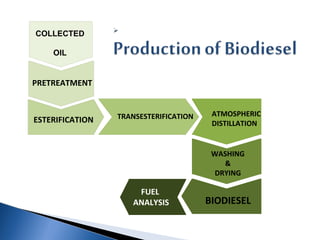
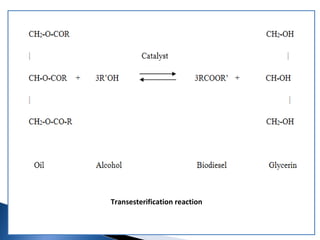
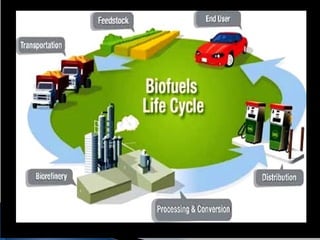
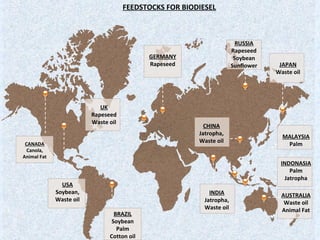
Biodiesel is a non-petroleum-based diesel fuel made from vegetable oils or animal fats through transesterification. Historically, Rudolf Diesel demonstrated the use of peanut oil in a diesel engine in 1900, and more recently, several countries, including India, have initiated programs to cultivate crops like jatropha for biodiesel production. Biodiesel is environmentally friendly, compatible with existing diesel engines, and has potential benefits in reducing dependence on foreign oil and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.