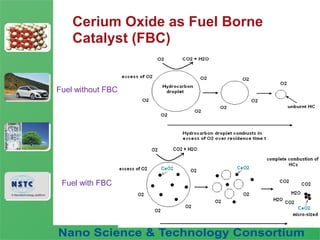
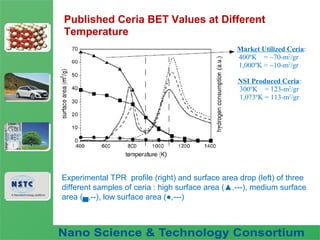
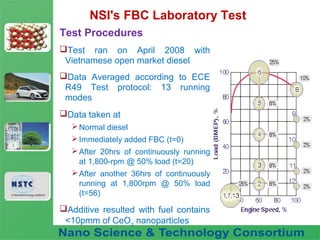
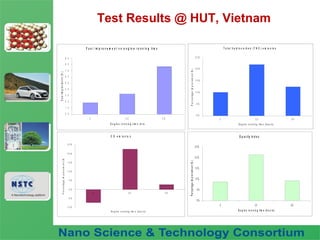
The document discusses a fuel nano-additive technology that uses cerium oxide nanoparticles as a fuel borne catalyst. It provides background on nanotechnology and describes how cerium oxide improves fuel combustion efficiency and reduces emissions when mixed into fuel at the nanoscale. Laboratory tests conducted on a diesel engine in Vietnam found that the nano-additive reduced fuel consumption and particulate emissions while increasing combustion pressure over 56 hours of operation with no adverse effects.












![Fuel Nano-Additive
Technology
Test Results @ HUT, Vietnam
N O x e m is s io n
-1 0 %
-8 %
-6 %
-4 %
-2 %
0 %
2 %
4 %
0 2 0 5 6
E n g i n e r u n n i n g tim e (h o u r s )
Percentageimprovement(%)
0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
7 0
- 9 0 - 8 0 - 7 0 - 6 0 - 5 0 - 4 0 - 3 0 - 2 0 - 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 0
C r a n k a n g l e [ d e g r e e ]
Pressure[bar]
p _ c y l i n d e r _ D i e s e l
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 _ L 1
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 _ L 2
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 _ L 3
0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
7 0
- 9 0 - 8 0 - 7 0 - 6 0 - 5 0 - 4 0 - 3 0 - 2 0 - 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 0
C r a n k a n g le [ d e g r e e ]
Pressure[bar]
p _ c y l i n d e r _ D i e s e l
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 _ L 1
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 - L 2
p _ c y l i n d e r _ C e O 2 _ L 3
0
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
5 0
6 0
7 0
- 9 0 - 8 0 - 7 0 - 6 0 - 5 0 - 4 0 - 3 0 - 2 0 - 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 9 0
C r a n k a n g l e [ d e g r e e ]
Pressure[bar]
P _ C y l i n d e r_ D i e s e l
p _ c y l i n d e r_ C e O 2 _ L 1
P _ C y l i n d e r_ C e O 2 _ L 2
p _ c y l i n d e r_ C e O 2 _ L 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuelnanoadditivetechnology-101127011408-phpapp01/85/Fuel-nano-additive-technology-18-320.jpg)



