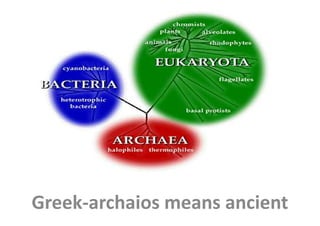
Archaea are a diverse group of microorganisms that inhabit extreme environments. They can be spherical, rod-shaped, or other morphologies, and exist as single cells or aggregates. Archaea are found in environments with high or low temperatures, pH, salt concentrations, or methane levels and can be aerobic, facultative anaerobes, or strictly anaerobes. They play important roles in ecosystems like methanogenesis and sulfate reduction. Archaea have unique cell walls and membranes adapted to extreme conditions like hyperthermophiles that can survive above 100°C. Major groups include methanogens, sulfate reducers, halophiles, and cell wall-less archaea. Archaea have economic importance in areas