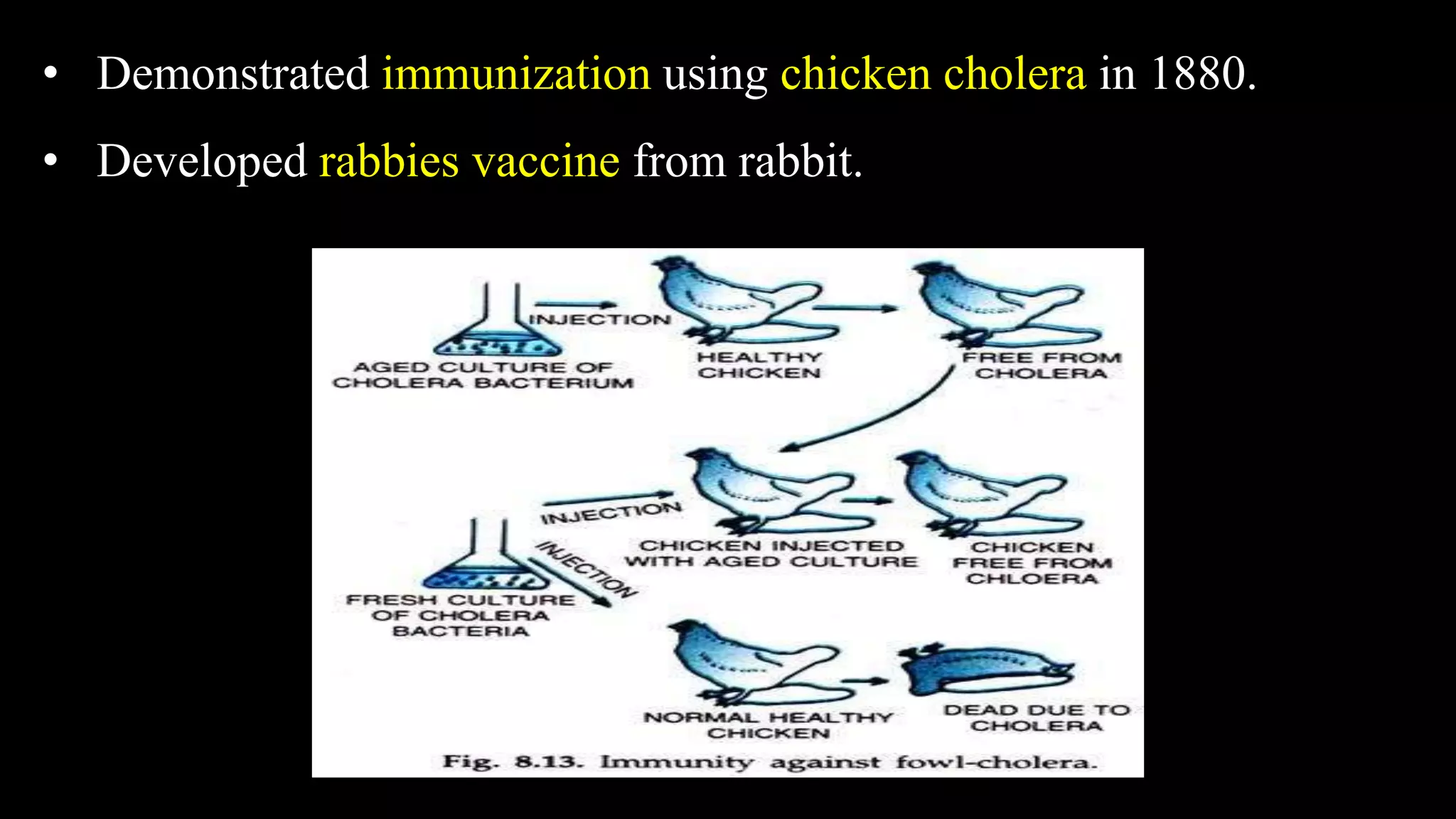
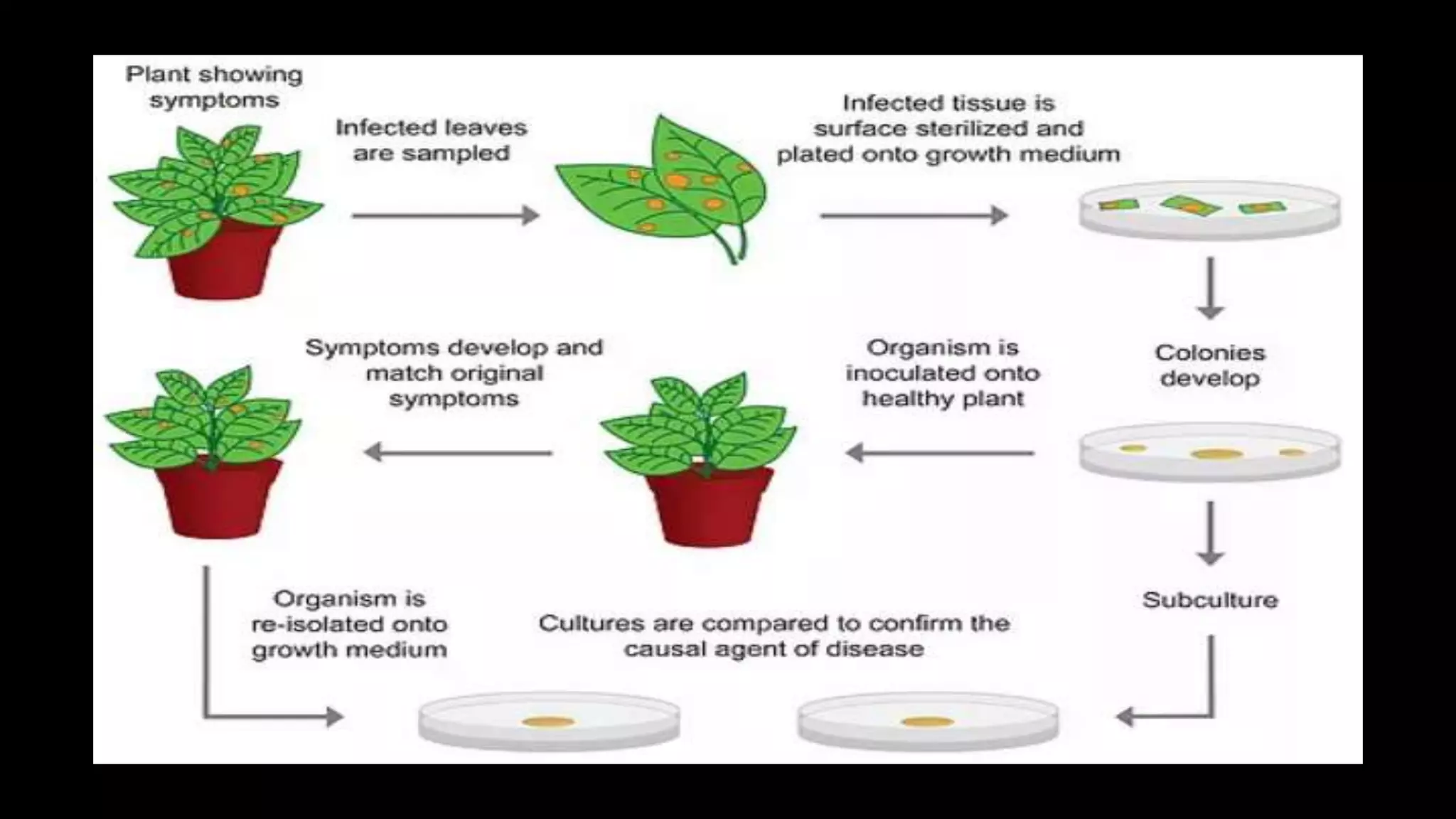
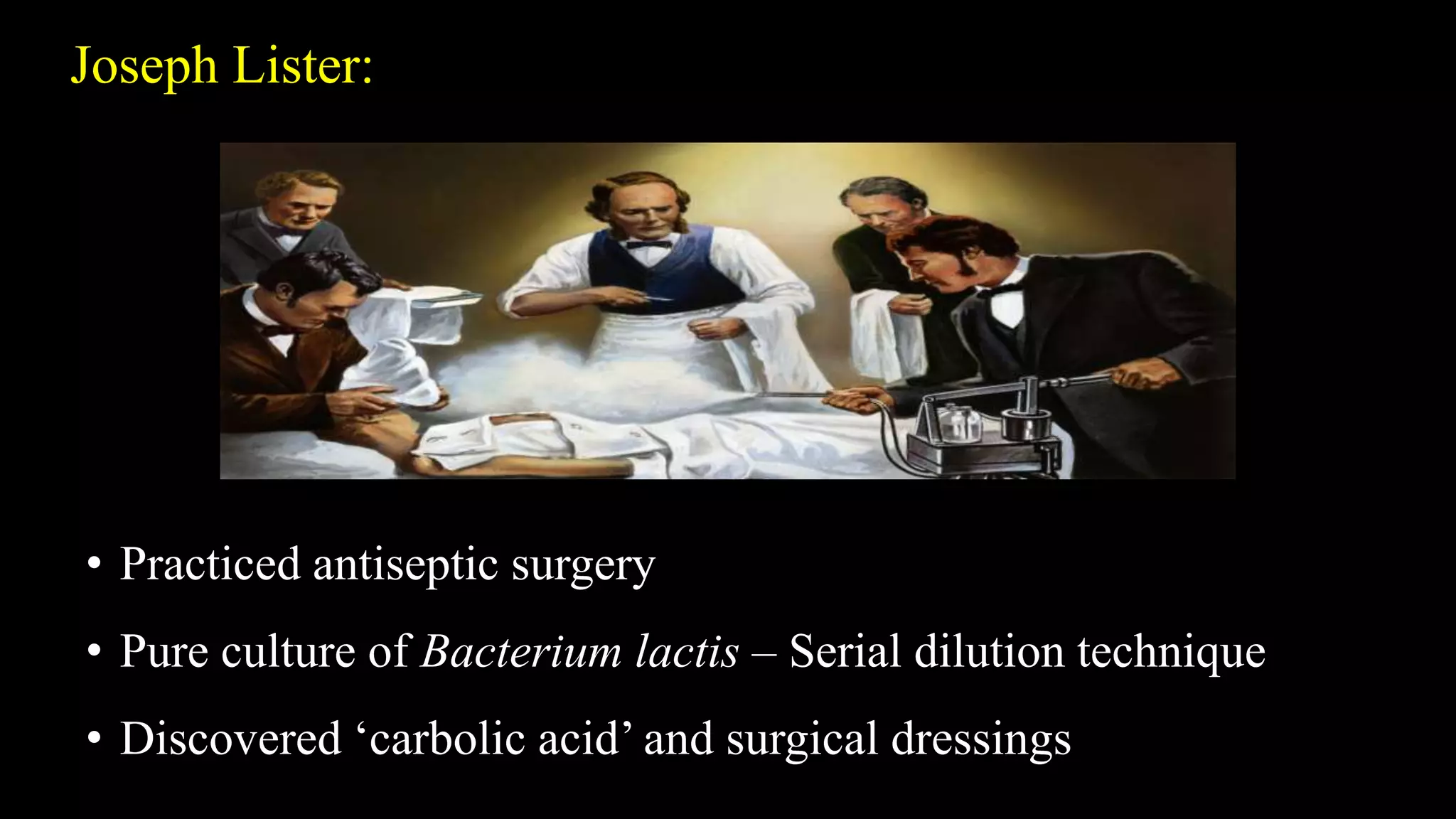
Robert Hooke first observed microorganisms in 1665 and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek observed and described microorganisms in 1677. The existence of microorganisms was suspected since ancient times. Louis Pasteur and John Tyndall disproved the theory of spontaneous generation in the 1860s through experiments demonstrating that microorganisms come from other microorganisms, not inanimate matter. Robert Koch established the germ theory of disease in the 1870s-1880s by proving specific diseases are caused by specific pathogens through experiments isolating bacteria from infected animals and transmitting disease through inoculation. Alexander Fleming discovered the antibiotic penicillin in 1928 from the Penicillium mold.