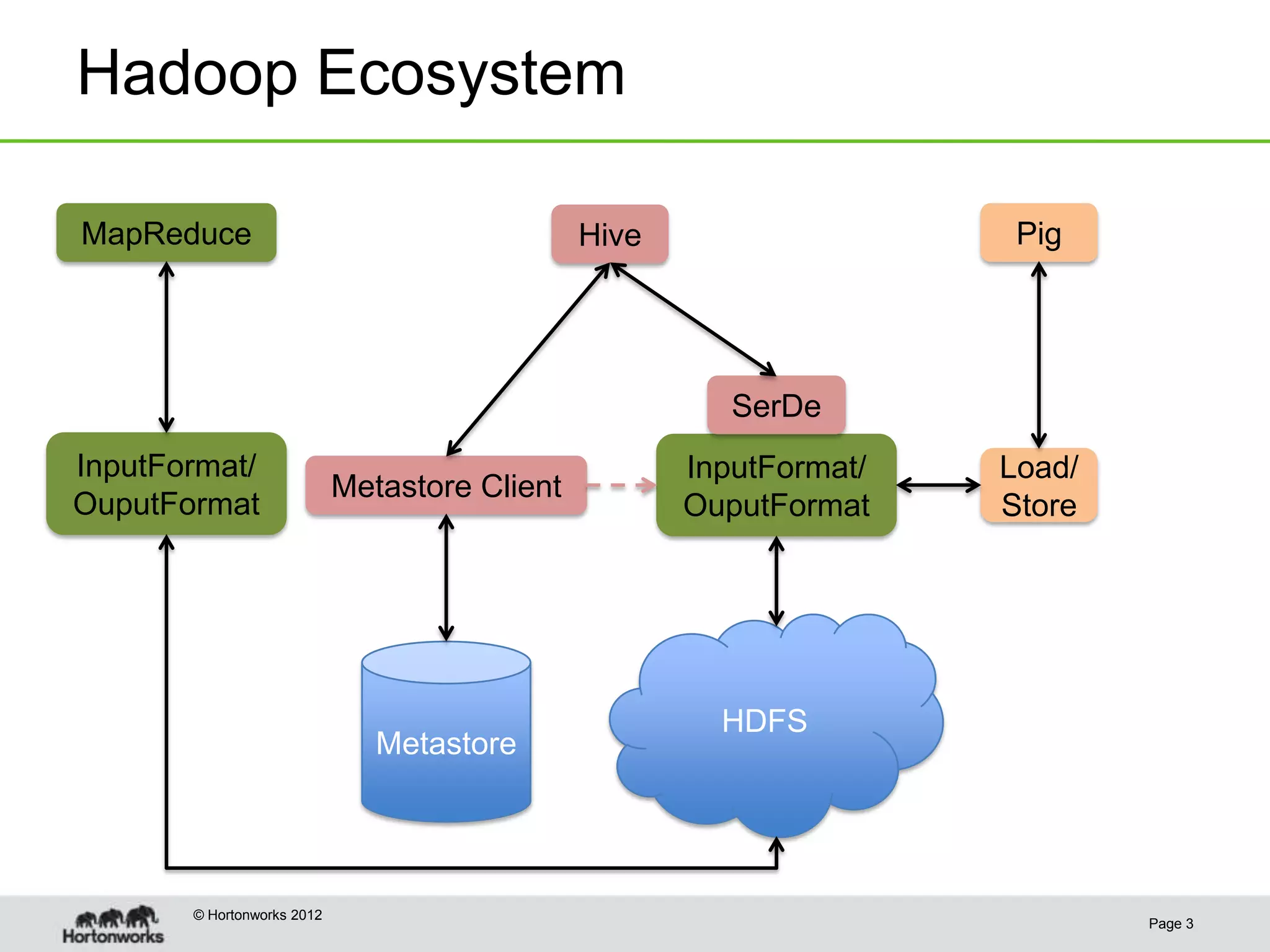
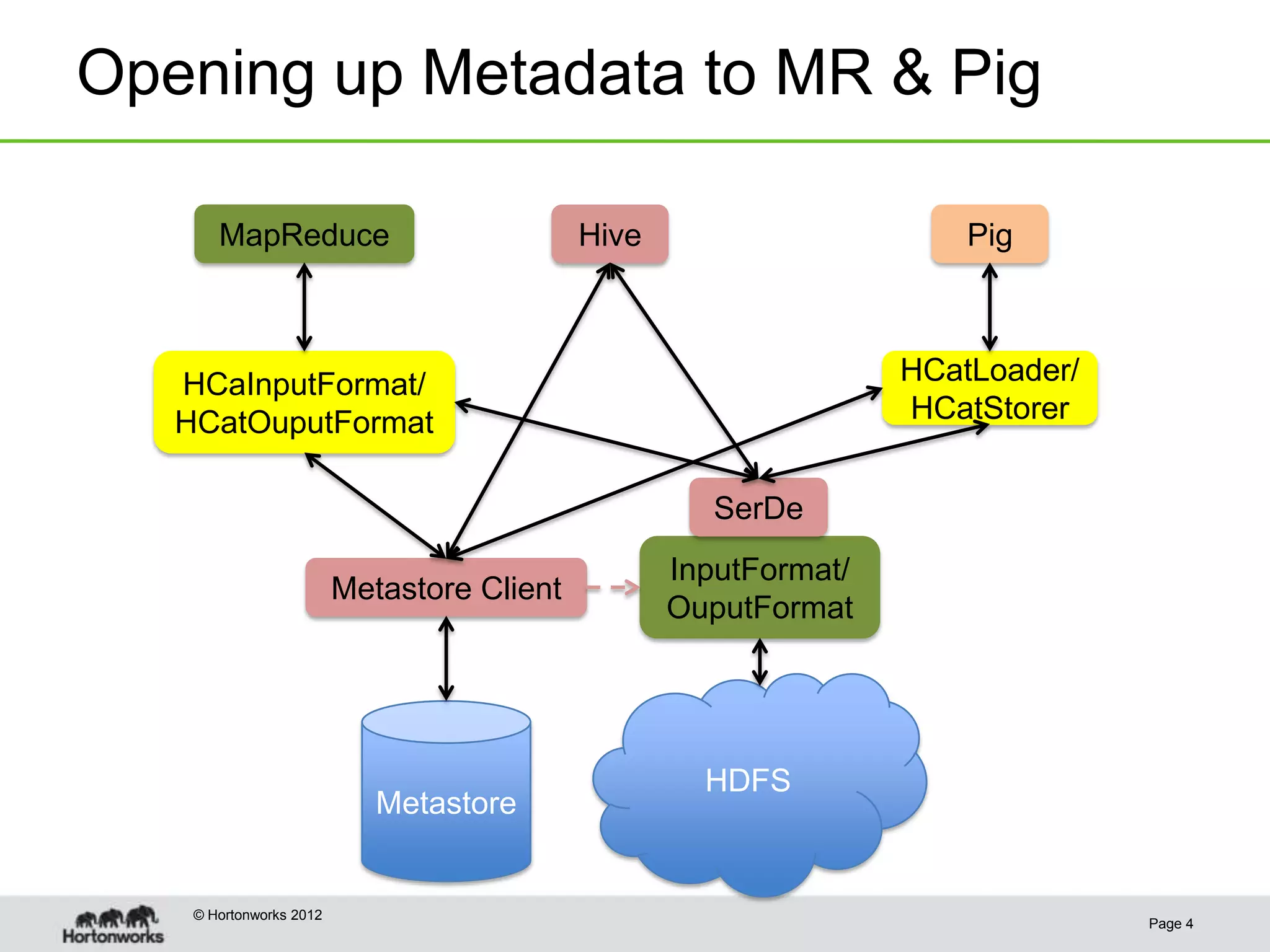
This document discusses the future of HCatalog, which provides a table abstraction and metadata layer for Hadoop data. It summarizes Alan Gates' background with Hadoop projects like Pig and Hive. It then outlines how HCatalog opens up metadata to MapReduce and Pig. It describes the Templeton REST API for HCatalog and how it allows creating, describing and listing tables. It proposes using HCatReader and HCatWriter to read and write data between Hadoop and parallel systems in a language-independent way. It also discusses using HCatalog to store semi-structured data and improving ODBC/JDBC access to Hive through a REST server.


![Templeton - REST API
• REST endpoints: databases, tables, partitions, columns, table properties
• PUT to create/update, GET to list or describe, DELETE to drop
Get a list of all tables in the default database:
GET
http://…/v1/ddl/database/default/table
Hadoop/
HCatalog
{
"tables": ["counted","processed",],
"database": "default"
}
© Hortonworks 2012
Page 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hcathadoopsummit2012-120615132235-phpapp01/75/Future-of-HCatalog-Hadoop-Summit-2012-5-2048.jpg)
![Templeton - REST API
• REST endpoints: databases, tables, partitions, columns, table properties
• PUT to create/update, GET to list or describe, DELETE to drop
Create new table “rawevents”
PUT
{"columns": [{ "name": "url", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "user", "type": "string"}],
"partitionedBy": [{ "name": "ds", "type": "string" }]}
http://…/v1/ddl/database/default/table/rawevents
Hadoop/
HCatalog
{
"table": "rawevents",
"database": "default”
}
© Hortonworks 2012
Page 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hcathadoopsummit2012-120615132235-phpapp01/75/Future-of-HCatalog-Hadoop-Summit-2012-6-2048.jpg)
![Templeton - REST API
• REST endpoints: databases, tables, partitions, columns, table properties
• PUT to create/update, GET to list or describe, DELETE to drop
Describe table “rawevents”
GET
http://…/v1/ddl/database/default/table/rawevents
Hadoop/
HCatalog
{
"columns": [{"name": "url","type": "string"},
{"name": "user","type": "string"}],
"database": "default",
"table": "rawevents"
}
• Included in HDP
• Not yet checked in, but you can find the code on Apache’s JIRA HCATALOG-182
© Hortonworks 2012
Page 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hcathadoopsummit2012-120615132235-phpapp01/75/Future-of-HCatalog-Hadoop-Summit-2012-7-2048.jpg)