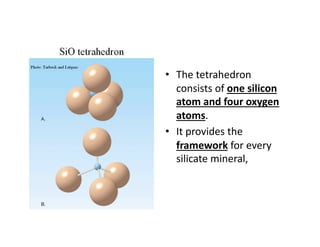
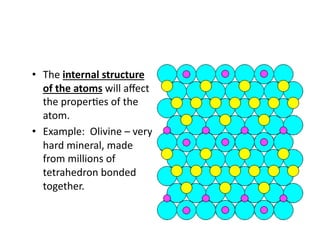
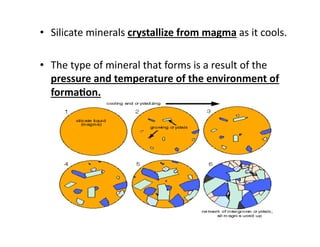
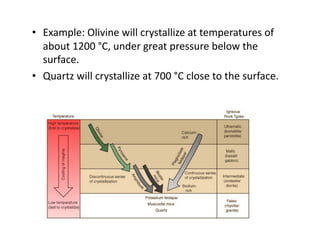
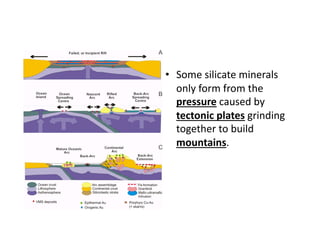
The document discusses two major mineral groups: silicates and carbonates. Silicates are the most abundant minerals in the earth's crust and are formed from the combination of silicon and oxygen atoms into tetrahedrons. Silicate minerals crystallize from cooling magma and their structure and composition provide clues about formation conditions. Carbonates are the second most common mineral group and contain carbon, oxygen, and metallic elements like calcium and magnesium. They are found in rocks like limestone and marble.