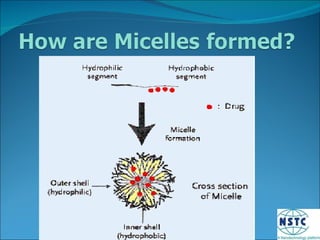
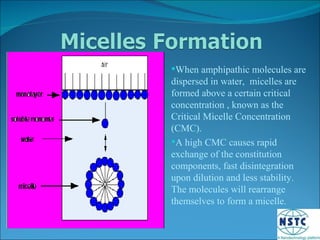
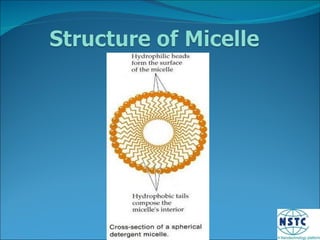
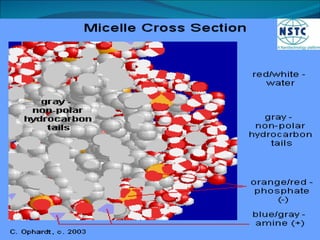
Micelles are small spherical structures composed of surfactant molecules that form to reduce surface tension in a cell membrane. When the concentration of surfactant reaches a critical point known as the critical micelle concentration, the hydrophobic tails organize to form micelles with the hydrophilic heads on the outside in water. Micelles can be used as drug carriers, with polymers forming stable spherical structures below a certain size that allow accumulation of drugs in tissues like tumors.