Embed presentation
Downloaded 232 times



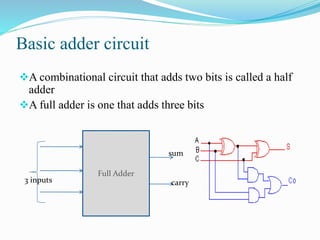
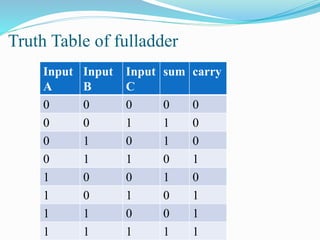

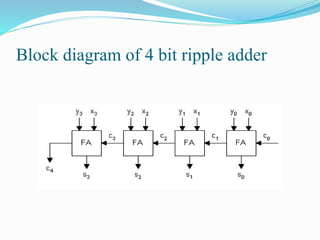
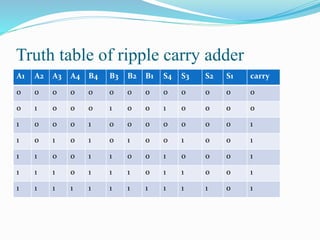
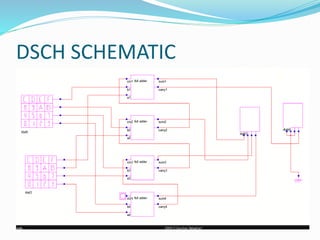
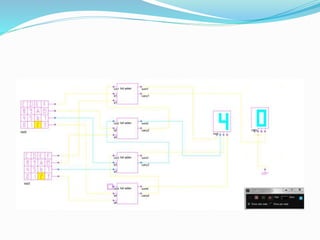
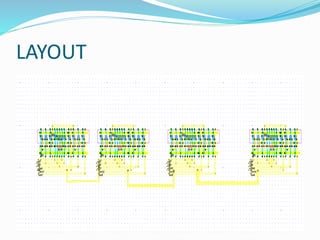


This document discusses binary addition and different types of adders used in digital circuits. It describes half adders, full adders, and ripple carry adders. A ripple carry adder is constructed by cascading full adder blocks in series, with the carryout of one stage feeding into the carry-in of the next stage. For an n-bit ripple carry adder, n full adders are required. The document provides truth tables for a full adder and ripple carry adder, and includes block diagrams and layout of a 4-bit ripple carry adder. Ripple carry adders are suitable for small bit applications and allow easy addition of two n-bit numbers.












