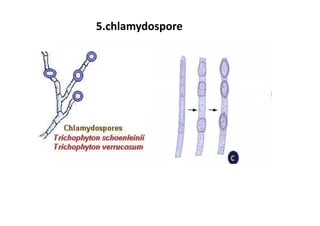
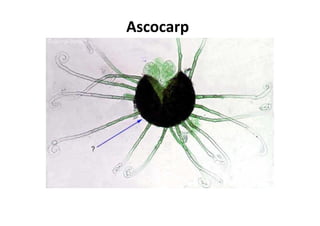
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that range from unicellular to multicellular, lack chlorophyll, and reproduce via spores. They play important roles in decomposition as saprophytes and have both beneficial and harmful effects. Beneficially, they are used in food production and to produce antibiotics, while some are plant and human pathogens. Fungi exhibit a variety of structures, including hyphae that make up the vegetative mycelium, and reproduce both sexually, forming spores, and asexually through processes like budding or fission.