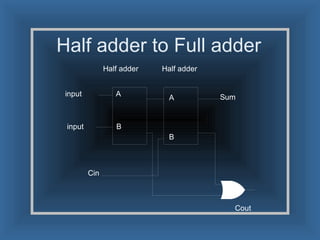
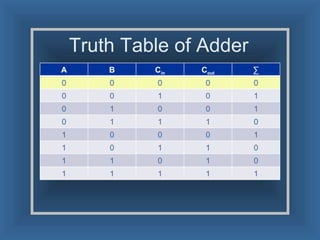
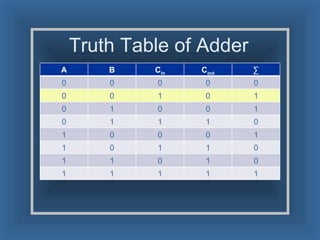
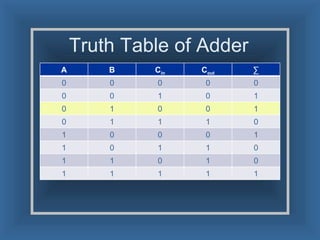
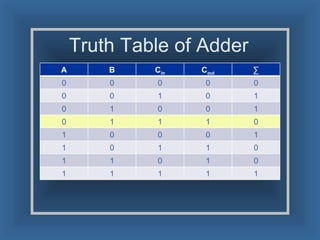
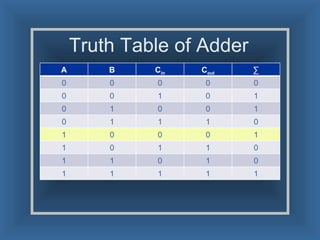
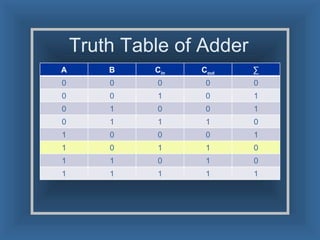
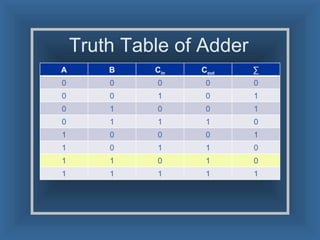
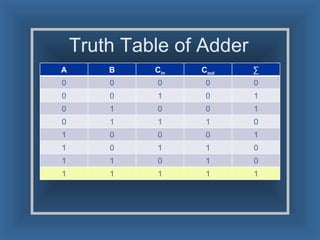
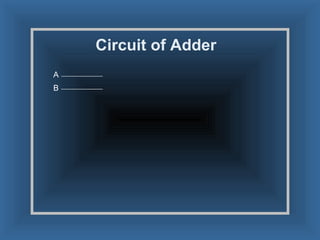
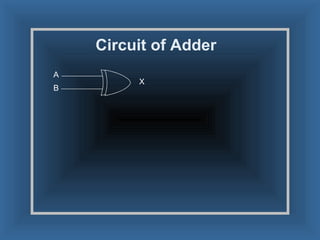
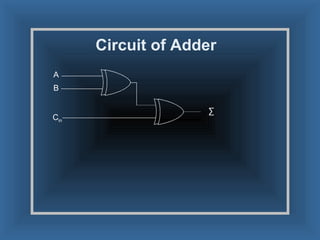
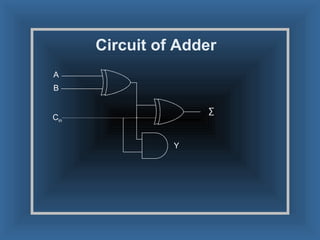
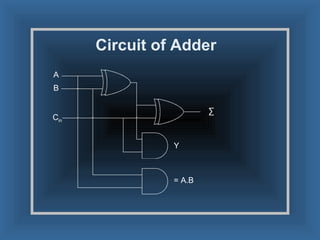
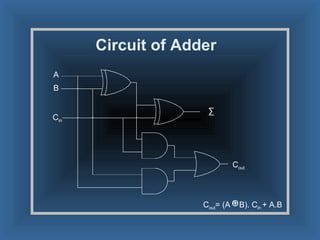
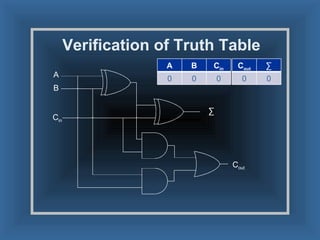
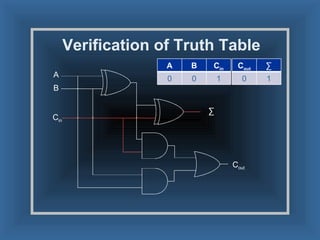
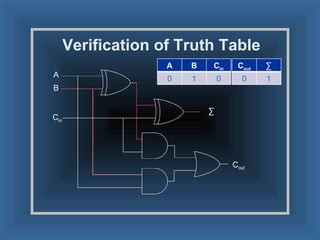
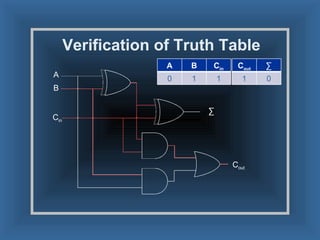
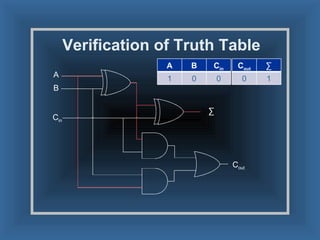
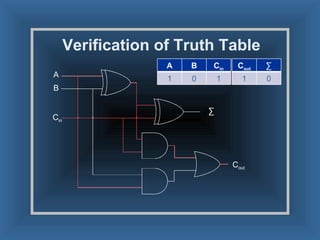
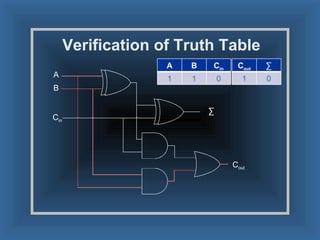
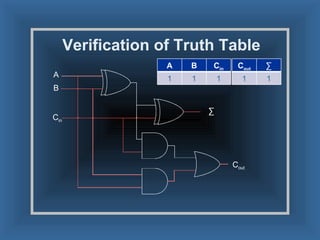
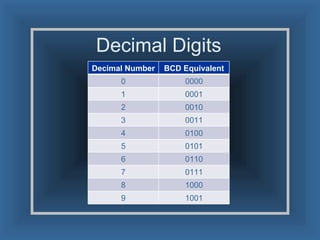
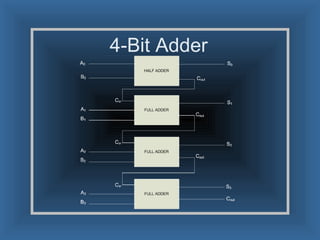
An adder is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. There are two main types: a half adder that adds two bits and produces a sum and carry bit, and a full adder that adds two bits and a carry bit to produce a sum and carry out bit. Adders are used in arithmetic logic units to perform arithmetic operations and are important in many digital systems that process numeric data.