The document discusses the rapid growth of data and the inadequacy of current RDBMS solutions, leading to the introduction of Apache Hadoop and Hive for data processing and analysis. Hive is a data warehousing infrastructure built on Hadoop that allows for SQL-like queries and supports various data-intensive applications. The document also covers Hive's architecture, configuration, CLI commands, and use cases, emphasizing its scalability and extensibility for processing large datasets.







![Type System
Primitive types
–Integers:TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT.
–Boolean: BOOLEAN.
–Floating point numbers: FLOAT, DOUBLE .
–String: STRING.
Complex types
–Structs: {a INT; b INT}.
–Maps: M['group'].
–Arrays: ['a', 'b', 'c'], A[1] returns 'b'.
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachehive-120925023430-phpapp01/85/Apache-Hive-9-320.jpg)



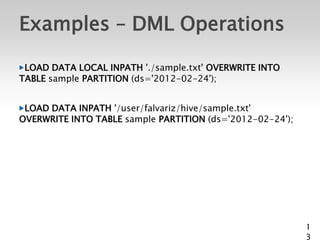
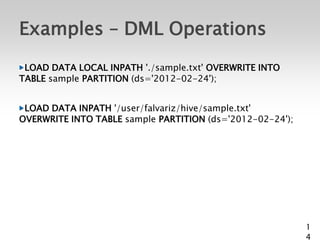









![Hive CLI Commands
Start a terminal and run
$ hive
Should see a prompt like:
hive>
Set a Hive or Hadoop conf prop:
– hive> set propkey=value;
List all properties and values:
– hive> set –v;
Add a resource to the DCache:
– hive> add [ARCHIVE|FILE|JAR] filename;
2
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachehive-120925023430-phpapp01/85/Apache-Hive-27-320.jpg)