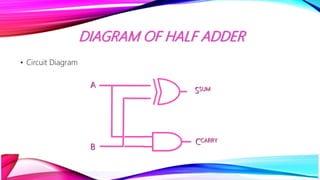
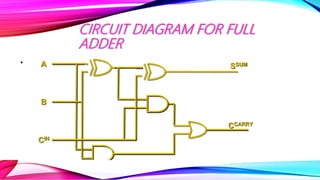
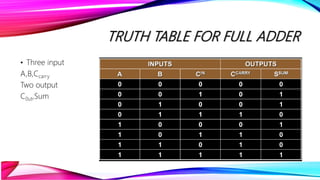
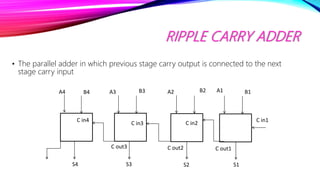
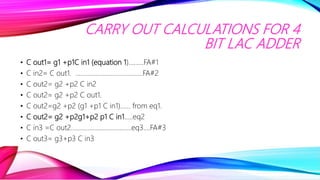
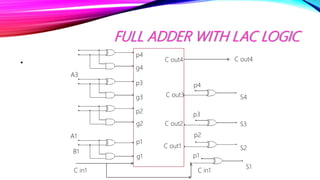
This document discusses half adders and full adders. It begins by explaining what an adder is and its importance in digital circuits. It then defines half and full adders. A half adder adds two bits and produces a sum and carry output, while a full adder adds three bits. Truth tables are provided for each. Circuit diagrams show the implementation of half and full adders using logic gates. The document also discusses parallel adders, comparing ripple carry adders which propagate the carry sequentially, to look ahead carry adders which pre-calculate carries to speed up addition.