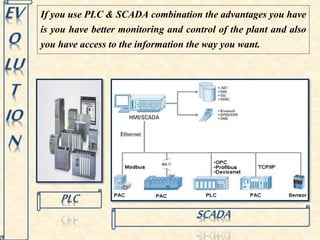
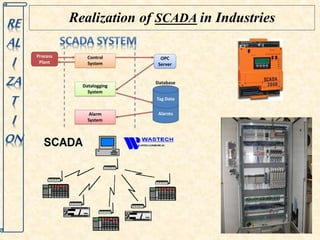
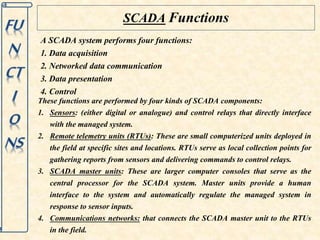
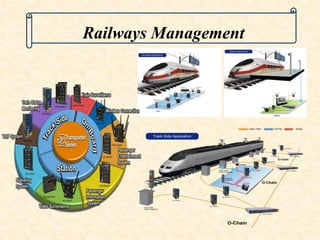
This document discusses supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes and infrastructure by collecting data from remote field devices and sensors. The document outlines the key components and functions of SCADA, including data acquisition, communication between remote terminal units and the central control system, data presentation to operators, and remote control capabilities. Examples are given of SCADA applications in various industries such as water distribution, manufacturing, oil and gas, and railways.