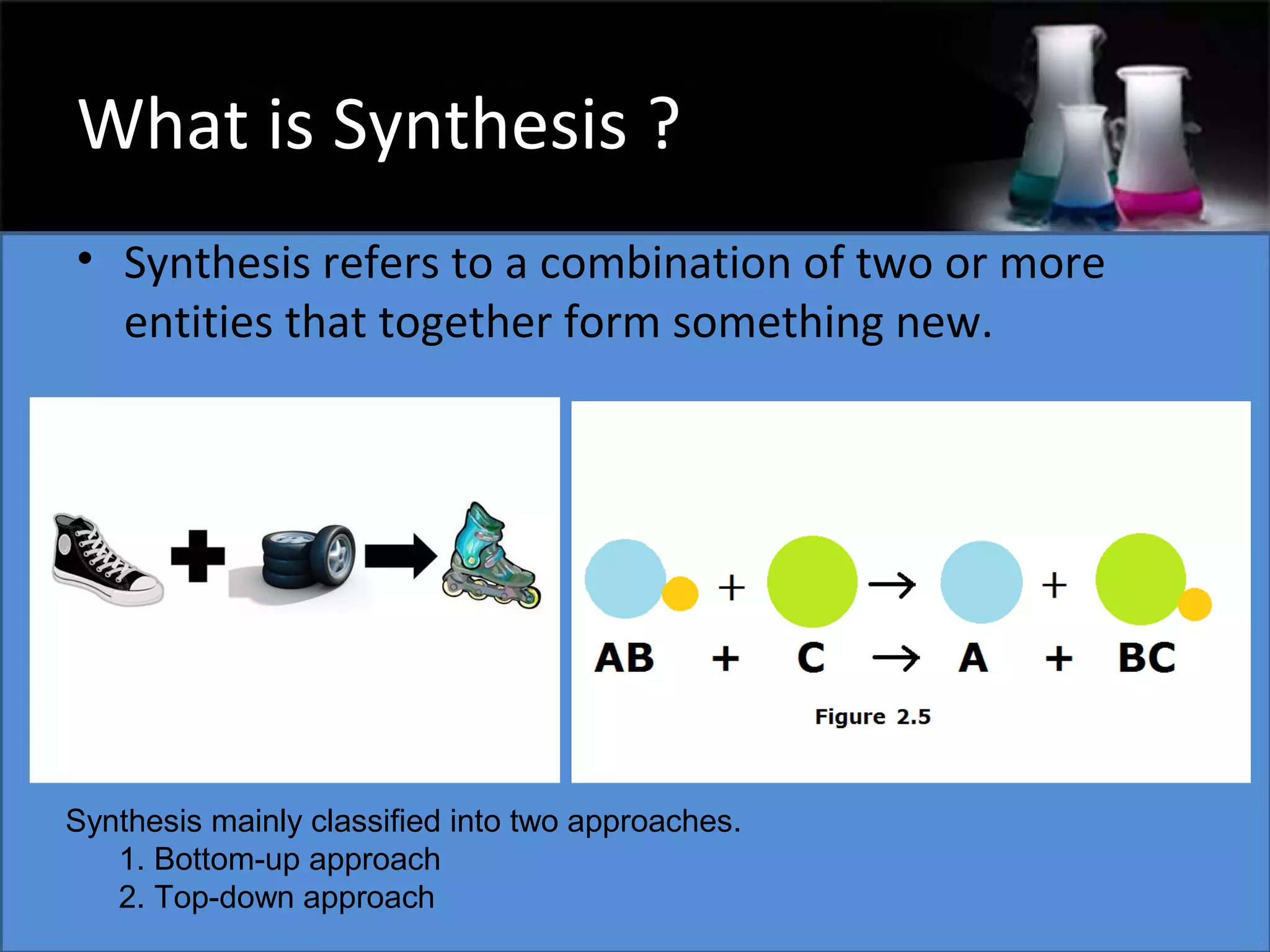
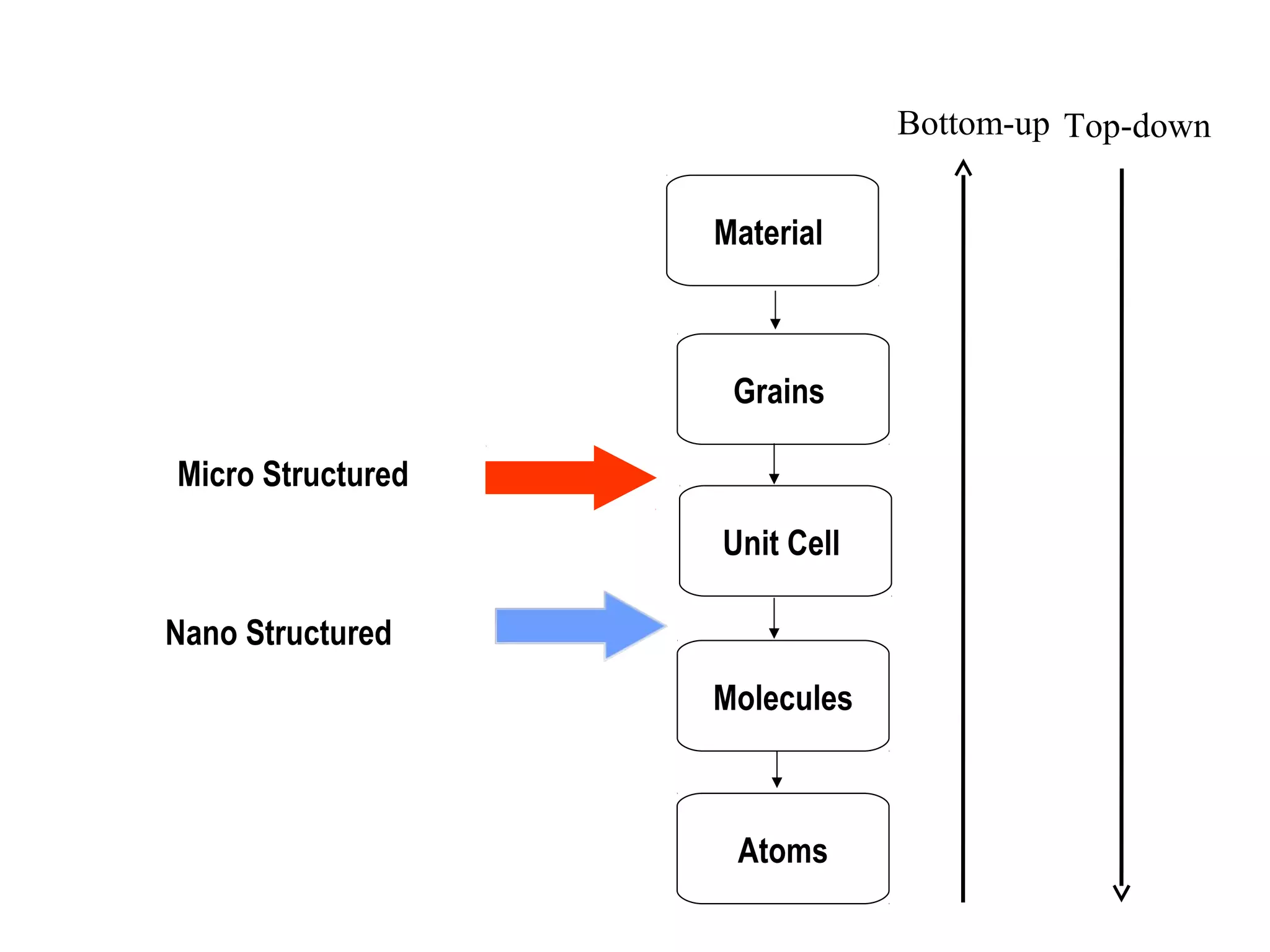
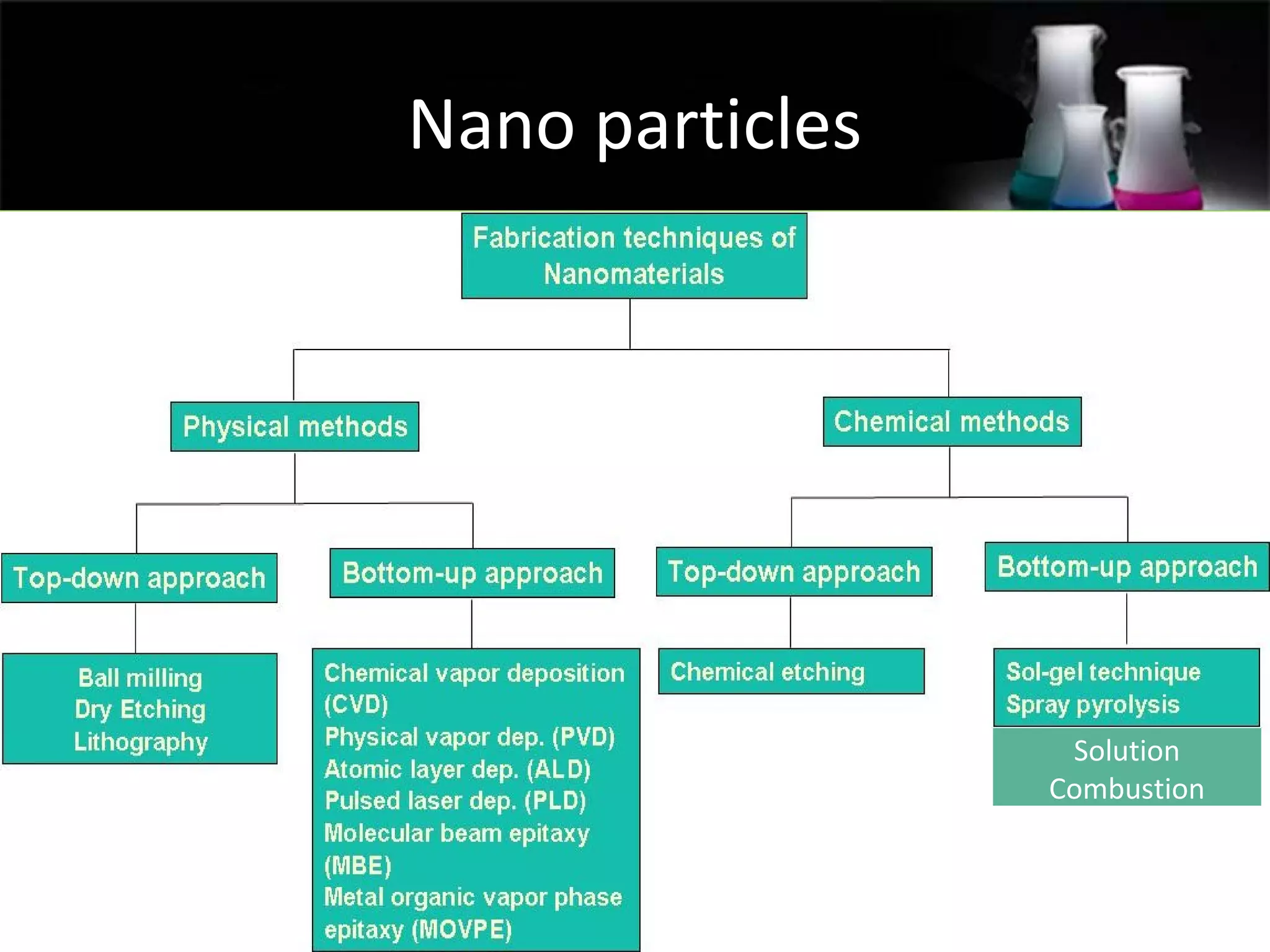
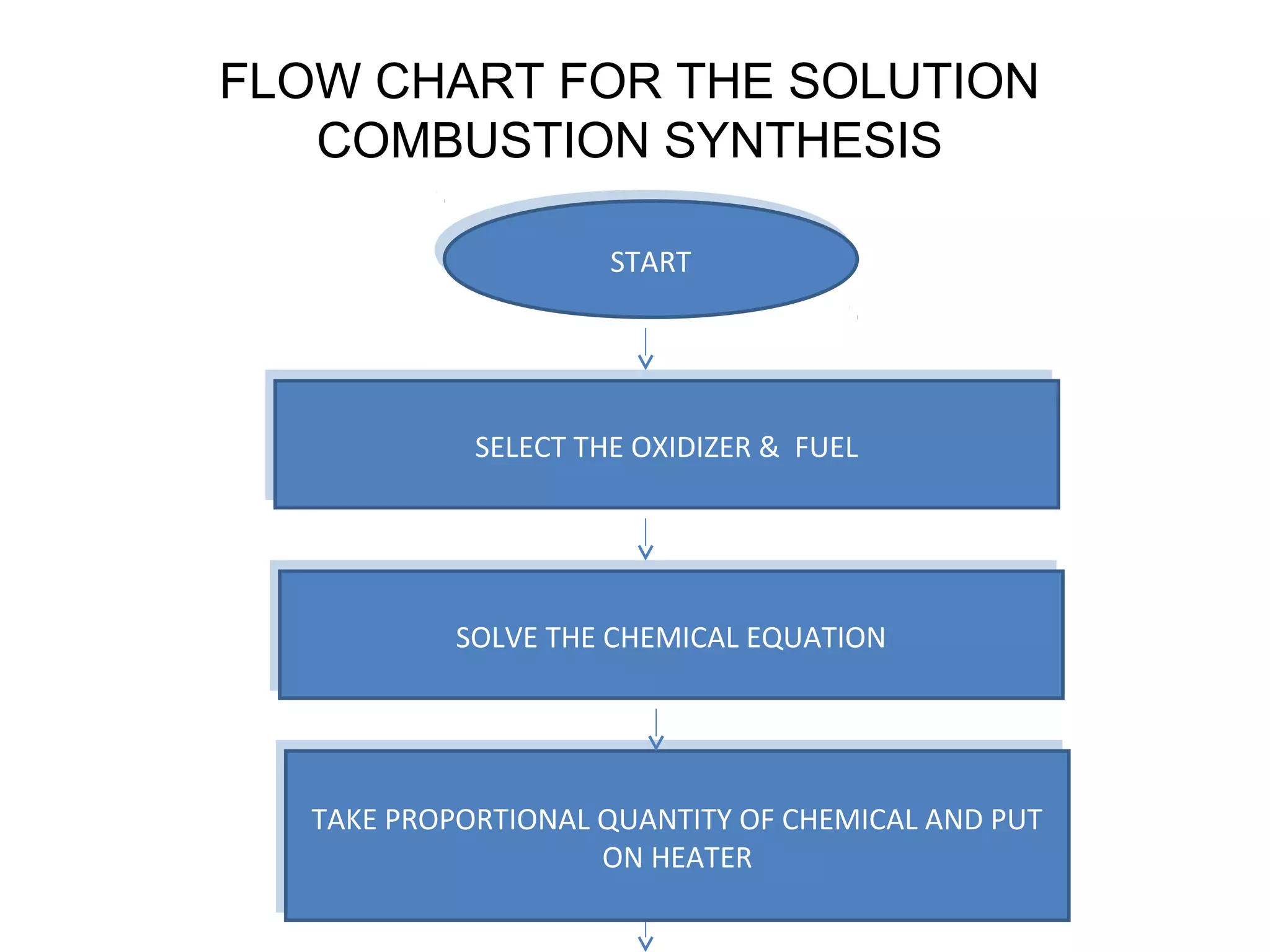
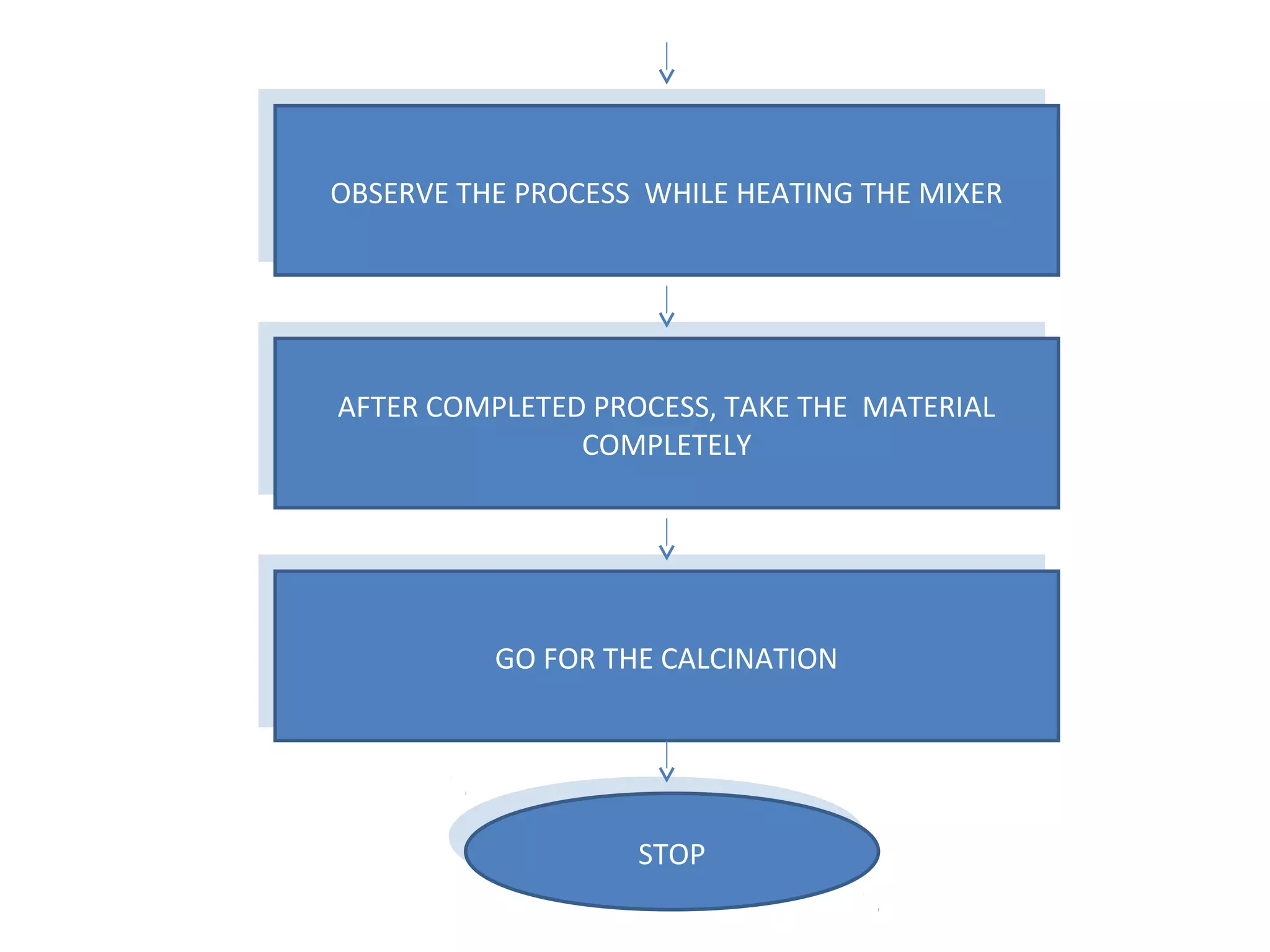
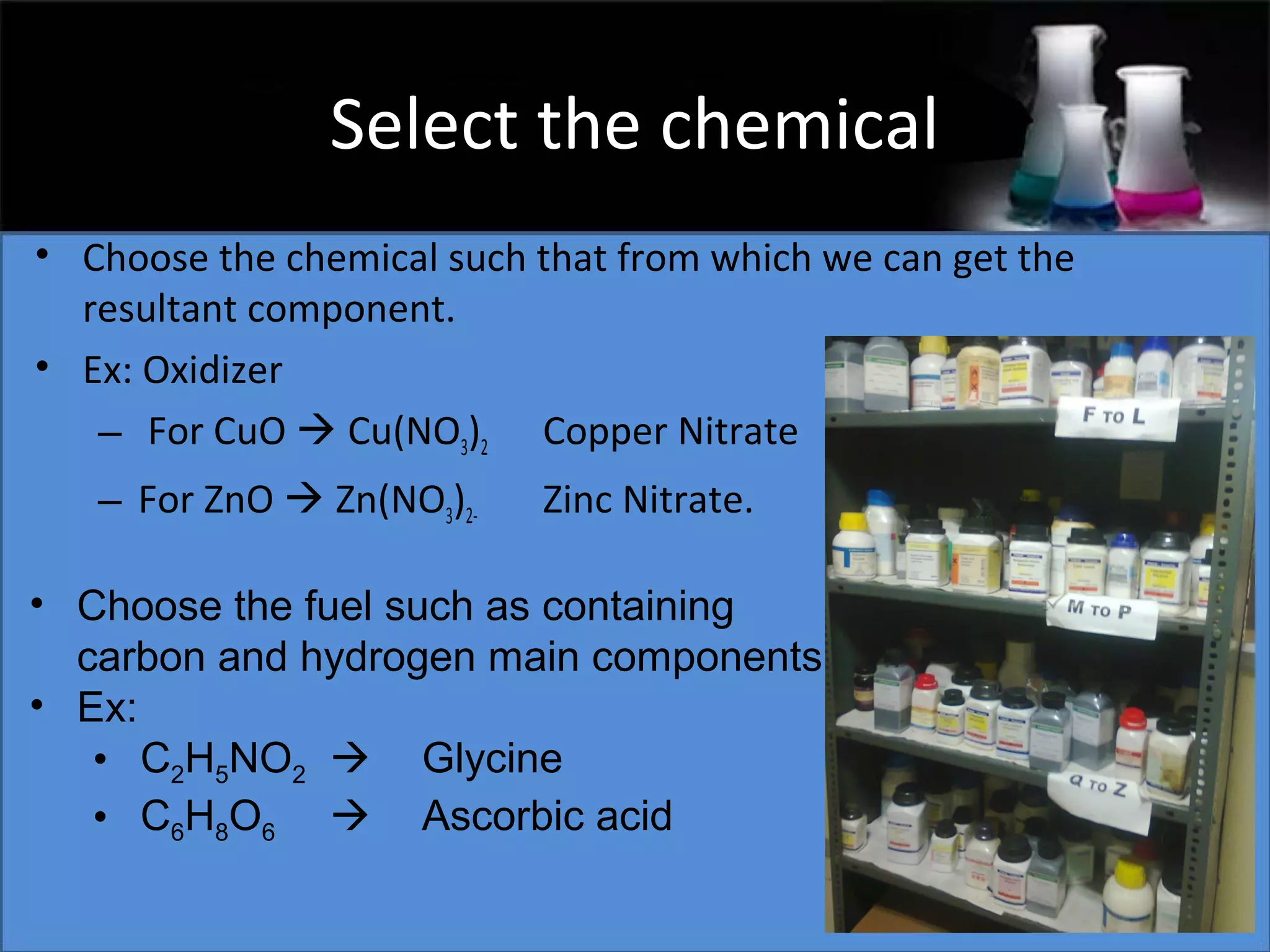
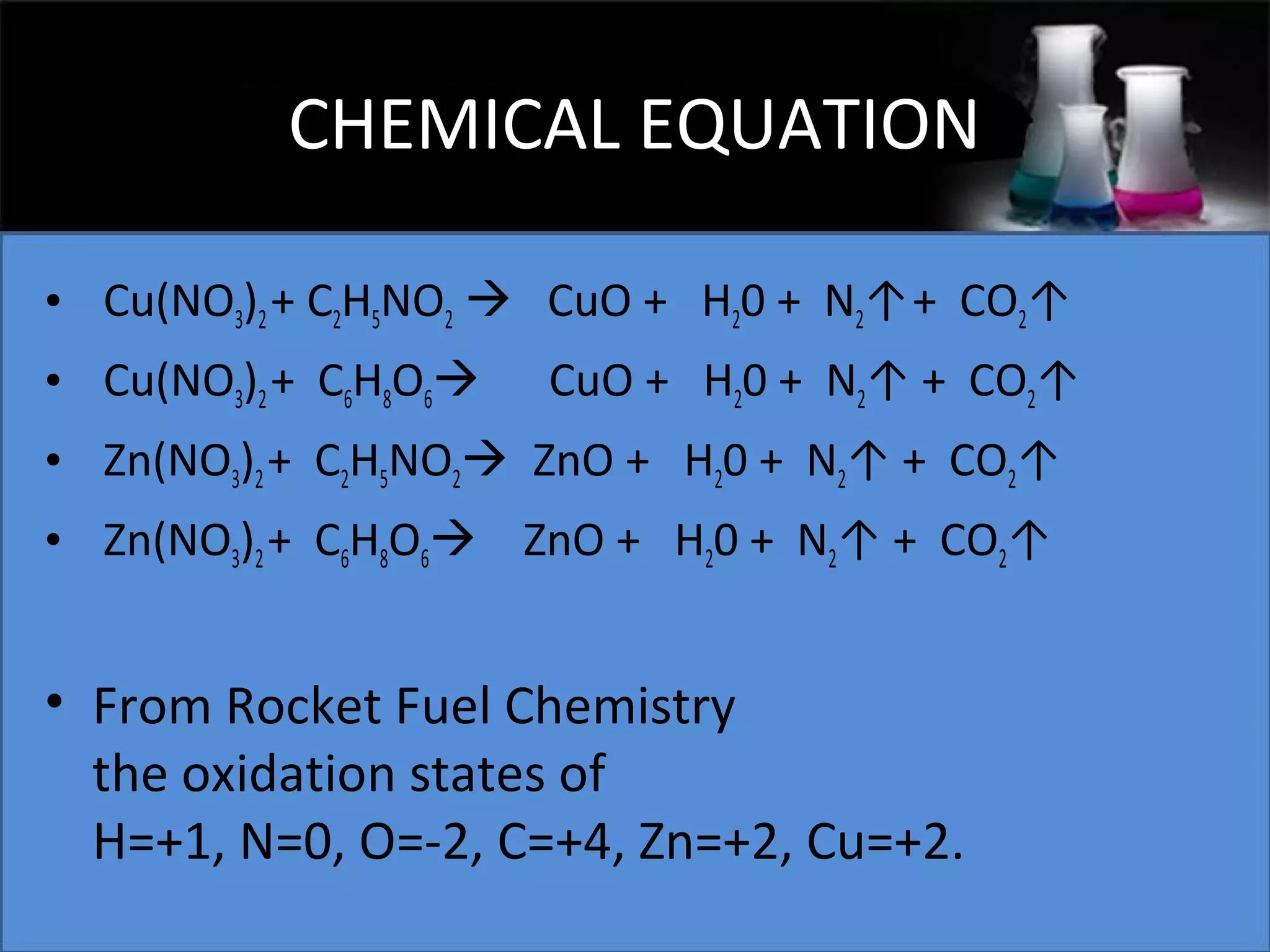
This document presents a seminar on the synthesis of nanoparticles using solution combustion. It describes the solution combustion synthesis process, which involves selecting an oxidizer and fuel, balancing the chemical equation, mixing the chemicals in solution and heating to initiate combustion. This self-sustaining combustion reaction produces nanoparticles that are then calcined at high temperatures. The method allows for rapid, low-cost synthesis of nanoparticles less than 50 nm in size, such as copper oxide and zinc oxide, without needing specialized equipment.