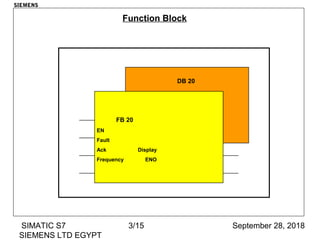
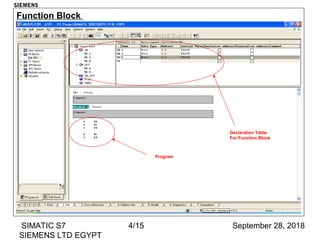
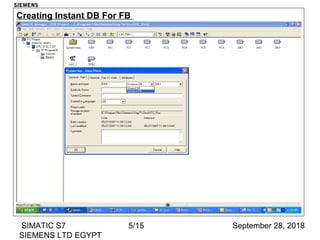
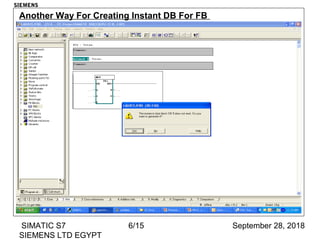
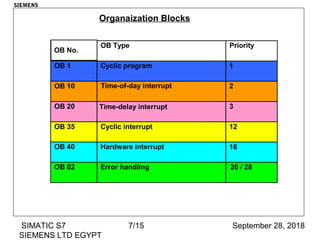
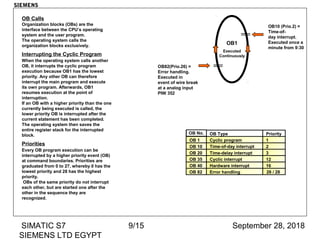
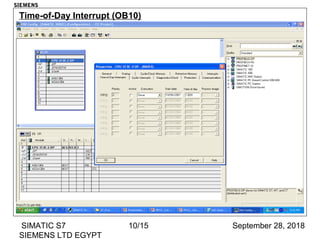
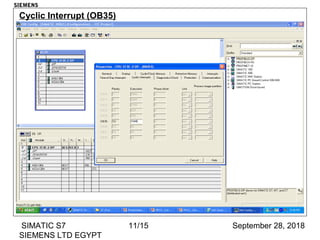
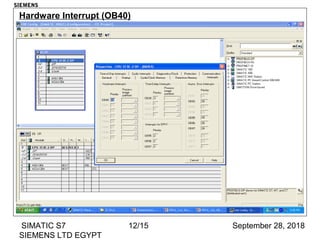
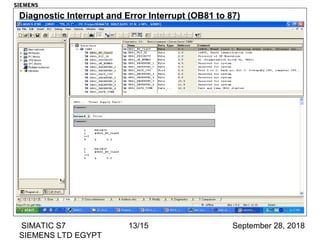
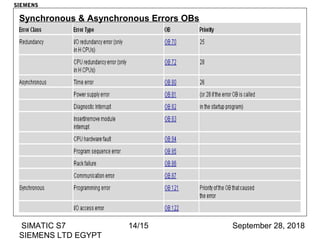
The document discusses function blocks and organization blocks in SIMATIC S7. It explains how to create a function block and its instance data block, and the different types of organization blocks and how they handle interrupts. Organization blocks are called by the operating system and can interrupt cyclic program execution based on their priority level. Higher priority events will interrupt lower priority organization blocks. The document provides examples of specific organization blocks including time-of-day interrupts, cyclic interrupts, hardware interrupts, and diagnostic/error interrupts.