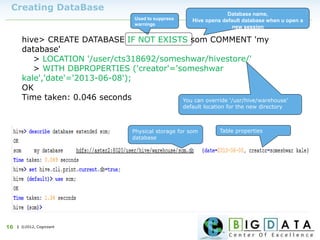
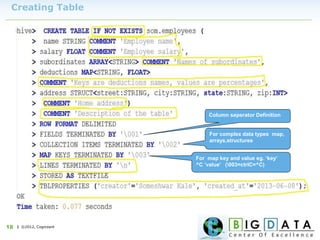
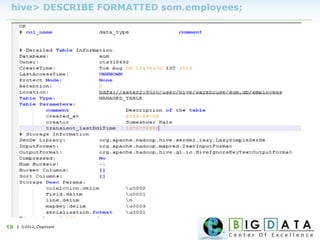
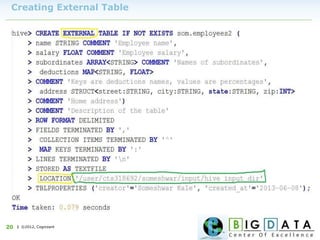
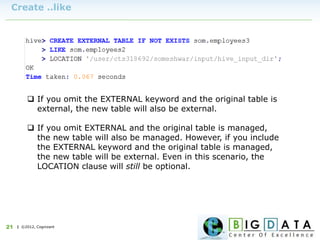
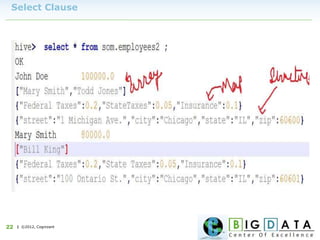
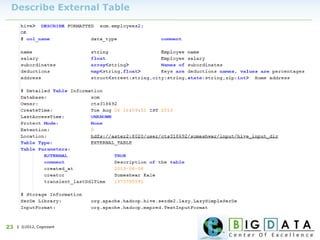
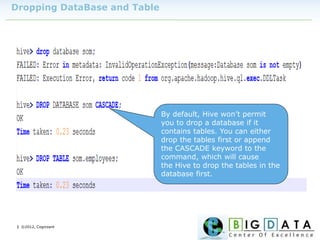
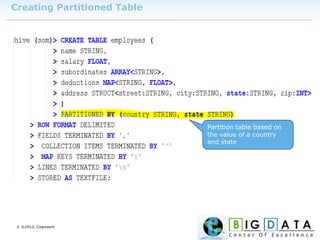
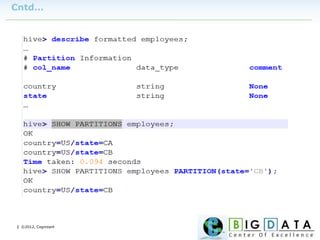
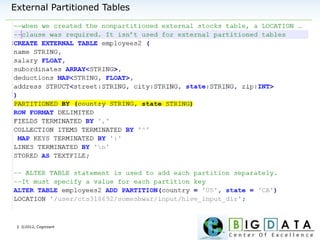
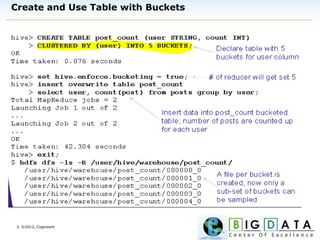
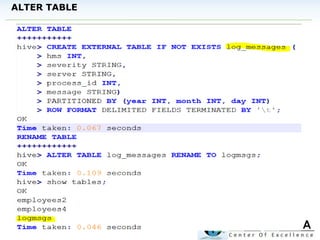
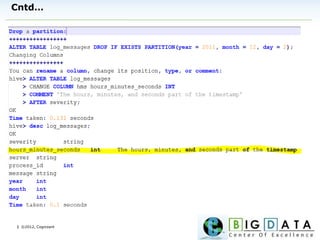
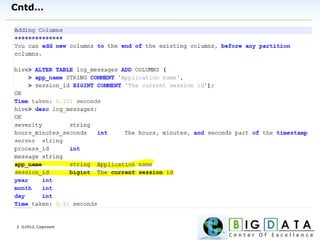
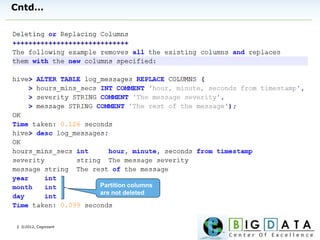
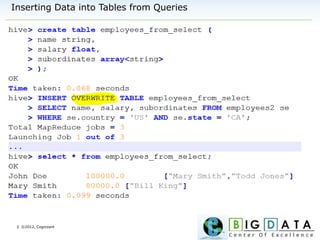
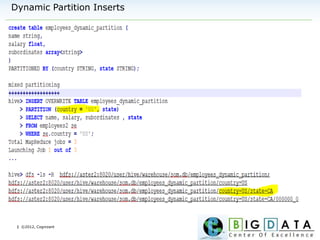
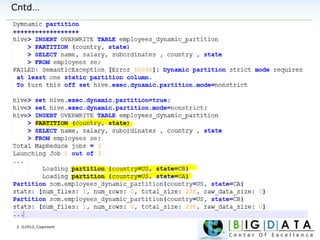
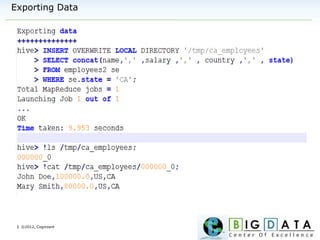
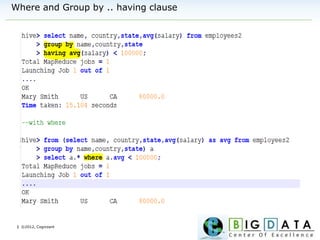
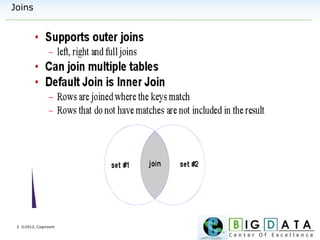
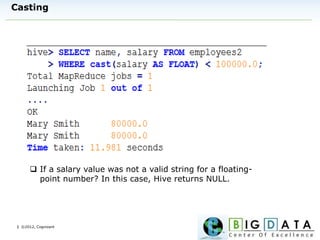
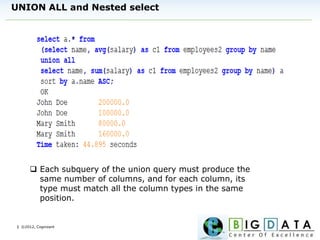
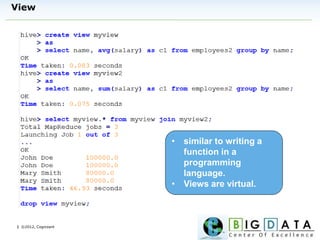
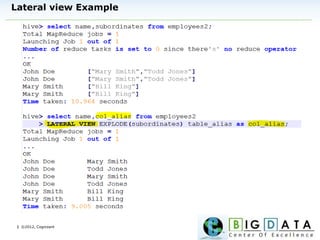
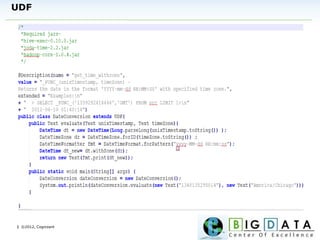
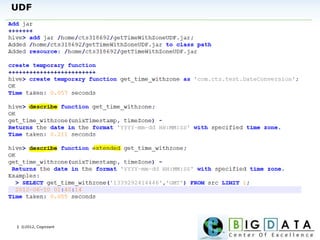
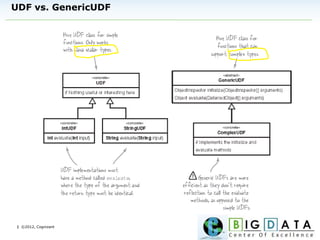
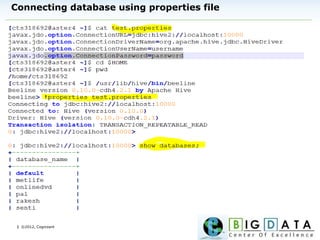
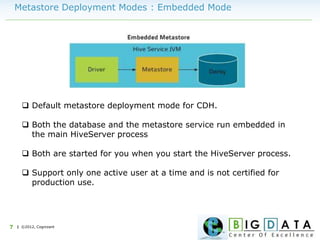
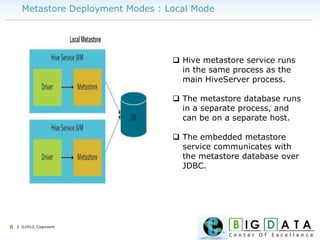
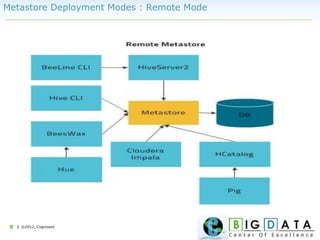
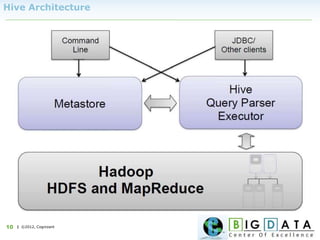
The document discusses Hive, a data warehousing solution built on Hadoop that provides a SQL-like query language called HiveQL, targeting data analysts. It emphasizes Hive's scalability and ease of use but notes its limitations regarding low latency and real-time queries. Additionally, it explains Hive's architecture, metastore options, data types, and features like partitioning and bucketing to enhance performance.





![| ©2012, Cognizant12
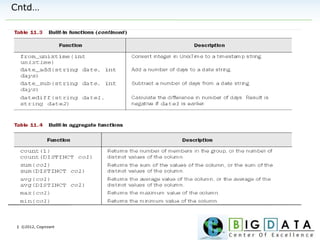
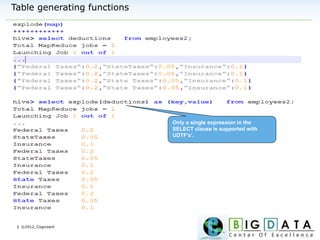
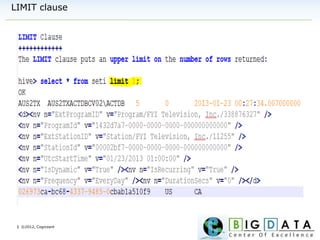
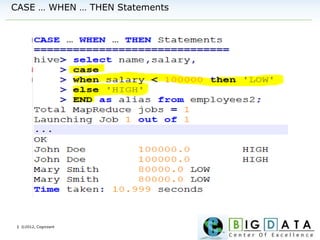
Data Types
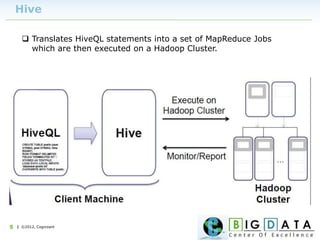
[cts318692@aster4 ~]$ hive
Logging initialized using configuration in
jar:file:/usr/lib/hive/lib/hive-common-0.10.0-cdh4.2.1.jar!/hive-
log4j.properties
Hive history
file=/tmp/cts318692/hive_job_log_cts318692_201308071622_200
5272769.txt
hive>
Launch Hive Command Line Interface
(CLI)
Location of the session’s log file
hive> !cat data/user-posts.txt;
user1,Funny Story,1343182026191
user2,Cool Deal,1343182133839
user4,Interesting Post,1343182154633
user5,Yet Another Blog,13431839394
hive>
Can execute local commands
within CLI, place a command
in between ! and ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hivework-150426044214-conversion-gate01/85/Learning-Apache-HIVE-Data-Warehouse-and-Query-Language-for-Hadoop-12-320.jpg)


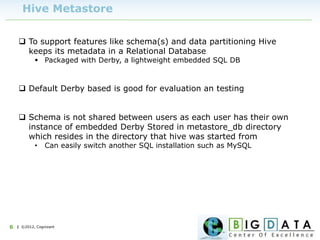
![| ©2012, Cognizant15
Check physical storage of hive
[cts318692@aster4 ~]$ hive -S -e "set" | grep warehouse
hive.metastore.warehouse.dir=/user/hive/warehouse
hive.warehouse.subdir.inherit.perms=true
This is the location where hive stores
its data.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hivework-150426044214-conversion-gate01/85/Learning-Apache-HIVE-Data-Warehouse-and-Query-Language-for-Hadoop-15-320.jpg)